Abstract
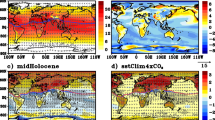
Changes of extreme events due to greenhouse effects (2 × CO2) over East Asia, with a focus on the China region as simulated by a regional climate model (RegCM2), are investigated. The model is nested to a global coupled ocean-atmosphere model (CSIRO R21L9 AOGCM). Analysis of the control run of the regional model indicates that it can reproduce well the extreme events in China. Statistically significant changes of the events are analyzed. Results show that both daily maximum and daily minimum temperature increase in 2 × CO2 conditions, while the diurnal temperature range decreases. The number of hot spell days increases while the number of cold spell days decreases. The number of rainy days and heavy rain days increases over some sub-regions of China. The 2 × CO2 conditions also cause some changes in the tropical storms affecting China.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dickinson, R. E., A. Henderson-Sellers, and P. J. Kennedy, 1993: Biosphere atmosphere transfer scheme (BATS) version le as coupled to the NCAR Community Climate Model, NCAR Tech. Note, NCAR / TN387+STR.
Durman, F., J. M. Gregory, D. H. Hassell, R. G. Jones, 2001: The comparison of extreme European daily precipitation simulated by a global and a regional climate model for present and future climates. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 127(573), 1005–1016.
Frei, Schar, D. Luthi, and H. Davies, 1998: Heavy precipitation processess in a warmer climate. Geophys. Res. Lett., 25, 1431–1434.
Gao, X. J., Z. -C. Zhao, Y. Ding, R. Huang, and F. Giorgi, 2001: Climate change due to greenhouse effects in China as simulated by a regional climate model. Advances in Atmospheric Sciences, 18(6), 1224–1230.
Giorgi, F. M. R. Marinucci, and G. T. Bates, 1993a: Development of a second-generation regional climate model (RegCM2). Part I: Boundary-layer and radiative transfer processes. Mon. Wea. Rev., 121, 2794–2813.
Giorgi, F. M. R. Marinucci, G.T. Bates, and G. DeCanio, 1993b: Development of a second-generation regional climate model (RegCM2). Part II: Convective processes and assimilation of lateral boundary conditions. Mon. Wea. Rev., 121, 2814–2832.
Giorgi, F., S. Brodeur, and G. Bates, 1994: Regional climate change scenarios over the United States produced with a nested regional climate model. J. Climate, 7, 375–399.
Giorgi, F., and Marinucci M. R., 1996: An investigation of the sensitivity of simulated precipitation to model resolution and its implications for climate studies. Mon. Wea. Rev., 124, 148–166.
Giorgi, F., L. Mearns, S. Shields, and L. McDaniel, 1998: Regional nested model simulations of present day and 2 × CO2 climate over the Central Great Plains of the United Slates. Climatic Change, 40, 457–493.
Giorgi, F., and C. Shields, 1999: Tests of precipitation parameterizations available in the latest version of the near regional climate model (RegCM) over the continental U.S. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 6353–6376.
Giorgi, F., and coauthors, 2001: Regional Climate Information-Evaluation and Projections. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis, Contribution of WGI to the Third Assessment Report of IPCC, J. T. Houghton., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., 583–638.
Gordon, H. and S. P. O′Farrell, 1997: Transient climate change in the CSIRO coupled model with dynamic sea ice. Mon. Wea. Rev., 125, 875–907.
Grell, G. A., 1993: Prognostic evaluation of assumptions used by cumulus parameterizations. Mon. Wea. Rev., 121, 764–787.
Hennessy, K. J., J. M. Greory, and J. F. B. Mitchell, 1997: Changes in daily precipitation under enhanced greenhouse conditions. Clim. Dyn., 13, 667–680.
Hirakuchi, H., and F. Giorgi, 1995: Multi-year present-day and 2 × CO2 simulations of monsoon-dominated climate over eastern Asia and Japan with a regional climate model nested in a general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 21,105-21,126.
Holtslag, A. A. M., E. I. F. Debruijin, H. L. Pan, 1990: A high resolution air mass transformation model for short-range weather forecasting. Mon. Wea. Rev., 118, 1561–1575.
IPCC, Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis, Summary for Policymakers and Technical Summary of WGI Third Assessment Report, eds. by J. T. Houghton, Y. Ding, et al., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 72pp.
Kiehl, J. T., J.J. Hack, G.B. Bonan, B.A. Bovlle, B.P. Briegleb, D.L. Williamson and P.J. Rasch (1996): Description of the NCAR Community Climate Model (CCM3). NCAR / TN-420+STR.
Mearns, L. Q., Bogardi, I., Giorgi, F., Matayasovszky, I., Palecki, M., 1999: Comparison of climate change scenarios generated daily temperature and precipitation from regional climate model experiments and statistical downscaling. J. Geophys. Res., 104, 6603–6621.
Mearns, L. O., and coauthors, 2001: Climate Scenario Development. Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis, Contribution of WGI to the Third Assessment Report of the IPCC, J. T. Houghton et al., Eds., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K., 739–768.
Schar, Frei, D. Luthi, and H. Davies, 1996: Surrogate climate change scenarios for regional climate models. Geophys. Res. Lett., 23, 669–672.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xuejie, G., Zongci, Z. & Giorgi, F. Changes of extreme events in regional climate simulations over East Asia. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 19, 927–942 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-002-0056-2
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-002-0056-2