Abstract
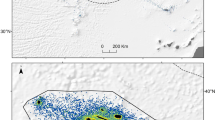
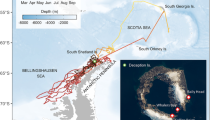
The foraging distribution of marine predator populations is important for effective modelling and management of pelagic marine systems. We tracked 31 juvenile southern elephant seals from Macquarie Island (158°57′E, 54°30′S) over their annual post-moult and mid-year trips to sea. We calculated the amount of time spent in regional fisheries management areas and within bounded oceanographic regions. During the austral summer, juvenile seals spent over 90% of their time south of the Antarctic Polar Front and ~80% within fisheries management regions [Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) and exclusive economic zones]. In winter, seals spent ~75% of their time in the region bounded by the Antarctic Polar Front and the southern boundary of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current, and ~60% within fisheries management regions. The time spent per region differed significantly between summer and winter. Our results demonstrate that juvenile southern elephant seals from Macquarie Island spent more time south of the Antarctic Polar Front and within fisheries management areas than previously suspected.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew DJ (1997) The CCAMLR ecosystem monitoring program. Antarct Sci 9:235–242
Arrigo KR, Worthen D, Schnell A, Lizotte MP (1998) Primary production in Southern Ocean waters. J Geophys Res 103:15587–15600
Barbraud C, Weimerskirch H (2001) Emperor penguins and climate change. Nature 411:183–186
Boyd IL, Arnbom TA, Fedak MA (1994) Biomass and energy consumption of the South Georgia population of the southern elephant seals. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behaviour, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 98–120
Bradshaw CJA, Hindell MA, Michael KJ, Sumner MD (2002) The optimal spatial scale for the analysis of elephant seal foraging as determined by geo-location in relation to sea surface temperatures. ICES J Mar Sci 59:770–781
Bradshaw CJA, Hindell MA, Best NJ, Phillips KL, Wilson G, Nichols PD (2003) You are what you eat: describing the foraging ecology of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) using blubber fatty acids. Proc R Soc London B 270:1283–1292
Brown DJ, Boyd IL, Cripps GC (1999) Fatty acid signature analysis from the milk of Antarctic fur seals and southern elephant seals from South Georgia: implications for diet determination. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 187:251–263
Budillon G, Rintoul SR (2003) Fronts and upper ocean thermal variability south of New Zealand. Antarct Sci 15:141–152
Burton HR, van den Hoff J (2002) Humans and the southern elephant seal Mirounga leonina. Aust Mammal 24:127–139
Clarke MR (1983) Cephalopod biomass—estimation from predation. Mem Nat Mus Victoria Melbourne 44:95–107
Constable AJ, Nicol S, Strutton, PG (2003) Southern Ocean productivity in relation to spatial and temporal variation in the physical environment. J Geophys Res 108:8079–9000
Croxall JP, Prince PA, Reid K (1999) Diet, provisioning and productivity responses of marine predators to differences in availability of Antarctic krill. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 177:115–131
Daneri GA, Carlini AR (2002) Fish prey of southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, at King George Island. Polar Biol 25:739–743
Daneri GA, Carlini AR, Rodhouse PGK (2000) Cephalopod diet of the southern elephant seal, Mirounga leonina, at King George Island, South Shetland Islands. Antarct Sci 12:11–16
Dauby P, Nyssen F, De Broyer C (2003) Amphipods as food sources for higher trophic levels in the Southern Ocean: a synthesis. In: Huskies AHL, Gieskes WWC, Rozema J, Schorno RML, av der Vries SM, Wolff WJ (eds) Antarctic biology in a global context. Proceedings of the VIIIth SCAR international biology symposium, pp 129–134
El-Sayed SZ (1988) Seasonal and inter-annual variabilities in Antarctic phytoplankton with reference to krill distribution. In: Sahrhage D (ed) Antarctic ocean and resource variability. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 101–119
Field I, Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Michael KJ (2001) Foraging strategies of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) in relation to frontal zones and water masses. Antarct Sci 13:371–379
Field IC, Bradshaw CJA, McMahon CR, Harrington J, Burton HR (2002) Intravenous anaesthesia of elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) using Tiletamine and Zolazepam: effects of age, size, condition and function of haul-out. Vet Rec 151:235–240
Furness RW, Greenwood JJD, Jarvis PJ (1993) Can birds be used to monitor the environment? In: Furness RW, Greenwood JJD (eds) Birds as monitors of environmental change. Chapman and Hall, London, pp 1–41
Goldsworthy SD, He X, Tuck GN, Lewis N, Williams R (2001) Trophic interactions between the Patagonian toothfish, its fishery, and seals and seabirds around Macquarie Island. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 218:283–302
Green K, Burton HR (1993) Comparison of the stomach contents of southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, at Macquarie and Heard Islands. Mar Mam Sci 9:10–22
Guinet C, Jouventin P, Weimerskirch H (1999) Recent population change of the southern elephant seal at Iles Crozet and Iles Kerguelen: the end of the decrease? Antarct Sci 11:193–197
Hindell MA, Burton HR (1988) Seasonal haul-out patterns of the southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina L.) at Macquarie Island. J Mammal 69:81–88
Hindell MA, Burton HR, Slip DJ (1991a) Foraging areas of southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina, as inferred from water temperature data. Aust J Mar Freshwater Res 42:115–128
Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR (1991b) The diving behaviour of adult male and female southern elephant seals, Mirounga leonina (Pinnipedia: Phocidae). Aust J Zool 39:595–619
Hindell MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR (1994) Possible causes of the decline of southern elephant seal populations in the southern Pacific and southern Indian Oceans. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 66–84
Hindell MA, McConnell BJ, Fedak MA, Slip DJ, Burton HR, Reijnders PJH, McMahon CR (1999) Environmental and physiological determinants of successful foraging by naive southern elephant seal pups during their first trip to sea. Can J Zool 77:1807–1821
Hindell MA, Bradshaw CJA, Harcourt RG, Guinet C (2003a) Ecosystem monitoring: are seals a potential tool for monitoring change in marine systems? In: Gales NJ, Hindell MA, Kirkwood R (eds) Marine mammals. fisheries, tourism and management issues. CSIRO, Melbourne, pp 330–343
Hindell MA, Bradshaw CJA, Sumner MD, Michael KJ, Burton HR (2003b) Dispersal of female southern elephant seals and their prey consumption during the austral summer: relevance to management and oceanographic zones. J Appl Ecol 40:703–715
Hosie GW, Fukuchi M, Kawaguchi S (2004) Development of the Southern Ocean Continuous Plankton Recorder. Prog Oceanogr (in press)
Irvine LG, Hindell MA, van den Hoff J, Burton HR (2000) The influence of body size on dive duration of under-yearling southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina). J Zool 251:463–471
Kerry KR, Clarke JR, Eberhard S, Gardner H, Lawless RM, Trémont R, Wienecke BC, Corsolini S, Focardi S, Franchi E, Rodary D, Thomson R (1997) The foraging range of Adélie penguins—implications for CEMP and interactions with the krill fishery. CCAMLR Sci 4:75–87
Kirkman SP, Bester MN, Pistorius PA, Hofmeyr GJG, Owen R, Mecenero S (2001) Participation in the winter haul-out by southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina). Antarct Sci 13:380–384
Le Boeuf BJ, Crocker DE, Costa DP, Blackwell SB, Webb PM, Houser DS (2000) Foraging ecology of northern elephant seals. Ecol Monogr 70:353–382
Lutjeharms JHE (1990) The oceanography and fish distribution of the Southern Ocean. In: Gon O, Heemstra PC (eds) Fishes of the Southern Ocean. Institute of Ichtyology, Grahamstown, pp 6–28
McConnell BJ, Fedak MA (1996) Movements of southern elephant seals. Can J Zool 74:1485–1496
McConnell BJ, Chambers C, Fedak MA (1992) Foraging ecology of southern elephant seals in relation to bathymetry and productivity of the Southern Ocean. Antarct Sci 4:393–398
McConnell BJ, Fedak MA, Burton HR, Englhard GH, Reijnders PHJ (2002) Movements and foraging areas of naive, recently weaned southern elephant seal pups. J Anim Ecol 74:1485–1496
McMahon CR (2003) A demographic comparison of two elephant seal populations. PhD Thesis, University of Pretoria
McMahon CR, van den Hoff J, Burton HR, Davis PD (1997) Evidence for precocious development in female pups of the southern elephant seal Mirounga leonina at Macquarie Island. In: Hindell M, Kemper C (eds) Marine mammal research in the Southern Hemisphere, vol 1: status, ecology and medicine. Beatty, Chipping Norton, pp 92–96
McMahon CR, Burton H, McLean S, Slip D, Bester M (2000) Field immobilisation of southern elephant seals with intravenous tiletamine and zolazepam. Vet Rec 146:251–254
McMahon CR, Burton HR, Bester MN (2003) A demographic comparison of two southern elephant seals populations. J Anim Ecol 72:61–74
Nicol S (1991) CCAMLR and its approaches to management of the krill fishery. Polar Rec 27:229–236
Nicol S, Endo Y (1999) Krill development, management and ecosystem implications. Aquat Living Resour 12:105–120
Nicol S, Foster J (2003) Recent trends in the fishery for Antarctic Krill. Aquat Living Resour 16:42–45
Nicol S, Pauly T, Bindoff NL, Wright S, Thiele D, Hosie GW, Strutton PG, Whoeler E (2000) Ocean circulation off east Antarctica affects ecosystem structure and sea-ice extent. Nature 406:504–507
Orsi AH, Whitworth T, Nowlin WD (1995) On the meridional extent and fronts of the Antarctic circumpolar current. Deep Sea Res 42:641–673
Piatkowski U, Vergani DF, Stanganelli ZB (2002) Changes in cephalopod diet of the southern elephant seal females at King George Island, during El Niño-La Niña events. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 82:913–916
Rintoul SR, Donguy JR, Roemmich DH (1997) Seasonal evolution of upper ocean thermal structure between Tasmania and Antarctica. Deep Sea Res 44:1185–1202
Rodhouse PG, White MG (1995) Cephalopods occupy the ecological niche of epipelagic fish in the Antarctic polar frontal zone. Biol Bull 189:77–80
Santos MB, Clarke MR, Pierce GJ (2001) Assessing the importance of cephalopods in the diets of marine mammals and other top predators: problems and solutions. Fish Res 52:21–139
Sibert JR, Musyl MK, Brill RW (2003) Horizontal movements of bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) near Hawaii determined by Kalman filter analysis of archival tagging data. Fish Oceanogr 12:141–151
Slip DJ (1995) The diet of southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) from Heard Island. Can J Zool 63:1519–1528
Slip DJ, Burton HR (1999) Population status and seasonal haulout patterns of the southern elephant seal (Mirounga leonina) at Heard Island. Antarct Sci 11:38–47
Slip DJ, Hindell MA, Burton HR (1994) Diving behavior of southern elephant seals from Macquarie Island: an overview. In: Le Boeuf BJ, Laws RM (eds) Elephant seals: population ecology, behavior, and physiology. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 253–270
Trites AW, Donnelly CP (2003) The decline of Steller sea lions Eumetopias jubatus in Alaska: a review of the nutritional stress hypothesis. Mammal Rev 33:3–28
van den Hoff J, Burton HR, Hindell MA, Sumner MD, McMahon CR (2002) Migrations and foraging of juvenile southern elephant seals from Macquarie Island within CCAMLR managed areas. Antarct Sci 14:134–145
van den Hoff J, Burton HR, Davies R (2003) Diet of male southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) hauled out at Vincennes Bay, East Antarctica. Polar Biol 26:27–31
Viet RR, Pyle P, McGowen JA (1996) Ocean warming and long-term change in the pelagic bird abundance within the California current system. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 139:11–18
Weimerskirch H, Inchausti P, Guinet C, Barbraud C (2003) Trends in bird and seal populations as indicators of a system shift in the Southern Ocean. Antarct Sci 15:249–256
Wheatley KE (2001) Behavioural and physiological aspects of the mid-year haul-out in southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) on Macquarie Island. MPhil Thesis, University of St. Andrews
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Australian Antarctic Division for logistic support, especially J. van den Hoff, and members of the 51st, 52nd and 53rd ANARE to Macquarie Island for their assistance during deployment and collection of the data loggers, especially K. Wheatley and M. Biuw. We also thank M. Bester, J. van den Hoff and two anonymous reviewers for comments on the manuscript. Data for this study was collected with Australian Antarctic Animal Ethics Committee approval (ASAC 2265 and 1171) and with Tasmanian Parks and Wildlife Service permits.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Field, I.C., Bradshaw, C.J.A., Burton, H.R. et al. Seasonal use of oceanographic and fisheries management zones by juvenile southern elephant seals (Mirounga leonina) from Macquarie Island. Polar Biol 27, 432–440 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-004-0615-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00300-004-0615-3