Abstract
Purpose
To describe the prenatal findings, treatments and outcomes of fetuses with pulmonary sequestrations (PS), which were retrospectively studied.
Methods
From May 2010 to January 2013, 292 women were referred to the Guangdong Women and Children Hospital, Guangzhou because obstetric ultrasound had demonstrated fetal lung lesions. In 68 fetuses, the echogenic lung masses were pulmonary sequestrations deriving arterial blood supply from clearly identifiable systemic arteries rather than the pulmonary artery. We examined records of the 68 fetuses and measured the lesions and congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation volume ratio (CVR), provided prenatal counseling and treatment, documented the CVR, location of lesion, gestational age at diagnosis, need for fetal intervention, perinatal clinical course (including the development of hydrops, effusions, and neonatal respiratory distress), gestational age at delivery, postnatal ultrasound and CT, operation treatment, survival and pathology.
Results
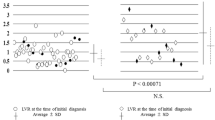
There were 68 PS in our study. All of 56 cases with CVR ≤1.6, survived without prenatal hydrops or postnatal respiratory symptoms. In 12 cases with CVR >1.6, 7 cases (58.3 %, 7/12) had hydrops, 10 cases (83.3 %, 10/12) survived, 2 cases (16.7 %, 2/12) of induced abortion, 8 cases (66 %, 8/12) were postnatal symptomatic. There was statistical significant difference in the incidence rate of hydrops and postnatal respiratory symptoms between the PS with CVR ≤1.6 and that with CVR >1.6. 66 cases postnatal survived, two cases of induced abortion. 64 cases had no prenatal treatment, two cases underwent thoracoamniotic shunt. The mean gestational age at birth was 38 weeks (range 34–40 weeks). 21 asymptomatic cases had no surgery. 45 cases (8 symptomatic and 37 asymptomatic) underwent surgical resections, 43 cases without postoperative complications, two cases of postoperative pneumothorax, no wound infection. Postoperative follow-up showed good growth in all surgery cases.
Conclusion
PS specific absence of hydrop was a congenital disorder with an excellent prognosis. CVR >1.6 was associated with fetal hydrops and postnatal symptoms. However, absolute CVR value cannot be used to select fetuses for fetal treatment before the development of hydrops. Surgery of PS in neonates or infants presented a good outcome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harriet JC, Gillian MH (2004) Pulmonary sequestration. Paediatr Respir Rev 5:59–68
Pryce DM (1946) Lower accessory pulmonary artery with intralobar sequestration of the lung: report of cases. J Pathol 58:457–467
Gezer S, Tastepe I, Sirmali M et al (2007) Pulmonary sequestration: a single-institutional series composed of 27 cases. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 133:955–959
Cooke CR (2006) Bronchopulmonary sequestration. Respir Care 51:661–664
Pedata R, Palermo M, Maiello M et al (2009) Fetal lung lesions diagnosis: the crucial role of ultrasonography. J Prenat Med 3(4):49–52
Sfakianaki AK, Copel JA (2012) Congenital cystic lesions of the lung: congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation and bronchopulmonary sequestration. Rev Obstet Gynecol 5(2):85–93
Adzick NS (1993) Fetal thoracic lesions. Semin Pediatr Surg 2:103–108
MacGillivray TE, Harrison MR, Goldstein RB et al (1993) Disappearing fetal lung lesions. J Pediatr Surg 28:1321–1325
John BL, Ruth BG, Gerald SL et al (1999) Fetal pulmonary sequestration a favourable congenital lung lesion. Obstet Gynecol 94:567–571
Wu D, Miller R, Simpson L et al (2006) Congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation (CCAM) volume ratio: risk of fetal hydrops. Am J Obstet Gynecol 195:173
Crombleholme TM, Coleman B, Hedrick H et al (2002) Cystic adenomatoid malformation volume ratio predicts outcome in prenatally diagnosed cystic adenomatoid malformation of the lung. Pediatr Surg 37(3):331–338
Sauerbrei E (1991) Lung sequestration duplex Doppler diagnosis at 19 weeks gestation. J Ultrasound Med 10:101–105
Norton M (1994) Nonimmune hydrops fetalis. Semin Perinatol 18:321–322
Swain S, Cameron AD, McNay MB et al (1999) Prenatal diagnosis and management of nonimmune hydrops fetalis. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol 39(3):285–290
Lin CH, Chuang CY, Hsia JY et al (2013) Pulmonary sequestration—differences in diagnosis and treatment in a single institution. J Chin Med Assoc 76(7):385–389
Marwede D, Tillig ER, Hirsch W (2008) Imaging findings and differential diagnosis of infradiaphragmatic pulmonary sequestration. Pediatr Int 50(6):821–823
Adzick NS, Harrison MR, Crombleholme TM et al (1998) Fetal lung lesions: management and outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol 179:884–889
Cass DL, Crombleholme TM, Howell LJ et al (1997) Cystic lung lesions with systemic arterial blood supply: a hybrid of congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation and bronchopulmonary sequestration. J Pediatr Surg 32:986–990
Samuel M, Burge DM (1999) Management of antenatally diagnosed pulmonary sequestration associated with congenital cystic adenomatoid malformation. Thorax 54:701–706
Bromley B, Parad R, Estroff JA et al (1995) Fetal lung masses: prenatal course and outcome. J Ultrasound Med 14:927–936
John PR, Beasley SW, Mayne V (1989) Reviews: pulmonary sequestration and related congenital disorders a clinico-radiological review of 41 cases. Pediatr Radiol 20:4–9
Ikezoe J, Murayama S, Godwin JD et al (1990) Bronchopulmonary sequestration: CT assessment. Radiology 176:375–379
Kaude KV, Laurin S (1984) Ultraonographic demonstration of systemic artery feeding extrapulmonary sequestration. Pediatr Radiol 14:226–227
Claudio RP, Adriano C, Edward AJ et al (2013) Diagnosis of intra-abdominal extralobar pulmonary sequestration by means of ultrasound in a neonate. Case Rep Pediatr 2013:623102. doi:10.1155/2013/623102
Witlox RS, Lopriore E, Oepkes D et al (2011) Neonatal outcome after prenatal interventions for congenital lung lesions. Early Hum Dev 87:611–618
Cavoretto P, Molina F, Poggi S et al (2008) Prenatal diagnosis and outcome of echogenic fetal lung lesions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 32:769–783
Anandakumar C, Biswas A, Chua TM et al (1999) Direct intrauterine fetal therapy in a case of bronchopulmonary sequestration associated with non-immune hydrops fetalis. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 13:263–265
Bratu I, Flageole H, Chen MF et al (2001) The multiple facets of pulmonary sequestration. J Pediatr Surg 36:784–790
Kestenholz PB, Schneiter D, Hillinger S et al (2006) Thoracoscopic treatment of pulmonary sequestration. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 29:815–818
Gluer S, Scharf A, Ure BM (2002) Thorascopic resection of extralobar sequestration in a neonate. J Pediatr Surg 37:1629–1631
Shen J-F, Zhang X-X, Li S-B et al (2013) Complete video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for pulmonary sequestration. J Thorac Dis 5(1):31–35
Lin T, Pimpalwar A (2010) Minimally invasive surgery in neonates and infants. J Indian Assoc Pediatr Surg 15(1):2–8
Conflict of interest
The authors report that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Tian, J., Chen, Z. et al. Retrospective study of prenatal diagnosed pulmonary sequestration. Pediatr Surg Int 30, 47–53 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3434-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-013-3434-1