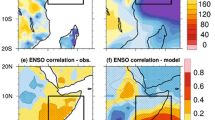
Abstract
Rainfall over eastern Africa (10°S–10°N; 35°E–50°E) is bimodal, with seasonal maxima during the "long rains" of March–April–May (MAM) and the "short rains" of October–November–December (OND). Below average precipitation during consecutive long and short rains seasons over eastern Africa can have devastating long-term impacts on water availability and agriculture. Here, we examine the forcing of drought during consecutive long and short rains seasons over eastern Africa by Indo-Pacific sea surface temperatures (SSTs). The forcing of eastern Africa precipitation and circulation by SSTs is tested using ten ensemble simulations of a global weather forecast model forced by 1950–2010 observed global SSTs. Since the 1980s, Indo-Pacific SSTs have forced more frequent droughts spanning consecutive long and short rains seasons over eastern Africa. The increased frequency of dry conditions is linked to warming SSTs over the Indo-west Pacific and to a lesser degree to Pacific Decadal Variability. During MAM, long-term warming of tropical west Pacific SSTs from 1950–2010 has forced statistically significant precipitation reductions over eastern Africa. The warming west Pacific SSTs have forced changes in the regional lower tropospheric circulation by weakening the Somali Jet, which has reduced moisture and rainfall over the Horn of Africa. During OND, reductions in precipitation over recent decades are oftentimes overshadowed by strong year-to-year precipitation variability forced by the Indian Ocean Dipole and the El Niño–Southern Oscillation.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abram NJ, Gagan MK, Cole JE, Hantoro WS, Mudelsee M (2008) Recent intensification of tropical climate variability in the indian ocean. Nat Geosci 1(12):849–853. doi:10.1038/ngeo357
Adler RF, Huffman GJ, Chang A, Ferraro R, Xie PP, Janowiak J, Rudolf B, Schneider U, Curtis S, Bolvin D, Gruber A, Susskind J, Arkin P, Nelkin E (2003) The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979 present). J Hydrometeorol 4(6):1147–1167. doi:10.1175/1525-7541(2003)004<1147:TVGPCP>2.0.CO;2
Black E, Slingo J, Sperber KR (2003) An observational study of the relationship between excessively strong short rains in coastal east africa and indian ocean SST. Mon Weather Rev 131(1):74–94 doi:10.1175/1520-0493(2003)131<0074:AOSOTR>2.0.CO;2
Camberlin P, Philippon N (2002) The east african March - May rainy season: Associated atmospheric dynamics and predictability over the 1968–97 period. J Clim 15(9):1002–1019. doi:10.1175/1520-0442(2002)015<1002:TEAMMR>2.0.CO;2
Compo GP, Sardeshmukh PD (2009) Removing ENSO-Related variations from the climate record. J Clim 23(8):1957–1978. doi:10.1175/2009JCLI2735.1
FEWSNET (2011) Past year one of the driest on record in the eastern horn, famine early warning system network report. Tech. rep., U.S. Agency for International Development, Washington, DC
Funk C, Dettinger MD, Michaelsen JC, Verdin JP, Brown ME, Barlow M, Hoell A (2008) Warming of the indian ocean threatens eastern and southern african food security but could be mitigated by agricultural development. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105(32):11081–11086. http://www.pnas.org/content/105/32/11081.abstract
Haile M (2005) Weather patterns, food security and humanitarian response in sub-saharan africa. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 360(1463):2169–2182. http://rstb.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/360/1463/2169.abstract
Hastenrath S, Nicklis A, Greischar L (1993) Atmospheric-hydrospheric mechanisms of climate anomalies in the western equatorial indian ocean. J Geophys Res 98(C11):20219–20235. doi:10.1029/93JC02330
Hillbruner C, Moloney G (2012) When early warning is not enough lessons learned from the 2011 somalia famine. Special Issue on the Somalia Famine of 2011–2012. Glob Food Secur 1(1):20–28 doi:10.1016/j.gfs.2012.08.001
Hoell A, Funk C (2013) The ENSO-related west pacific sea surface temperature gradient. J Clim. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00344.1
Hoell A, Funk C, Barlow M (2013) The regional forcing of northern hemisphere drought during recent warm tropical west Pacific Ocean la nina events. Clim Dyn. doi:10.1007/s00382-013-1799-4
Indeje M, Semazzi FH, Ogallo LJ (2000) ENSO signals in east african rainfall seasons. Int J Climatol 20(1):19–46. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(200001)20:1<19::AID-JOC449>3.0.CO;2-0
L/’Heureux ML, Lee S, Lyon B (2013) Recent multidecadal strengthening of the walker circulation across the tropical pacific. Nat Clim Change. doi:10.1038/nclimate1840
Lyon B, DeWitt DG (2012) A recent and abrupt decline in the east african long rains. Geophys Res Lett 39(2):L02702. doi:10.1029/2011GL050337
Mantua NJ, Hare SR, Zhang Y, Wallace JM, Francis RC (1997) A pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull Am Meteorol Soc 78(6):1069–1079. doi:10.1175/1520-0477(1997)078<1069:APICOW>2.0.CO;2
Nicholson S, Selato J (2000) The influence of La Nina on african rainfall. Int J Climatol 20(14):1761–1776. doi:10.1002/1097-0088(20001130)20:14<1761::AID-JOC580>3.0.CO;2-W
Nicholson SE, Kim J (1997) The relationship of the El nino-southern oscillation to african rainfall. Int J Climatol 17(2):117–135. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0088(199702)17:2<117::AID-JOC84>3.0.CO;2-O
Ogallo LJ (1988) Relationships between seasonal rainfall in east africa and the southern oscillation. J Climatol 8(1):31–43. doi:10.1002/joc.3370080104
Rasmusson EM, Carpenter TH (1982) Variations in tropical sea surface temperature and surface wind fields associated with the southern Oscillation/El nino. Mon Weather Rev 110(5):354–384. doi:10.1175/1520-0493(1982)110<0354:VITSST>2.0.CO;2
Saji NH, Goswami BN, Vinayachandran PN, Yamagata T (1999) A dipole mode in the tropical indian ocean. Nature 401(6751):360–363
Smith TM, Reynolds RW, Peterson TC, Lawrimore J (2008) Improvements to NOAAs historical merged land–ocean surface temperature analysis (1880–2006). J Clim 21(10):2283–2296. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI2100.1
Solomon A, Newman M (2012) Reconciling disparate twentieth-century Indo-Pacific ocean temperature trends in the instrumental record. Nat Clim Change 2(9):691–699. doi:10.1038/nclimate1591
Tierney JE, Smerdon JE, Anchukaitis KJ, Seager R (2013) Multidecadal variability in east African hydroclimate controlled by the Indian ocean. Nature 493(7432):389–392. doi:10.1038/nature11785
Verdin J, Funk C, Senay G, Choularton R (2005) Climate science and famine early warning. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 360(1463):2155–2168. http://rstb.royalsocietypublishing.org/content/360/1463/2155
Wang C, Weisberg RH, Virmani JI (1999) Western pacific interannual variability associated with the El nio-southern oscillation. J Geophys Res 104(C3):5131–5149. doi:10.1029/1998JC900090
Washington R, Downing TE (1999) Seasonal forecasting of african rainfall: prediction, responses and household food security. Geogr J 165(3):255–274. doi:10.2307/3060442. ArticleType: research-article / Full publication date: Nov., 1999 / Copyright 1999 The Royal Geographical Society (with the Institute of British Geographers)
Williams A, Funk C (2011) A westward extension of the warm pool leads to a westward extension of the walker circulation, drying eastern africa. Clim Dyn 37(11–12):2417–2435. doi:10.1007/s00382-010-0984-y
Yeh SW, Ham YG, Lee JY (2012) Changes in the tropical pacific SST trend from CMIP3 to CMIP5 and its implication of ENSO*. J Clim 25(21):7764–7771. doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00304.1
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank two anonymous reviewers whose comments and suggestions helped to improve the manuscript. This research builds upon a multi-year research project carried out under a U.S. Agency for International Development-funded Famine Early Warnings System Network agreement with the U.S. Geological Survey.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoell, A., Funk, C. Indo-Pacific sea surface temperature influences on failed consecutive rainy seasons over eastern Africa. Clim Dyn 43, 1645–1660 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1991-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1991-6