Abstract
Background
Postprandially induced oxidative stress can cause damage to mitochondrial components and initiate cellular degradative processes; which are related to obesity comorbidities.
Aim of the study
This trial sought to determine whether weight loss induced by caloric restriction provides antioxidant protection to reduce the postprandial response of mitochondrial function and oxidative stress markers.
Methods
A group of overweight/obese volunteers (n = 17; 39 ±7 years, 32.5 ± 4.8 kg/m2) followed an 8-week hypocaloric diet. Volunteers provided blood samples at fasting and 2-h after a test drink (CHO: 95% E, PROT: 5% E and containing antioxidants) and these were examined for postprandial oxidative stress responses, before and after the nutritional intervention. The expression of four mitochondrial-related genes, COX15, NDUFS2, MGST2 and TNF-alfa, was measured in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) by quantitative RT-PCR. Lipid peroxidation and nitrosative stress biomarkers, total antioxidant capacity (AOP), uric acid and glutathione peroxidase were also determined.
Results
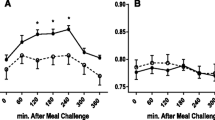
Before nutritional treatment, the test drink induced a postprandial increase in lipid peroxidation and nitrosative stress biomarkers with a concomitant increase in the AOP. The increase in postprandial oxidative stress biomarkers was accompanied by a decrease in PBMC COX15 mRNA levels. Interestingly, after the weight loss period (−5.8 ± 2.3%), the postprandial-induced changes were lower than at the beginning of the study and involved oxidative stress biomarkers and the COX15 and MGST2 transcripts. This finding suggests the occurrence of a tachyphylactic process.
Conclusions
We demonstrate for the first time that the well-known effect of energy restriction on oxidative stress is accompanied by a tolerance mechanism on the postprandial oxidative stress response and mitochondrial function-related genes. Indeed, the COX15 and MGST2 gene expression assays in PBMC emerged as valuable nutrigenomic biomarkers of the oxidative response under energy-restriction conditions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AOP:
-
Serum total antioxidant capacity
- BMI:
-
Body mass index (kg/m2)
- COX15:
-
Cytochrome c oxidase assembly protein
- CR:
-
Caloric restriction
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MGST2:
-
Microsomal glutathione S-transferase
- NDUFS2:
-
NADH-Coenzyme Q reductase
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NT:
-
Nitrotyrosine
- Ox-LDL:
-
Oxidized-LDL
- PBMC:
-
Peripheral blood mononuclear cell
- TNFAIP8L1:
-
Tumor necrosis factor alfa-related gen
- UA:
-
Uric acid
- UV:
-
Ultraviolet visible
References
Abete I, Parra D, Martinez JA (2008) Energy-restricted diets based on a distinct food selection affecting the glycemic index induce different weight loss and oxidative response. Clin Nutr 27:545–551
Bergmann MM, Görman U, Mathers JC (2008) Bioethical considerations for human nutrigenomics. Annu Rev Nutr 28:447–467
Block G, Dietrich M, Norkus EP, Morrow JD, Hudes M, Caan B, Packer L (2002) Factors associated with oxidative stress in human populations. Am J Epidemiol 156:274–285
Bo S, Gambino R, Guidi S, Silli B, Gentile L, Cassader M, Pagano GF (2005) Plasma nitrotyrosine levels, antioxidant vitamins and hyperglycaemia. Diabet Med 22:1185–1189
Bonnard C, Durand A, Peyrol S, Chanseaume E, Chauvin MA, Morio B, Vidal H, Rieusset J (2008) Mitochondrial dysfunction results from oxidative stress in the skeletal muscle of diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. J Clin Invest 118:789–800
Cadenas E, Davies KJ (2000) Mitochondrial free radical generation, oxidative stress, and aging. Free Radic Biol Med 29:222–230
Crujeiras AB, Parra D, Abete I, Martinez JA (2007) A hypocaloric diet enriched in legumes specifically mitigates lipid peroxidation in obese subjects. Free Radic Res 41:498–506
Crujeiras AB, Parra D, Goyenechea E, Abete I, González-Muniesa P, Martínez JA (2008) Energy restriction in obese subjects impact differently two mitochondrial function markers. J Physiol Biochem 64:211–220
Crujeiras AB, Parra D, Goyenechea E, Martínez JA (2008) Sirtuin gene expression in human mononuclear cells is modulated by caloric restriction. Eur J Clin Invest 38:672–678
Crujeiras AB, Parra D, Milagro FI, Goyenechea E, Larrarte E, Margareto J, Martinez JA (2008) Differential expression of oxidative stress and inflammation related genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in response to a low-calorie diet: a nutrigenomics study. OMICS 12:251–261
Crujeiras AB, Parra MD, Rodriguez MC, Martinez de Morentin BE, Martinez JA (2006) A role for fruit content in energy-restricted diets in improving antioxidant status in obese women during weight loss. Nutrition 22:593–599
Chung HY, Sung B, Jung KJ, Zou Y, Yu BP (2006) The molecular inflammatory process in aging. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:572–581
Dandona P, Aljada A, Chaudhuri A, Mohanty P, Garg R (2005) Metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive perspective based on interactions between obesity, diabetes, and inflammation. Circulation 111:1448–1454
Dandona P, Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Aljada A, Browne R, Hamouda W, Prabhala A, Afzal A, Garg R (2001) The suppressive effect of dietary restriction and weight loss in the obese on the generation of reactive oxygen species by leukocytes, lipid peroxidation, and protein carbonylation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:355–362
Fenster CP, Darley-Usmar VM, Landar AL, Gower BA, Weinsier RL, Hunter GR, Patel RP (2004) Weight loss and race modulate nitric oxide metabolism in overweight women. Free Radic Biol Med 37:695–702
Kadenbach B, Huttemann M, Arnold S, Lee I, Bender E (2000) Mitochondrial energy metabolism is regulated via nuclear-coded subunits of cytochrome c oxidase. Free Radic Biol Med 29:211–221
Kay CD, Holub BJ (2003) The postprandial effects of dietary antioxidants in humans. Curr Atheroscler Rep 5:452–458
Labayen I, Diez N, Parra D, Gonzalez A, Martinez JA (2004) Basal and postprandial substrate oxidation rates in obese women receiving two test meals with different protein content. Clin Nutr 23:571–578
Li X, Liu Z, Luo C, Jia H, Sun L, Hou B, Shen W, Packer L, Cotman CW, Liu J (2008) Lipoamide protects RPE cells from oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Free Radic Biol Med 44:1465–1474
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Marti A, Martinez-Gonzalez MA, Martinez JA (2008) Interaction between genes and lifestyle factors on obesity. Proc Nutr Soc 67:1–8
Martinez JA (2006) Mitochondrial oxidative stress and inflammation: an slalom to obesity and insulin resistance. J Physiol Biochem 62:303–306
Matsuzawa-Nagata N, Takamura T, Ando H, Nakamura S, Kurita S, Misu H, Ota T, Yokoyama M, Honda M, Miyamoto K, Kaneko S (2008) Increased oxidative stress precedes the onset of high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity. Metabolism 57:1071–1077
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Mera RTH, Prasad C (1998) How to calculate sample size for an experiment: a case-based description. Nutr Neurosci 1:87–91
Milagro FI, Campion J, Martinez JA (2007) 11-beta Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 expression in white adipose tissue is strongly correlated with adiposity. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 104:81–84
Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Hamouda W, Aljada A, Garg R, Dandona P (2002) Both lipid and protein intakes stimulate increased generation of reactive oxygen species by polymorphonuclear leukocytes and mononuclear cells. Am J Clin Nutr 75:767–772
Mohanty P, Hamouda W, Garg R, Aljada A, Ghanim H, Dandona P (2000) Glucose challenge stimulates reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation by leucocytes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:2970–2973
Natella F, Ghiselli A, Guidi A, Ursini F, Scaccini C (2001) Red wine mitigates the postprandial increase of LDL susceptibility to oxidation. Free Radic Biol Med 30:1036–1044
OMS-WHO (2000) Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of WHO consultation. Word Health Organ Tech Resp Ser 894:1–253
Patel C, Ghanim H, Ravishankar S, Sia CL, Viswanathan P, Mohanty P, Dandona P (2007) Prolonged reactive oxygen species generation and nuclear factor-kappaB activation after a high-fat, high-carbohydrate meal in the obese. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:4476–4479
Perez de Obanos MP, Lopez-Zabalza MJ, Arriazu E, Modol T, Prieto J, Herraiz MT, Iraburu MJ (2007) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) mediate the effects of leucine on translation regulation and type I collagen production in hepatic stellate cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773:1681–1688
Valerio A, Cardile A, Cozzi V, Bracale R, Tedesco L, Pisconti A, Palomba L, Cantoni O, Clementi E, Moncada S, Carruba MO, Nisoli E (2006) TNF-alpha downregulates eNOS expression and mitochondrial biogenesis in fat and muscle of obese rodents. J Clin Invest 116:2791–2798
Vincent HK, Taylor AG (2006) Biomarkers and potential mechanisms of obesity-induced oxidant stress in humans. Int J Obes (Lond) 30:400–418
Wiswedel I, Hirsch D, Kropf S, Gruening M, Pfister E, Schewe T, Sies H (2004) Flavanol-rich cocoa drink lowers plasma F(2)-isoprostane concentrations in humans. Free Radic Biol Med 37:411–421
Zhao G, Etherton TD, Martin KR, Gillies PJ, West SG, Kris-Etherton PM (2007) Dietary alpha-linolenic acid inhibits proinflammatory cytokine production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells in hypercholesterolemic subjects. Am J Clin Nutr 85:385–391
Acknowledgments
Thanks are given to Linea Especial about Nutrition, Obesity and Health (University of Navarra LE/97) and IBERCAJA for financial support as well as to Friends of University of Navarra and CAIXANOVA that supports AB Crujeiras with a fellowship. We also wish to thank our physician Blanca E Martínez de Morentin, our nurse Salomé Pérez, our dietician María Hernandez and our technicians Ana Lorente and Verónica Ciaurriz, for excellent clinical and technical assistance. We also thank Paul Miller from the Foreign Language Institute at the University of Navarra for careful reading of the last version of this manuscript for English grammar and style.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Crujeiras, A.B., Parra, D., Goyenechea, E. et al. Tachyphylaxis effects on postprandial oxidative stress and mitochondrial-related gene expression in overweight subjects after a period of energy restriction. Eur J Nutr 48, 341–347 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-009-0019-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-009-0019-9