Abstract
Purpose
Tissue engineering of the oesophagus has been proposed as a therapeutic alternative to organ transplantation. We previously demonstrated that a detergent enzymatic treatment (DET) is a valid method to obtain an acellular matrix with preservation of the native architecture. In this study, we aimed to develop a natural acellular matrix from pig oesophagus, as a valid framework for oesophageal replacement.
Methods
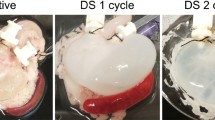
Pig oesophagi (n = 4) were decellularized with continuous luminal infusion of DET. To evaluate the efficiency of the decellularization, samples were assessed by histology and DNA quantification. Moreover, the ultra-structural characteristics of the acellular matrix were investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM).
Results
Decellularization of the oesophagus was achieved after three cycles of DET. Histological analysis showed the maintenance of tissue matrix architecture with absence of cellular elements, verified by measurement of DNA. SEM and TEM analysis confirmed preservation of the ultra-structural characteristics of the native tissue.
Conclusions
Oesophageal acellular matrix can be successfully obtained by decellularization of pig oesophagus using a gentle DET via the oesophageal lumen. This decellularization method preserves the ultrastructure of the native tissue and could represent the basis for a tissue-engineered oesophagus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spitz L, Kiely E, Pierro A (2004) Gastric transposition in children—a 21-year experience. J Pediat Surg 39:276–281. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2003.11.032 (discussion 276–281)
Allum WH, Blazeby JM, Griffin SM, Cunningham D, Jankowski JA, Wong R (2011) Association of upper gastrointestinal surgeons of great Britain and Ireland, the British Society of Gastroenterology and the British Association of Surgical Oncology. Guidelines for the management of oesophageal and gastric cancer. Gut 60:1449–1472. doi:10.1136/gut.2010.228254
Ludman L, Spitz L (2003) Quality of life after gastric transposition for oesophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg 38:53–57. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2003.50009 (discussion 53–57)
Ure BM, Slany E, Eypasch EP, Gharib M, Holschneider AM, Troidl H (1995) Long-term functional results and quality of life after colon interposition for long-gap oesophageal atresia. Eur J Pediatr Surg 5:206–210. doi:10.1055/s-2008-1066206
Orlando G, Wood KJ, Stratta RJ et al (2011) Regenerative medicine and organ transplantation: past, present, and future. Transplantation 91:1310–1317. doi:10.1097/TP.0b013e318219ebb5
Zani A, Pierro A, Elvassore N, De Coppi P (2009) Tissue engineering: an option for esophageal replacement? Semin Pediatr Surg 18:57–62. doi:10.1053/j.sempedsurg.2008.10.011
Atala A, Bauer SB, Soker S, Yoo JJ, Retik AB (2006) Tissue-engineered autologous bladders for patients needing cystoplasty. Lancet 367:1241–1246. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(06)68438-9
Raya-Rivera A, Esquiliano DR, Yoo JJ, Lopez-Bayghen E, Soker S, Atala A (2011) Tissue engineered autologous urethras for patients who need reconstruction: an observational study. Lancet 377:1175–1182. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62354-9
Macchiarini P, Jungebluth P, Go T, Asnaghi MA, Rees LE, Cogan TA et al (2008) Clinical transplantation of a tissue-engineered airway. Lancet 372:2023–2030. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61598-6
Laurance J (2010) British boy receives trachea transplant built with his own stem cells. BMJ 340:c1633. doi:10.1136/bmj.c1633
Fishman JM, De Coppi P, Elliott MJ, Atala A, Birchall MA, Macchiarini P (2011) Airway tissue engineering. Expert Opin Biol Ther 11(12):1623–1635. doi:10.1517/14712598.2011.623696
Baiguera S, Jungebluth P, Burns A, Mavilia C, Haag J, De Coppi P, Macchiarini P (2010) Tissue engineered human tracheas for in vivo implantation. Biomaterials 31(34):8931–8938. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.08.005
Elliott MJ, De Coppi P, Speggiorin S, Roebuck D, Butler CR, Samuel E, Crowley C, McLaren C, Fierens A, Vondrys D, Cochrane L, Jephson C, Janes S, Beaumont NJ, Cogan T, Bader A, Seifalian AM, Hsuan JJ, Lowdell MW, Birchall MA (2012) Stem-cell-based, tissue engineered tracheal replacement in a child: a 2-year follow-up study. Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)61345-8 (Epub ahead of print)
Orlando G, García-Arrarás JE, Soker T, Booth C, Wang Z, Ross CL, Farney AC, Rogers J, De Coppi P, Stratta RJ (2012) Regeneration and bioengineering of the gastrointestinal tract: current status and future perspectives. Dig Liver Dis 44(9):714–720. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2012.04.005
Orlando G, Bendala JD, Shupe T, Bergman C, Bitar KN, Booth C, Carbone M, Koch K, Lerut JP, Neuberger J, Petersen BE, Ricordi C, Atala A, Stratta RJ, Soker S (2012) Cell and organ bioengineering technology as applied to gastrointestinal diseases. Gut. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2011-301111
Takimoto Y, Nakamura T, Teramachi M, Kiyotani T, Shimizu Y (1995) Replacement of long segments of the esophagus with a collagen-silicone composite tube. ASAIO J 41:M605–M608. doi:10.1097/00002480-199507000-00082
Takimoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamamoto Y, Kiyotani T, Teramachi M, Shimizu Y (1998) The experimental replacement of a cervical esophageal segment with an artificial prosthesis with the use of collagen matrix and a silicone stent. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 116:98–106. doi:10.1016/S0022-5223(98)70247-8
Yamamoto Y, Nakamura T, Shimizu Y, Matsumoto K, Takimoto Y, Kiyotani T, Sekine T, Ueda H, Liu Y, Tamura N (1999) Intrathoracic esophageal replacement in the dog with the use of an artificial esophagus composed of a collagen sponge with a double-layered silicone tube. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 118:276–286. doi:10.1016/S0022-5223(99)70218-7
Badylak S, Meurling S, Chen M, Spievack A, Simmons-Byrd A (2000) Resorbable bioscaffold for esophageal repair in a dog model. J Pediatr Surg 35:1097–1103. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2000.7834
Badylak SF, Hoppo T, Nieponice A, Gilbert TW, Davison JM, Jobe BA (2011) Esophageal preservation in five male patients after endoscopic inner-layer circumferential resection in the setting of superficial cancer: a regenerative medicine approach with a biologic scaffold. Tissue Eng Part A 17:1643–1650. doi:10.1089/ten.tea.2010.0739
Clough A, Ball J, Smith GS, Leibman S (2011) Porcine small intestine submucosa matrix (Surgisis) for esophageal perforation. Ann Thorac Surg 91:e15–e16. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2010.10.011
Lopes MF, Cabrita A, Ilharco J, Pessa P, Paiva-Carvalho J, Pires A, Patrício J (2006) Esophageal replacement in rat using porcine intestinal submucosa as a patch or a tube-shaped graft. Dis Esophagus 19:254–259. doi:10.1111/j.1442-2050.2006.00574.x
Doede T, Bondartschuk M, Joerck C, Schulze E, Goernig M (2009) Unsuccessful alloplastic esophageal replacement with porcine small intestinal submucosa. Artif Organs 33:328–333. doi:10.1111/j.1525-1594.2009.00727.x
Lopes MF, Cabrita A, Ilharco J, Pessa P, Patrício J (2006) Grafts of porcine intestinal submucosa for repair of cervical and abdominal esophageal defects in the rat. J Invest Surg 19:105–111. doi:10.1080/08941930600569621
Badylak SF, Vorp DA, Spievack AR, Simmons-Byrd A, Hanke J, Freytes DO, Thapa A, Gilbert TW, Nieponice A (2005) Esophageal reconstruction with ECM and muscle tissue in a dog model. J Surg Res 128:87–97. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2005.03.002
Ott HC, Matthiesen TS, Goh SK et al (2008) Perfusion-decellularized matrix: using nature’s platform to engineer a bioartificial heart. Nat Med 14:213–221. doi:10.1038/nm1684
Uygun BE, Soto-Gutierrez A, Yagi H et al (2010) Organ reengineering through development of a transplantable recellularized liver graft using decellularized liver matrix. Nat Med 16:814–820. doi:10.1038/nm.2170
Baptista PM, Siddiqui MM, Lozier G et al (2011) The use of whole organ decellularization for the generation of a vascularized liver organoid. Hepatology 53:604–617. doi:10.1002/hep.24067
Ott HC, Clippinger B, Conrad C et al (2010) Regeneration and orthotopic transplantation of a bioartificial lung. Nat Med 16:927–933. doi:10.1126/science.1189345
Totonelli G, Maghsoudlou P, Garriboli M, Riegler J, Orlando G, Burns AJ, Sebire NJ, Smith VV, Fishman JM, Ghionzoli M, Turmaine M, Birchall MA, Atala A, Soker S, Lythgoe MF, Seifalian A, Pierro A, Eaton S, De Coppi P (2012) A rat decellularized small bowel 15 scaffold that preserves villus-crypt architecture for intestinal regeneration. Biomaterials 33(12):3401–3410. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.012
Saxena AK, Ainoedhofer H, Hollwarth ME (2009) Esophagus tissue engineering: in vitro generation of esophageal epithelial cell sheets and viability on scaffold. J Pediatr Surg 44:896–901. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2009.01.019
Saxena AK, Ainoedhofer H, Hollwarth ME (2010) Culture of ovine esophageal epithelial cells and in vitro esophagus tissue engineering. Tissue Eng Part C Methods 16:109–114. doi:10.1089/ten.tec.2009.0145
Conconi MT, De Coppi P, Di Liddo R, Vigolo S, Zanon GF, Parnigotto PP et al (2005) Tracheal matrices, obtained by a detergent-enzymatic method, support in vitro the adhesion of chondrocytes and tracheal epithelial cells. Transpl Int 18:727–734. doi:10.1111/j.1432-2277.2005.00082.x
Marzaro M, Vigolo S, Oselladore B, Conconi MT, Ribatti D, Giuliani S, Nico B, Perrino G, Nussdorfer GG, Parnigotto PP (2006) In vitro and in vivo proposal of an artificial esophagus. J Biomed Mater Res A 77(4):795–801. doi:10.1002/jbm.a.30666
Acknowledgments
We thank Michael Boyd of the Royal Veterinary College’s Biological Unit for providing the animal tissue. This investigation was supported by Great Ormond Street Hospital charity, the Fondation Eugenio Litta (Geneva, Switzerland), the Medical Research Council, the Royal College of Surgeons of England, the Sparks Children’s Medical Charity, the British Foreign Office for the UK/USA Stem Cell Collaboration Award and the Mittal Research Fund. We would also like to thank the Royal Society/Wolfson Foundation for the tissue engineering laboratory refurbishment grant obtained for the Pediatric Surgery Department in the Institute of Child Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Totonelli, G., Maghsoudlou, P., Georgiades, F. et al. Detergent enzymatic treatment for the development of a natural acellular matrix for oesophageal regeneration. Pediatr Surg Int 29, 87–95 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-012-3194-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-012-3194-3