Abstract
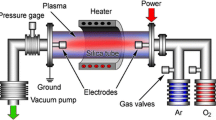
Crystalline ZnSe nano-needles have been grown by pulsed laser deposition on Ni-coated substrates. In order to study the mechanism for the growth of ZnSe nano-needles, the experiment conditions including catalyst layer, substrate material, substrate temperature and deposition duration were changed respectively. The catalyst layer plays an important role in the growth of ZnSe nano-needles. The substrate material and substrate temperature also strongly affect the morphologies and structures of the as-grown ZnSe nano-crystals. On 300–400°C Ni-coated silicon (100) substrates, the crystalline ZnSe nano-needles can be grown densely with the middle diameters of about 20–80 nm, and the lengths of 100–400 nm. Two models for the growth of the ZnSe nano-needles and sphere-leading nano-wires under different substrate temperatures are proposed and verified experimentally.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Katayama, H. Yao, F. Nakanishi, H. Doi, A. Saegusa, T. Shirakawa, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 102 (1998)
H. Ishikura, T. Abe, N. Fukuda, H. Kasada, K. Ando, Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1069 (2000)
J.D. Holmes, K.P. Johnston, R.C. Doty, B.A. Korgel, Science 287, 1471 (2000)
M.S. Gudiksen, L.J. Lauhon, J. Wang, D.C. Smith, C.M. Lieber, Nature 415, 617 (2002)
C.H. Hsiao, S.J. Chang, S.B. Wang, S.P. Chang, T.C. Li, W.J. Lin, C.H. Ko, T.M. Kuan, B.R. Huang, J. Electrochem. Soc. 156, 73 (2009)
K. Wang, J. Chen, W. Zhou, Y. Zhang, Y. Yan, J. Pern, A. Mascarenhas, Adv. Mater. 20, 3248 (2008)
E. Galoppini, J. Rochford, H. Chen, G. Saraf, Y. Lu, A. Hagfeldtand, G. Boschloo, J. Phys. Chem. B 110, 16159 (2006)
X.T. Zhang, K.M. Ip, Z. Liu, Y.P. Leung, Q. Li, S.K. Hark, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84, 2641 (2004)
X.T. Zhang, Z. Liu, Y.P. Leung, Q. Li, S.K. Hark, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 5533 (2003)
Y.C. Zhu, Y. Bando, Chem. Phys. Lett. 377, 367 (2003)
B. Xiang, H.Z. Zhang, G.H. Li, F.H. Yang, F.H. Su, R.M. Wang, J. Xu, X.C. Lu, X.C. Sun, Q. Zhao, D.P. Yu, Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 3330 (2002)
Y.F. Chan, X.F. Duan, S.K. Chan, I.K. Sou, X.X. Zhang, N. Wang, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 2665 (2003)
R. Solanki, J. Huo, J.L. Freeouf, Appl. Phys. Lett. 81, 3864 (2002)
T. Zhang, T. Shen, W. Hu, J. Sun, J. Wu, Z. Ying, N. Xu, J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 25, 1823 (2007)
Y.R. Ryu, S. Zhu, S.W. Han, H.W. White, P.F. Miceli, H.R. Chandrasekhar, Appl. Surf. Sci. 127, 496 (1998)
J.W. Park, C.M. Rouleau, D.H. Lowndes, J. Cryst. Growth 193, 516 (1998)
R.S. Wagner, W.C. Ellis, Appl. Phys. Lett. 4, 89 (1964)
T.I. Kamins, R.S. Williams, D.P. Basile, T. Hasjedal, S. Harris, J. Appl. Phys. 89, 1008 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lai, J.S., Chen, L., Fu, X.N. et al. Effects of the experimental conditions on the growth of crystalline ZnSe nano-needles by pulsed laser deposition. Appl. Phys. A 102, 477–483 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-010-5941-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-010-5941-4