Abstract
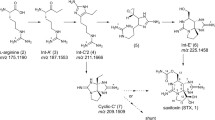
Sulfotransferase (ST) is the first enzyme discovered in association with paralytic shellfish poisoning (PSP) toxin biosynthesis in toxic dinoflagellates. This study investigates the ST activity in crude enzyme extraction of a toxic dinoflagellate species, Alexandrium tamarense CI01. The results show that crude enzyme can transfer a sulfate group from 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate (PAPS) to N-21 in the carbamoyl group of gonyautoxin 2/3 (GTX2/3) to produce C1/C2, but is inactive toward STX to produce GTX5. The crude enzyme is optimally active at pH 6.0 and 15°C. The activity is enhanced by Co2+, Mg2+, Mn2+ and Ca2+ individually, but is inhibited by Cu2+. Moreover, the activity shows no difference when various sulfur compounds are used as sulfate donors. These results demonstrate that the ST specific to GTX2/3 is present in the cells of A. tamarense CI01 and is involved in PSP toxin biosynthesis. In addition, the ST from different dinoflagellates is species-specific, which explains well the various biosynthesis pathways of the PSP toxins in toxic dinoflagellates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D. M., D. M. Kulis, J. J. Sullivan and S. Hall, 1990. Toxin composition variations in one isolate of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense. Toxicon 28: 885–893.
Boczar, B. A., M. A. Beitler, J. Liston, J. J. Sullivan and C. A. Cattolico, 1988. Paralytic shellfish toxins in Protogonyaulax tamarensis and Protogonyaulax catenella in axenic culture. Plant. Physiol. 88: 1 285–1 290.
Boyer, G. L., J. J. Sullivan, R. J. Anderson, P. J. Harrison and F. J. R. Taylor, 1987. Effects of nutrient limitation on toxin production and composition in the marine dinoflagellate Protogonyaulax tamarensis. Mar. Biol. 96: 123–128.
Cembella, A. D., 1998. Ecophysiology and metabolism of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine microalgae. In: DM Anderson, AD Cembella and GM Hallegraeff ed., Physiological Ecology of Harmful Blooms. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, p. 381–403.
Flynn, K. J., K. J. Jones and K. J. Flynn, 1996. Comparisons among species of Alexandrium grown in nitrogen-or phosphorus-limiting batch culture. Mar. Biol. 126: 9–18.
Hall, S., 1982. Toxins and Toxicity of Protogonyaulax from the Northeast Pacific. Ph.D. Thesis. University of Alaska.
Hamasaki, K., M. Horie, A. Tokimitsu, A. Toda and S. Taguchi, 2001. Variability in toxicity of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense isolated from Hiroshima Bay, western Japan, as a reflection of changing environmental conditions. J. Plank. Res. 23: 271–278.
Hwang, D. F. and Y. H. Lu, 2001. Influence of environmental and nutritional factor on growth, toxicity, and toxin profile of dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. Toxicon 38: 1 491–1 503.
Kodama, M., 2000. Ecology, classification and origin. In: LM Botana ed., Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology and Detection. Marcel Dekker, Inc. USA, p.125–150.
Matsui, M. and H. Homma, 1994. Biochemistry and molecular biology of drug-metabolizing sulfotransferase. Int. J. Biochem. 26: 1 234–1 247.
Oshima, Y., 1995a. Chemical and enzymatic transformation of paralytic shellfish toxins in marine organisms. In: P Lassus ed., Harmful Marine Algal Blooms, Lavoisier, New York, p. 475–480.
Oshima, Y., 1995b. Post-column derivatization liquid chromatographic method for paralytic shellfish toxins. J. AOAC Int. 78: 528–532.
Oshima, Y., S. J. Blackburn and G. M. Hallegraeff, 1993. Comparative study on paralytic shellfish toxin profiles of the dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum from three different countries. Mar. Biol. 116: 471–476.
Parkhill, J. P. and A. D. Cembella, 1999. The effects of salinity, light and inorganic nitrogen on the growth and toxigenicity of the marine dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. J. Plank. Res. 21: 939–955.
Plumley, F. G., 1997. Marine algal toxins: biochemistry, genetics, and molecular biology. Limnol. Oceanogr. 42: 1 240–1 251.
Plumley, F. G., 2001. Purification of an enzyme involved in saxitoxin synthesis. J. Phycol. 37: 926–928.
Saidha, T. and J. A. Schiff, 1994. Purification and properties of a phenol sulfotransferase from Euglena using L-tyrosine as substrate. J. Biochem. 298: 45–50.
Sako, Y., T. Yoshida, A. Uchida, O. Arakawa, T. Noguchi and Y. Ishida, 2001. Purification and characterization of a sulfotransferase specific to N-21 of saxitoxin and gonyautoxin 2+3 from the toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum (Dinophyceae). J. Phycol. 37: 1 044–1 051.
Shimizu, Y., 1979. Dinoflagellate toxin. In: PJ Scheuer ed, Marine Natural products-Chemical and Biological Perspectives. Academic Press, New York, p. 1–42.
Shimizu, Y., 1993. Microalgal metabolite. Chem. Rev. 93: 1 685–1 698.
Shimizu, Y., 1996. Microalgal metabolites-a new perspective. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 50: 431–465.
Taroncher-Oldenbugr, G., D. Kulis and D. M. Anderson, 1997. Toxin variability during the cell cycle of the dinoflagellate Alexandrium fundyense. Limnol. Oceanogr. 42: 1 177–1 188.
Wang, D. Z and D. P. H. Hsieh, 2001. Dynamics of C2 toxin and chlorophyll-a formation in the dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense during large-scale cultivation. Toxicon 39: 1 533–1 536.
Wang D Z, AYD Ho and DPH Hsieh, 2002. Production of C2 toxin by Alexandrium tamarense CI01 using different culture methods. J. Appl. Phycol. 14:461–468.
Wang, D. Z., T. J. Jiang and D. P. H. Hsieh, 2005. Toxin composition variations in cultures of Alexandrium species isolated from the coastal waters of Southern China. Harmful Algae 4: 109–121.
Yoshida, T., Y. Sako, A. Uchida, Y. Ishida, O. Arakawa and T. Noguchi, 1996. Purification and properties of paralytic shellfish poisoning toxins sulfotransferase from toxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium catenatum. In: T Yasumoto, Y Oshima and Y Fukuyo eds., Harmful and Toxic Algal Blooms. IOC (UNESCO), Paris, p.499–502.
Yoshida, T., Y. Sako, T. Kakutani, A. Fujii, A. Uchida, Y. Ishida, O. Arakawaand and T. Noguchi, 1998. Comparative study of two sulfotransferase for sulfation to N-21 of Gymnodinium catenatum and Alexandrium catenella toxins. In: B. Reguera, J. Blanco, M. L. Fernandez and T. Wyatt eds., Harmful Algae. Xunta de Galicia and IOC of UNESCO, Vigo, p. 366–369.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.40376032) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China (No.2001CB409700).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Zhang, S. & Hong, H. A sulfotransferase specific to N-21 of gonyautoxin 2/3 from crude enzyme extraction of toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense CI01. Chin. J. Ocean. Limnol. 25, 227–234 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-007-0227-1
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-007-0227-1