Abstract
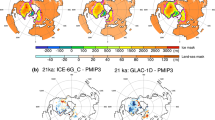
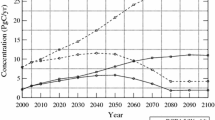
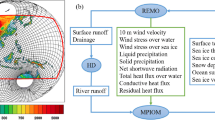
The atmosphere–ocean general circulation models (AOGCMs) used for the IPCC 4th Assessment Report (IPCC AR4) are evaluated for the Greenland ice sheet (GrIS) current climate modelling. The most suited AOGCMs for Greenland climate simulation are then selected on the basis of comparison between the 1970–1999 outputs of the Climate of the twentieth Century experiment (20C3M) and reanalyses (ECMWF, NCEP/NCAR). This comparison indicates that the representation quality of surface parameters such as temperature and precipitation are highly correlated to the atmospheric circulation (500 hPa geopotential height) and its interannual variability (North Atlantic oscillation). The outputs of the three most suitable AOGCMs for present-day climate simulation are then used to assess the changes estimated by three IPCC greenhouse gas emissions scenarios (SRES) over the GrIS for the 2070–2099 period. Future atmospheric circulation changes are projected to dampen the zonal flow, enhance the meridional fluxes and therefore provide additional heat and moisture to the GrIS, increasing temperature over the whole ice sheet and precipitation over its northeastern area. We also show that the GrIS surface mass balance anomalies from the SRES A1B scenario amount to −300 km3/year with respect to the 1970–1999 period, leading to a global sea-level rise of 5 cm by the end of the 21st century. This work can help to select the boundaries conditions for AOGCMs-based downscaled future projections.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appenzeller C, Schwander J, Sommer S, Stocker TF (1998) The North Atlantic Oscillation and its imprint on precipitation and ice accumulation in Greenland. Geophys Res Lett 25(11):1939–1942
Bales RC, Guo Q, Shen D, McConnell JR, Du G, Burkhart JF, Spikes VB, Hanna E, Cappelen J (2009) Annual accumulation for Greenland updated using ice core data developed during 2000–2006 and analysis of daily coastal meteorological data. Geophys Res Lett 114:D06116. doi:10.1029/2008JD011208
Barry RG, Kiladis GN (1982) Climatic characteristics of Greenland. In: Radok U (ed) Climatic and Physical Characteristics of the Greenland ice sheet. CIRES, Boulder, CO, USA, pp 7–33
Bond G, Broecker W, Johnsen S, McManus J, Labeyrie L, Jouzel J, Bonami G (1993) Correlations between climate records from North Atlantic sediments and Greenland Ice. Nature 365:143–147
Box JE (2002) Survey of Greenland instrumental temperature records: 1873–2001. Int J Climatol 22:1829–1847
Box JE, Bromwich DH, Bai LS (2004) Greenland ice sheet surface mass balance for 1991–2000: application of Polar MM5 mesoscale model and in–situ data. J Geophys Res 109(D16):D16105. doi:10.1029/2003JD004451
Box JE, Bromwich DH, Veenhuis BA, Bai LS, Stroeve JC, Rogers JC, Steffen K, Haran T, Wang SH (2006) Greenland ice sheet surface mass balance variability (1988–2004) from calibrated Polar MM5 output. J Clim 19(12):2783–2800
Box JE, Bai LS, Benson R, Bhattacharya I, Bromwich DH, Cappelen J, Decker D, DiGirolamo N, Fettweis X, Hall D, Hanna E, Mote T, Tedesco M, van de Wal R, van den Broeke M (2009) Greenland climate in 2008. In: State of the climate in 2008. Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society, vol 90, no 8, pp S1–S196. doi:10.1175/BAMS-90-8-StateoftheClimate
Bromwich DH, Chen QS, Li YF, Cullather RI (1999) Precipitation over Greenland and its relation to the North Atlantic Oscillation. J Geophys Res 104(D18):22103–22115
Burgess EW, Forster RR, Box JE, Smith LC, Bromwich DH (2009) Greenland ice sheet annually-resolved accumulation rates (1958–2007), a spatially calibrated model. J Geophys Res (provisionally accepted)
Cappelen J, Jorgensen BV, Laursen EV, Stannius LS, Thomsen RS (2001) The observed climate of Greenland, 1958–99—with climatological standard normals, 1961–1990. Tech Rep 00–18, Danish Meteorological Institute, Copenhagen
Chen QS, Bromwich DH, Bai L (1997) Precipitation over Greenland retrieved by a dynamic method and its relation to cyclonic activity. J Clim 10:839–870
Chylek P, Box JE, Lesins G (2004) Global warming and the Greenland ice sheet. Clim Change 63:201–221
Comiso C, Parkinson CL, Gerttsen R, Stock L (2008) Accelerated decline in the Arctic sea ice cover. Geophys Res Lett 35:L01703. doi:10.1029/2007GL031972
Connolley WM, Bracegirdle TJ (2007) An Antarctic assessment of IPCC AR4 coupled models. Geophys Res Lett 34:L22505. doi:10.1029/2007GL031648
Cuffey KM, Marshall SJ (2000) Substantial contribution to sea level rise during the last interglacial from the Greenland ice sheet. Nature 404:591–594
Dethloff K, Schwager M, Christensen JH, Kiilsholm S, Rinke A, Dorn W, Jung-Rothenhusler F, Fischer H, Kipfstuhl S, Miller H (2002) Recent Greenland accumulation estimated from regional model simulations and ice core analysis. J Clim 15:2821–2832
Fettweis X, Galle H, Lefebre L, van Ypersele JP (2005) Greenland surface mass balance simulated by a regional climate model and comparison with satellite derived data in 1990–1991. Clim Dyn 24:623–640. doi:10.1007/s00382-005-0010-y
Fettweis X (2007) Reconstruction of the 1979–2006 Greenland ice sheet surface mass balance using the regional climate model MAR. The Cryosphere 1:21–40
Fettweis X, Hanna E, Galle H, Huybrechts P, Erpicum M (2008) Estimation of the Greenland ice sheet surface mass balance for the 20th and 21st centuries. The Cryosphere 2:117–129
Gallée H, Duynkerke P (1997) Air–snow interactions and the surface energy and mass balance over the melting zone of West Greenland during GIMEX. J Geophys Res 102:13813–13824
Gregory JM, Dixon K, Stouffer RJ, Weaver A, Driesschaert E, Eby M, Fichefet T, Hasumi H, Hu A, Jungclaus J, Kamenkovich I, Levermann A, Montoya M, Murakami S, Nawrath S, Oka A, Solokov A, Thorpe R (2005) A model intercomparison of changes in the Atlantic thermohaline circulation in response to increasing atmospheric concentration. J Geophys Res 32:L12703. doi:10.1029/2005GL023209
Gregory JM, Huybrechts P (2006) Ice-sheet contributions to future sea-level change. Phil Trans R Soc A 364:1709–1731. doi:10.1098/rsta.2006.1796
Hanna E, Huybrechts P, Steffen K, Cappelen J, Huff R, Shuman C, Irvine–Fynn T, Wise S, Griffiths M (2008) Increased runoff from melt from the Greenland ice sheet: a response to global warming. J Clim 21:331–341. doi:10.1175/2007JCLI1964.1
Hurrell JW (1995) Decadal trends in the North Atlantic oscillation: regional temperatures and precipitation. Science 269:676–679
IPCC (2007) In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental panel on Climate change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA
Jones PD, New M, Parker DE, Martin S, Rigor IG (1999) Surface air temperature and its changes over the past 150 years. Rev Geophys 37(2):173–199
Kapsner WR, Alley RB, Shuman CA, Anandakrishnan S, Grootes PM (1995) Dominant influence of atmospheric circulation on snow accumulation in Greenland over the last 18,000 years. Nature 373:52–54. doi:10.1038/373052a0
Kiilsholm S, Christensen JH, Dethloff K, Rinke A (2003) Net accumulation of the Greenland ice sheet: high-resolution climate modelling of regional climate change in the Arctic. Geophys Res Lett 30:1485. doi:10.1029/2002GL015742
Krinner G, Julien N (2007) High-resolution simulations of the surface mass balance of Greenland at the end of this century. The Cryosphere Discuss 1:351–383
Kristjánsson JE, McInnes H (1999) The impact of Greenland on cyclone evolution in the North Atlantic. Quart J R Meteorol Soc 125:2819–2834
Kwok R, Rothrock DA (1999) Variability of Fram Strait ice flux and North Atlantic Oscillation. J Geophys Res 104(C3):5177–5189
Lefebvre W, Goosse H (2007) Analysis of the projected regional sea–ice changes in the Southern Ocean during the twenty-first century. Clim Dyn 30:59–76. doi:10.1007/s00382-007-0273-6
Leloup J, Lengaigne M, Boulanger JP (2007) Twentieth century ENSO characteristics in the IPCC database. Clim Dyn 30:277–291. doi:10.1007/s00382-007-0284-3
Meehl GA, Stocker TF, Collins WD, Friedlingstein P, Gaye AT, Gregory JM, Kitoh A, Knutti R, Murphy JM, Noda A, Raper SCB, Watterson IG, Weaver AJ, Zhao ZC (2007) Global climate projections. In: Solomon S, Qin D, Manning M, Chen Z, Marquis M, Averyt KB, Tignor M, Miller HL (eds) Climate change 2007: the physical science basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK and New York, NY, USA
Mernild SH, Liston GE, Hiemstra CA, Steffen K (2008) Surface melt area and water balance modeling on the Greenland ice sheet 1995–2005. J Hydrometeorol 9(6):1191–1211
Mosley-Thompson E, Readinger CR, Craigmile P, Thompson LG, Calder CA (2005) Regional sensitivity of Greenland precipitation to NAO variability. Geophys Res Lett 32:L24707. doi:10.1029/2005GL024776
Mote TL (2003) Estimation of runoff rates, mass balance, and elevation changes on the Greenland ice sheet from passive microwave observations. J Geophys Res 108(D2):4056. doi:10.1029/2001JD002032
Ohmura A, Reeh N (1991) New precipitation and accumulation maps for Greenland. J Glaciol 37:140–148
Parkinson CL, Cavalieri DJ, Gloersen P, Zwally HJ, Comiso JC (1999) Arctic sea ice extents, areas, and trends, 1978–1996. J Geophys Res 104(C9):20837–20856
Rahmstorf S, Crucifix M, Ganopolski A, Goosse H, Kamenkovich I, Knutti R, Lohmann G, Marsh R, Mysak LA, Wang Z, Weaver AJ (2005) Thermohaline circulation hysteresis: a model intercomparison. Geophys Res Lett 32(23):L23605. doi:10.1029/2005GL023655
Rogers JC (1997) North Atlantic storm track variability and its association to the North Atlantic Oscillation and climate variability of Northern Europe. J Clim 10(7):1635–1647
Stendel M, Christensen JH, Petersen D (2008) Arctic climate and climate change with a focus on Greenland. Adv Ecol Res 40:13–43. doi:10.1016/S0065-2504(07)00002-5
Steffen K (1995) Surface energy exchange at the equilibrium line on the Greenland ice sheet during onset of melt. Ann Glaciol 21:13–18
Steffen K, Box J (2001) Surface climatology of the Greenland ice sheet: Greenland climate network 1995–1999. J Geophys Res 106(D24):33951–33964
Swingedouw D, Braconnot P, Marti O (2006) Sensitivity of the Atlantic meridional overturning circulation to the melting from northern glaciers in climate change experiments. Geophys Res Lett 33:L10503. doi:10.1029/2006GL026075
Tedesco M, Serreze M, Fettweis X (2008a) Diagnosing the extreme surface melt event over southwestern Greenland in 2007. The Cryosphere 2:159–166
Tedesco M, Fettweis X, van den Broeke MR, van de Wal RSW, Smeets CJPP (2008b) Extreme snowmelt in Northern Greenland during summer 2008. Eos Trans AGU 89(41). doi:10.1029/2008EO410004
Thompson DWJ, Wallace JM (1998) The Artic Oscillation signature in the wintertime geopotential height and temperature fields. Geophys Res Lett 9:1297–1300
Van Loon H, Rogers JC (1978) The seesaw in winter temperatures between Greenland and northern Europe: Part 1, general description. Mon Weather Rev 106(3):296–310
Walsh JE, Chapman WL, Romanovsky V, Christensen JH, Stendel M (2008) Global climate model performance over Alaska and Greenland. J Clim 21:6156–6174. doi:10.1175/2008JCLI2163.1
Wouters B, Chambers D, Schrama EJO (2008) GRACE observes small-scale mass loss in Greenland. Geophys Res Lett 35:L20501. doi:10.1029/2008GL034816
Zuo Z, Oerlemans J (1997) Contribution of glacier melt to sea-level rise since AD 1865: a regionally differentiated calculation. Clim Dyn 13(12):835–845
Acknowledgements
Bruno Franco is a research fellow from the Belgian National Fund for Scientific Research (FNRS). We acknowledge the modelling groups, the Program for Climate Model Diagnosis and Intercomparison (PCMDI) and the WCRP’s Working Group on Coupled Modelling (WGCM) for their roles in making available the WRCP CMIP3 multi-model dataset. Support of this dataset is provided by the Office of Science, US Department of Energy. We also thank the European Centre for Medium–Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) for ECMWF reanalysis. The NCEP/NCAR reanalysis is provided by the NOAA/OAR/ESRL PSD, Boulder, Colorado, USA, from their Web site at http://www.cdc.noaa.gov/. Finally, the authors want to thank A. Prick for her precious spell check in this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franco, B., Fettweis, X., Erpicum, M. et al. Present and future climates of the Greenland ice sheet according to the IPCC AR4 models. Clim Dyn 36, 1897–1918 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0779-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0779-1