Abstract
Background
Previous studies using conventional cTnI assays reported conflicting results on the evolution of cTnI levels during hemodialysis. The determinants and prognostic significance of changes in cTnI during hemodialysis are presently unknown. The aim of this prospective study was to characterize the determinants and prognostic significance of intra-dialysis changes in cTnI using a sensitive assay.
Methods
cTnI was measured before and after hemodialysis with a sensitive assay in 90 chronic patients without acute cardiac symptoms. Multivariable regression analyses were used to identify factors that were associated with intra-dialysis rise in cTnI. The prognostic effect of an intra-dialysis rise in cTnI during a 52-month follow-up was evaluated using Cox regression models. The primary and secondary endpoint was the incidence of major adverse cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality, respectively.
Results
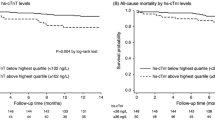
Pre-dialysis cTnI was elevated in 31 patients (34 %). cTnI increased significantly during dialysis and this had a trend to be associated with longer dialysis vintage. A greater intra-dialysis rise in cTnI was associated with a significantly higher incidence of cardiovascular events, also after correction for age, gender, dialysis vintage, residual diuresis, previous cardiovascular events, and pre-dialysis cTnI levels (HR per 10 ng/L rise in cTnI: 1.21; CI 1.06–1.38; p 0.005).
Conclusion
TnI levels rise significantly during hemodialysis and a greater intra-dialysis rise in cTnI is associated with an increased incidence of cardiovascular events. These findings suggest that hemodialysis has an acute deleterious effect on the heart. An intra-dialysis rise in cTnI may help identify patients who are susceptible to the hemodynamic stress of hemodialysis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Troyanov S, Ly QH, Schampaert E, Ammann H, Lalumiere G, Madore F, Querin S (2005) Diagnostic specificity and prognostic value of cardiac troponins in asymptomatic chronic haemodialysis patients: a three year prospective study. Heart 91:1227–1228
Wang AY, Lai KN (2008) Use of cardiac biomarkers in end-stage renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 19:1643–1652
Wayand D, Baum H, Schatzle G, Scharf J, Neumeier D (2000) Cardiac troponin T and I in end-stage renal failure. Clin Chem 46:1345–1350
Apple FS, Murakami MM, Pearce LA, Herzog CA (2002) Predictive value of cardiac troponin I and T for subsequent death in end-stage renal disease. Circulation 106:2941–2945
Khan NA, Hemmelgarn BR, Tonelli M, Thompson CR, Levin A (2005) Prognostic value of troponin T and I among asymptomatic patients with end-stage renal disease: a meta-analysis. Circulation 112:3088–3096
Gaiki MR, Devita MV, Michelis MF, Panagopoulos G, Rosenstock JL (2012) Troponin I as a prognostic marker of cardiac events in asymptomatic hemodialysis patients using a sensitive troponin I assay. Int Urol Nephrol 44(6):1841–1845
Dasselaar JJ, Slart RH, Knip M, Pruim J, Tio RA, McIntyre CW, de Jong PE, Franssen CF (2009) Haemodialysis is associated with a pronounced fall in myocardial perfusion. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:604–610
McIntyre CW, Burton JO, Selby NM, Leccisotti L, Korsheed S, Baker CS, Camici PG (2008) Hemodialysis-induced cardiac dysfunction is associated with an acute reduction in global and segmental myocardial blood flow. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 3:19–26
Tun A, Khan IA, Win MT, Hussain A, Hla TA, Wattanasuwan N, Vasavada BC, Sacchi TJ (1998) Specificity of cardiac troponin I and creatine kinase-MB isoenzyme in asymptomatic long-term hemodialysis patients and effect of hemodialysis on these cardiac markers. Cardiology 90:280–285
Farkouh ME, Robbins MJ, Zafar MU, Shimbo D, Davidson KW, Puttappa R, Winston J, Halperin JL, Epstein EM, Patel M, Talor Z, Chesebro JH (2003) Association between troponin I levels and mortality in stable hemodialysis patients. Am J Med 114:224–226
Deleaval P, Descombes E, Magnin JL, Martin PY, Fellay G (2006) Differences in cardiac troponin I and T levels measured in asymptomatic hemodialysis patients with last generation immunoassays. Nephrol Ther 2:75–81
Lippi G, Tessitore N, Montagnana M, Salvagno GL, Lupo A, Guidi GC (2008) Influence of sampling time and ultrafiltration coefficient of the dialysis membrane on cardiac troponin I and T. Arch Pathol Lab Med 132:72–76
Reichlin T, Hochholzer W, Bassetti S, Steuer S, Stelzig C, Hartwiger S, Biedert S, Schaub N, Buerge C, Potocki M, Noveanu M, Breidthardt T, Twerenbold R, Winkler K, Bingisser R, Mueller C (2009) Early diagnosis of myocardial infarction with sensitive cardiac troponin assays. N Engl J Med 361:858–867
Reiter M, Twerenbold R, Reichlin T, Benz B, Haaf P, Meissner J, Hochholzer W, Stelzig C, Freese M, Heinisch C, Balmelli C, Drexler B, Freidank H, Winkler K, Campodarve I, Gea J, Mueller C (2012) Early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in patients with pre-existing coronary artery disease using more sensitive cardiac troponin assays. Eur Heart J 33(8):988–997
Konno T, Shimizu M, Ino H, Fujino N, Hayashi K, Uchiyama K, Kaneda T, Inoue M, Fujita T, Masuta E, Funada A, Mabuchi H (2005) Differences in diagnostic value of four electrocardiographic voltage criteria for hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a genotyped population. Am J Cardiol 96:1308–1312
Iliou MC, Fumeron C, Benoit MO, Tuppin P, Courvoisier CL, Calonge VM, Moatti N, Buisson C, Jacquot C, Chronic Haemodialysis and New Cardiac Markers Evaluation (CHANCE) Study (2001) Factors associated with increased serum levels of cardiac troponins T and I in chronic haemodialysis patients: chronic haemodialysis and new cardiac markers evaluation (CHANCE) study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 16:1452–1458
Conway B, McLaughlin M, Sharpe P, Harty J (2005) Use of cardiac troponin T in diagnosis and prognosis of cardiac events in patients on chronic haemodialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2759–2764
Metra M, Bettari L, Pagani F, Lazzarini V, Lombardi C, Carubelli V, Bonetti G, Bugatti S, Parrinello G, Caimi L, Felker GM, Dei Cas L (2012) Troponin T levels in patients with acute heart failure: clinical and prognostic significance of their detection and release during hospitalisation. Clin Res Cardiol 101:663–672
Mueller M, Celik S, Biener M, Vafaie M, Schwoebel K, Wollert KC, Januzzi JL, Katus HA, Giannitsis E (2012) Diagnostic and prognostic performance of a novel high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T assay compared to a contemporary sensitive cardiac troponin I assay in patients with acute coronary syndrome. Clin Res Cardiol 101:837–845
Celik S, Giannitsis E, Wollert KC, Schwobel K, Lossnitzer D, Hilbel T, Lehrke S, Zdunek D, Hess A, Januzzi JL, Katus HA (2011) Cardiac troponin T concentrations above the 99th percentile value as measured by a new high-sensitivity assay predict long-term prognosis in patients with acute coronary syndromes undergoing routine early invasive strategy. Clin Res Cardiol 100:1077–1085
Beciani M, Tedesco A, Violante A, Cipriani S, Azzarito M, Sturniolo A, Splendiani G (2003) Cardiac troponin I (2nd generation assay) in chronic haemodialysis patients: prevalence and prognostic value. Nephrol Dial Transplant 18:942–946
Kumar N, Michelis MF, DeVita MV, Panagopoulos G, Rosenstock JL (2011) Troponin I levels in asymptomatic patients on haemodialysis using a high-sensitivity assay. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26:665–670
Ritz E, Rambausek M, Mall G, Ruffmann K, Mandelbaum A (1990) Cardiac changes in uraemia and their possible relationship to cardiovascular instability on dialysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 5(Suppl 1):93–97
McIntyre CW (2009) Effects of hemodialysis on cardiac function. Kidney Int 76:371–375
Assa S, Dasselaar JJ, Slart RH, de Jong PE, Voors AA, Tio RA, Franssen CF (2012) Comparison of cardiac positron emission tomography perfusion defects during stress induced by hemodialysis versus adenosine. Am J Kidney Dis 59:862–864
Burton JO, Jefferies HJ, Selby NM, McIntyre CW (2009) Hemodialysis-induced cardiac injury: determinants and associated outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:914–920
Assa S, Hummel YM, Voors AA, Kuipers J, Westerhuis R, de Jong PE, Franssen CF (2012) Hemodialysis-induced regional left ventricular systolic dysfunction: prevalence, patient and dialysis treatment-related factors, and prognostic significance. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7:1615–1623
Apple FS, Pearce LA, Smith SW, Kaczmarek JM, Murakami MM (2009) Role of monitoring changes in sensitive cardiac troponin I assay results for early diagnosis of myocardial infarction and prediction of risk of adverse events. Clin Chem 55:930–937
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assa, S., Gansevoort, R.T., Westerhuis, R. et al. Determinants and prognostic significance of an intra-dialysis rise of cardiac troponin I measured by sensitive assay in hemodialysis patients. Clin Res Cardiol 102, 439–445 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-013-0551-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-013-0551-8