Abstract
Introduction
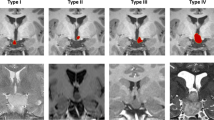
There is increasing evidence that removal or disconnection of hypothalamic hamartomas can lead to seizure control and improvement in behavior. The purpose of this study is to report our experiences with endoscopic removal of these hamartomas.
Methods
This is a prospective review of the early outcome of 44 patients undergoing endoscopic resection utilizing frameless stereotaxis and a micromanipulator.
Results
All patients had normal-sized ventricles. Complete removal was possible in 14 patients, 13 of whom were seizure free at follow-up. Four patients suffered complications that have persisted for more than 3 months: One had significant hemiparesis and three had persistent difficulties with short-term memory. Postoperatively, no patient suffered a permanent hormonal deficiency. In one patient who had undergone a previous attempt at transcallosal resection, the procedure was abandoned because of the lack of internal anatomic landmarks. In a second patient, insufficient mass could be removed due to the size of the lesion and the distorted anatomy. Consequently, 1 week later, the patient underwent a transcallosal approach.
Conclusion
In appropriately selected patients, sessile hypothalamic hamartomas can be removed completely or they can be completely disconnected from the hypothalamus with an acceptable risk. At least a year after surgery is needed to evaluate the efficacy of the procedure in terms of control of seizures and improvements in behavior and emotional ability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akai T, Okamoto K, Iizuka H, Kakinuma H, Nojima T (2002) Treatments of hamartoma with neuroendoscopic surgery and stereotactic radiosurgery: a case report. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 45:235–239
Albright AL, Lee PA (1998) Surgery for hypothalamic hamartomas. J Neurosurg 88:353
Barajas MA, Ramirez-Guzman MG, Rodriguez-Vazquez C, Toledo-Buenrostro V, Cuevas-Solorzano A, Rodriguez-Hernandez G (2005) Gamma knife surgery for hypothalamic hamartomas accompanied by medically intractable epilepsy and precocious puberty: experience in Mexico. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):53–55
Berkovic SF, Arzimanoglou A, Kuzniecky R, Harvey AS, Palmini A, Andermann F (2003) Hypothalamic hamartoma and seizures: a treatable epileptic encephalopathy. Epilepsia 44:969–973
Choi JU, Yang KH, Kim TG, Chang JH, Chang JW, Lee BI, Kim DS (2004) Endoscopic disconnection for hypothalamic hamartoma with intractable seizure. Report of four cases. J Neurosurg 100:506–511
Delalande O, Fohlen M (2003) Disconnecting surgical treatment of hypothalamic hamartoma in children and adults with refractory epilepsy and proposal of a new classification. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 43:61–68
Fahlbusch R, Schrell U (1985) Surgical therapy of lesions within the hypothalamic region. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 75:125–135
Feiz-Erfan I, Horn EM, Rekate HL, Spetzler RF, Ng YT, Rosenfeld JV, Kerrigan JF, III (2005) Surgical strategies for approaching hypothalamic hamartomas causing gelastic seizures in the pediatric population: transventricular compared with skull base approaches. J Neurosurg 103:325–332
Fohlen M, Lellouch A, Delalande O (2003) Hypothalamic hamartoma with refractory epilepsy: surgical procedures and results in 18 patients. Epileptic Disord 5:267–273
Fujimoto Y, Kato A, Saitoh Y, Ninomiya H, Imai K, Hashimoto N, Kishima H, Maruno M, Yoshimine T (2005) Open radiofrequency ablation for the management of intractable epilepsy associated with sessile hypothalamic hamartoma. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 48:132–135
Harvey AS, Freeman JL, Berkovic SF, Rosenfeld JV (2003) Transcallosal resection of hypothalamic hamartomas in patients with intractable epilepsy. Epileptic Disord 5:257–265
Kerrigan JF, Ng YT, Chung S, Rekate HL (2005) The hypothalamic hamartoma: a model of subcortical epileptogenesis and encephalopathy. Semin Pediatr Neurol 12:119–131
Lekovic GP, Gonzalez LF, Feiz-Erfan I, Rekate HL (2006) Endoscopic resection of hypothalamic hamartoma using a novel variable aspiration tissue resector. Neurosurgery 58 (Suppl 1):ONS 166–169
Machado HR, Hoffman HJ, Hwang PA (1991) Gelastic seizures treated by resection of a hypothalamic hamartoma. Childs Nerv Syst 7:462–465
Ng YT, Rekate HL, Kerrigan J (2006) Transcallosal resection of hypothalamic hamartomas with intractable epilepsy. Epilepsia (in press)
Parrent AG (1999) Stereotactic radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of gelastic seizures associated with hypothalamic hamartoma. Case report. J Neurosurg 91:881–884
Regis J, Bartolomei F, de TB, Genton P, Kobayashi T, Mori Y, Takakura K, Hori T, Inoue H, Schrottner O, Pendl G, Wolf A, Arita K, Chauvel P (2000) Gamma knife surgery for epilepsy related to hypothalamic hamartomas. Neurosurgery 47:1343–1351
Regis J, Hayashi M, Eupierre LP, Villeneuve N, Bartolomei F, Brue T, Chauvel P (2004) Gamma knife surgery for epilepsy related to hypothalamic hamartomas. Acta Neurochir (Suppl 91):33–50
Regis Y, Roberts DW (1999) Gamma Knife radiosurgery relative to microsurgery: epilepsy. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 72 (Suppl 1):11–21
Rosenfeld JV, Harvey AS, Wrennall J, Zacharin M, Berkovic SF (2001) Transcallosal resection of hypothalamic hamartomas, with control of seizures, in children with gelastic epilepsy. Neurosurgery 48:108–118
Siwanuwatn R, Deshmukh P, Feiz-Erfan I, Rekate HL, Zabramski JM, Spetzler RF, Rosenfeld JV (2005) Microsurgical anatomy of the transcallosal anterior interforniceal approach to the third ventricle. Neurosurgery 56:390–396
Souweidane MM (2005) Endoscopic surgery for intraventricular brain tumors in patients without hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery 57:312–318
Unger F, Schrottner O, Haselsberger K, Korner E, Ploier R, Pendl G (2000) Gamma knife radiosurgery for hypothalamic hamartomas in patients with medically intractable epilepsy and precocious puberty. Report of two cases. J Neurosurg 92:726–731
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rekate, H.L., Feiz-Erfan, I., Ng, YT. et al. Endoscopic surgery for hypothalamic hamartomas causing medically refractory gelastic epilepsy. Childs Nerv Syst 22, 874–880 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0125-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0125-4