Abstract
Object
The diagnosis of diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas (DIPGs) has been generally made mainly by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and clinical course. However, the accuracy of MRI-based diagnosis has not been fully confirmed yet. Our aim was to review efficacy of biopsy for decision making of the treatments.
Methods
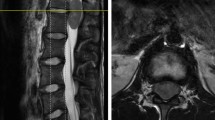
We retrospectively analyzed pediatric patients undergoing biopsy for intrinsic brainstem lesions which were considered atypical for DIPGs by MRI findings. The lesion was evaluated atypical when it extended beyond the pons or it had a well-margined localized enhancing portion.
Results
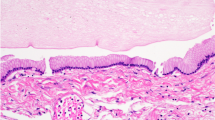
Seven patients underwent biopsy. Preoperative MRI revealed a lesion extending beyond the pons in five patients and a focal enhancing lesion in four. Two patients had both of these. Open biopsy was performed via midline suboccipital approach in six patients and retrosigmoid approach in one. No intraoperative complications were observed. Histopathological examination revealed diffuse brainstem glioma in five patients, primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) in one, and pilocytic astrocytoma in one. In the case with PNET, chemotherapy and radiotherapy were effective and the patient had been stable for 12 months without recurrence. The patient with pilocytic astrocytoma did not undergo radiotherapy and has been stable without regrowth of the tumor for 9 months.
Conclusions
Open biopsy of intrinsic brainstem lesions is considered to be safe and effective for selecting an appropriate course of therapy. Patients with intrinsic pontine lesions which extend beyond the pons or with localized enhancing portion seem to be benefited from the biopsy.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright AL, Packer RJ, Zimmerman R, Rorke LB, Boyett J, Hammond GD (1993) Magnetic resonance scans should replace biopsies for the diagnosis of diffuse brain stem gliomas: a report from the Children’s Cancer Group. Neurosurgery 33:1026–1030
Blond S, Lejeune JP, Dupard T, Parent M, Clarisse J, Christiaens JL (1991) The stereotactic approach to brain stem lesions: a follow- up of 29 cases. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 52:75–77
Cartmill M, Punt J (1999) Diffuse brain stem glioma. A review of stereotactic biopsies. Childs Nerv Syst 15:235–238
Chico-Ponce de León F, Perezpeña-Diazconti M, Castro-Sierra E, Guerrero-Jazo FJ, Gordillo-Domínguez LF, Gutiérrez-Guerra R et al (2003) Stereotactically-guided biopsies of brainstem tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 19:305–310
Coffey RJ, Lunsford LD (1985) Diagnosis and treatment of brainstem mass lesions by CT-guided stereotactic surgery. Appl Neurophysiol 48:467–471
Dellaretti M, Touzet G, Reyns N, Dubois F, Gusmão S, Pereira JL, Blond S (2011) Correlation among magnetic resonance imaging findings, prognostic factors for survival, and histological diagnosis of intrinsic brainstem lesions in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 8:539–543
Epstein F, Constantini S (1996) Practical decisions in the treatment of pediatric brain stem tumors. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:24–34
Frank F, Fabrizi AP, Frank-Ricci R, Gaist G, Sedan R, Peragut JC (1988) Stereotactic biopsy and treatment of brain stem lesions: combined study of 33 cases (Bologna-Marseille). Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 42:177–181
Franzini A, Allegranza A, Melcarne A, Giorgi C, Ferraresi S, Broggi G (1988) Serial stereotactic biopsy of brain stem expanding lesions. Considerations on 45 consecutive cases. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 42:170–176
Giunta F, Grasso G, Marini G, Zorzi F (1989) Brain stem expanding lesions: stereotactic diagnosis and therapeutical approach. Acta Neurochir Suppl (Wien) 46:86–89
Godano U, Frank F, Fabrizi AP, Ricci RF (1987) Stereotactic surgery in the management of deep intracranial lesions in infants and adolescents. Childs Nerv Syst 3:85–88
Goncalves-Ferreira AJ, Herculano-Carvalho M, Pimentel J (2003) Stereotactic biopsies of focal brainstem lesions. Surg Neurol 60:311–320
Morota N, Deletis V, Epstein FJ, Kofler M, Abbott R, Lee M, Ruskin K (1995) Brain stem mapping: neurophysiological localization of motor nuclei on the floor of the fourth ventricle. Neurosurgery 37:922–929
Morota N, Ihara S, Deletis V (2010) Intraoperative neurophysiology for surgery in and around the brainstem: role of brainstem mapping and corticobulbar tract motor-evoked potential monitoring. Childs Nerv Syst 26:513–521
Pincus DW, Richter EO, Yachnis AT, Bennett J, Bhatti MT, Smith A (2006) Brainstem stereotactic biopsy sampling in children. J Neurosurg 104:108–114
Rachinger W, Grau SJ, Holtmannspötter M, Herms J, Tonn JC, Kreth FW (2009) Serial stereotactic biopsy of brainstem lesions in adults improves diagnostic accuracy compared with MRI only. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 80:1134–1139
Roujeau T, Machado G, Garnett MR, Miquel C, Puget S, Geoerger B et al (2007) Stereotactic biopsy of diffuse pontine lesions in children. J Neurosurg 107(1 Supp):l1–l4
Steck J, Friedman WA (1995) Stereotactic biopsy of brainstem mass lesions. Surg Neurol 43:563–568
St. George EJ, Walsh AR, Sgouros S (2004) Stereotactic biopsy of brain tumours in the paediatric population. Childs Nerv Syst 20:163–167
Sufit A, Donson AM, Birks DK, Knipstein JA, Fenton LZ, Jedlicka P, Hankinson TC, Handler MH, Foreman NK (2012) Diffuse intrinsic pontine tumors: a study of primitive neuroectodermal tumors versus the more common diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:81–88
Valdés-Gorcía J, Espinoza-Díaz DM, Paredes-Díaz E (1998) Stereotactic biopsy of brain stem and posterior fossa lesions in children. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 140:899–903
Zagzag D, Miller DC, Knopp E, Farmer JP, Lee M, Biria S et al (2000) Primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the brainstem: investigation of seven cases. Pediatrics 106:1045–1053
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogiwara, H., Morota, N. The efficacy of a biopsy of intrinsic brainstem lesions for decision making of the treatments. Childs Nerv Syst 29, 833–837 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2042-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-013-2042-7