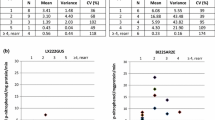
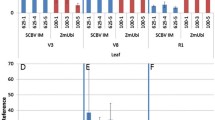
Abstract
Several matrix-attachment regions (MARs) from animals have been shown to block interactions between an enhancer and promoter when situated between the two. Since a similar function for plant MARs has not been discerned, we tested the Zea mays ADH1 5′ MAR, Nicotiana tabacum Rb7 3′ MAR and a transformation booster sequence (TBS) MAR from Petunia hybrida for their ability to impede enhancer–promoter interactions in Arabidopsis thaliana. Stable transgenic lines containing vectors in which one of the three MAR elements or a 4 kb control sequence were interposed between the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S enhancer and a flower-specific AGAMOUS second intron-derived promoter (AGIP)::β-glucuronidase (GUS) fusion were assayed for GUS expression in vegetative tissues. We demonstrate that the TBS MAR element, but not the ADH1 or Rb7 MARs, is able to block interactions between the 35S enhancer and AGIP without compromising the function of either with elements from which they are not insulated.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MAR:
-
Matrix attachment region
- TBS :
-
Transformation booster sequence
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- AGIP :
-
AGAMOUS second intron-derived promoter
- 35S :
-
35S cauliflower mosaic virus promoter/enhancer
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
References
Abranches R, Shultz RW, Thompson WF, Allen GC (2005) Matrix attachment regions and regulated transcription increase and stabilize transgene expression. Plant Biotechnol J 3:535–543
Allen GC, Hall GE Jr, Childs LC, Weissinger AK, Spiker S, Thompson WF (1993) Scaffold attachment regions increase reporter gene expression in stably transformed plant cells. Plant Cell 5:603–613
Allen GC, Hall GE Jr, Michalowski S, Newman W, Spiker S, Weissinger AK, Thompson WF (1996) High-level transgene expression in plant cells: effects of a strong scaffold attachment region from tobacco. Plant Cell 8:899–913
Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ et al (2003) Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301:653–657
Andika IB, Kondo H, Tamada T (2005) Evidence that RNA silencing-mediated resistance to beet necrotic yellow vein virus is less effective in roots than in leaves. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 18:194–204
Avramova Z, Bennetzen JL (1993) Isolation of matrices from maize leaf nuclei: identification of matrix-binding site adjacent to the Adh1 gene. Plant Mol Biol 22:1135–1143
Avramova Z, San Miguel P, Georgieva E, Bennetzen JL (1995) Matrix attachment regions and transcribed sequences within a long chromosomal continuum containing maize Adh1. Plant Cell 7:1667–1680
Bell AC, West AG, Felsenfeld G (1999) The protein CTCF is required for the enhancer blocking activity of vertebrate insulators. Cell 98:387–396
Bevan M (1984) Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 12:8711–8721
Bode J, Stengert-Iber M, Kay V, Schlake T, Dietz-Pfeilstetter A (1996) Scaffold/matrix-attached regions: topological switches with multiple regulatory functions. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 6:115–138
Breyne P, Van Montagu M, Depicker A, Gheysen G (1992) Characterization of a plant scaffold attachment region in a DNA fragment that normalizes transgene expression in tobacco. Plant Cell 4:463–471
Brouwer C, Bruce W, Maddock S, Avramova Z, Bowen B (2002) Suppression of transgene silencing by matrix attachment regions in maize: a dual role for the maize 5′ ADH1 matrix attachment region. Plant Cell 14:2251–2264
Buising CM, Benbow RM (1994) Molecular analysis of transgenic plants generated by microprojectile bombardment: effect of petunia transformation booster sequence. Mol Gen Genet 243:71–81
Charrier B, Champion A, Kreis M (2002) Expression profiling of the whole Arabidopsis Shaggy-like kinase multigene family by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Plant Physiol 130:1–14
Cheng Z, Targolli J, Wu R (2001) Tobacco matrix attachment region sequence increased transgene expression levels in rice plants. Mol Breeding 7:317–327
Chung JH, Whiteley M, Felsenfeld G (1993) A 5′ element of the chicken β-globin domain serves as an insulator in human erythroid cells and protects against position effect in Drosophila. Cell 74:505–514
Clough SJ, Bent AF (1998) Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16:735–743
Conkling MA, Cheng C-L, Yamamoto YT, Goodman HM (1990) Isolation of transcriptionally regulated root-specific genes from tobacco. Plant Physiol 93:1203–1211
Conte C, Dastugue B, Vaury C (2002) Coupling of enhancer and insulator properties identified in two retrotransposons modulates their mutagenic impact on nearby genes. Mol Cell Biol 22:1767–1777
Datla RSS, Hammerlindl JK, Pelcher LE, Selvaraj G, Crosby WL (1990) Bifunctional gene fusion between neomycin phosphotransferase and β-glucuronidase: a broad spectrum genetic marker for plants. UCLA Symposium on Molecular and Cellular Biology. J Cell Biochem 14 (Suppl E):279
De Folter S, Urbanus SL, van Zuijlen LGC, Kaufmann K, Angenent GC (2007) Tagging of MADS domain proteins for chromatin immunoprecipitation. BMC Plant Biol 7:47–57
Dunn KL, Zhao H, Davie JR (2003) The insulator binding protein CTCF associates with the nuclear matrix. Exp Cell Res 288:218–223
Engels P, Meyer P (1992) Comparison of homologous recombination frequencies in somatic cells of petunia and tobacco suggest two distinct recombination pathways. Plant J 21:59–67
Galliano H, Müller AE, Lucht JM, Meyer P (1995) The transformation booster sequence from Petunia hybrida is a retrotransposon derivative that binds to the nuclear scaffold. Mol Gen Genet 247:614–622
Gaszner M, Vazquez J, Schedl P (1999) The Zw5 protein, a component of the scs chromatin domain boundary, is able to block enhancer-promoter interaction. Genes Dev 13:2098–2107
Gerasimova TI, Byrd K, Corces VG (2000) A chromatin insulator determines the nuclear localization of DNA. Mol Cell 6:1025–1035
Geyer PK, Spana C, Corces VG (1986) On the molecular mechanism of gypsy-induced mutations at the yellow locus of Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J 5:2657–2662
Goderis IJWM, De Bolle MFC, François IEJA, Wouters PFJ, Broekaert WF, Cammue BPA (2002) A set of modular plant transformation vectors allowing flexible insertion of up to six expression units. Plant Mol Biol 50:17–27
Hajdukiewicz P, Svab Z, Maliga P (1994) The small, versatile pPZP family of Agrobacterium binary vectors for plant transformation. Plant Mol Biol 25:989–994
Halweg C, Thompson WF, Spiker S (2005) The Rb7 matrix attachment region increases the likelihood and magnitude of transgene expression in tobacco cells: a flow cytometric study. Plant Cell 17:418–429
Hebbes TR, Clayton AL, Thorne AW, Crane-Robinson C (1994) Core histone hyperacetylation co-aps with generalized DNase I sensitivity in the chicken β-globin chromosomal domain. EMBO J 13:1823–1830
Hily JM, Liu Z (2009) A simple and sensitive high-throughput GFP screening in woody and herbaceous plants. Plant Cell Rep 28:493–501
Hogga I, Karch F (2002) Transcription through the iab-7 cis-regulatory domain of the bithorax complex interferes with maintenance of Polycomb-mediated silencing. Development 129:4915–4922
Holmes-Davis R, Comai L (1998) Nuclear matrix attachment regions and plant gene expression. Trends Plant Sci 3:91–97
Jagannath A, Bandyopadhyay P, Arumugam N, Gupta V, Kumar P, Pental D (2001) The use of a Spacer DNA fragment insulates the tissue-specific expression of a cytotoxic gene (barnase) and allow high-frequency generation of transgenic male sterile lines in Brassica juncea L. Mol Breeding 8:11–23
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kay R, Chan A, Daly M, McPherson J (1987) Duplication of CaMV 35S promoter sequences creates a strong enhancer for plant genes. Science 236:1299–1302
Kellum R, Schedl P (1991) A position-effect assay for boundaries of higher order chromosomal domains. Cell 64:941–950
Kellum R, Schedl P (1992) A group of scs elements function as domain boundaries in an enhancer-blocking assay. Mol Cell Biol 12:2424–2431
Kobayashi N, Horikoshi T, Katsuyama H, Handa T, Takayanagi K (1998) A simple and efficient DNA extraction method for plants, especially woody plants. Plant Tissue Cult Biotechnol 4:76–80
Kohwi-Shigematsu T, Maass K, Bode J (1997) A thymocyte factor SATB1 suppresses transcription of stably integrated matrix-attachment region-linked reporter genes. Biochem J 36:12005–12010
Laemmli UK, Käs E, Poljak L, Adachi Y (1992) Scaffold-associated regions: cis-acting determinants of chromatin structural loops and functional domains. Curr Opin Genet Dev 2:275–285
Liu Z, Liu Z (2008) The second intron of AGAMOUS drives carpel- and stamen-specific expression sufficient to induce complete sterility in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep 27:855–863
Liu J, Bramblett D, Zhu Q, Losano M, Kobayashi R, Ross SR, Dudley JP (1997) The matrix attachment region-binding protein SATB1 participates in negative regulation of tissue-specific gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 17:5275–5287
Majumder P, Cai H (2003) The functional analysis of insulator interactions in the Drosophila embryo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5223–5228
Meyer P, Kartzke S, Niedenhof I, Heidmann I, Bussmann K, Saedler H (1988) A genomic DNA segment from Petunia hybrida leads to increased transformation frequencies and simple integration patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8568–8572
Mlynárová L, Keizer LCP, Stiekema WJ, Nap J-P (1996) Approaching the lower limits of transgene variability. Plant Cell 8:1589–1599
Nabirochkin S, Ossokina M, Heidmann T (1998) A nuclear matrix/scaffold attachment region co-localizes with the gypsy retrotransposon insulator sequence. J Biol Chem 273:2473–2479
Odell JT, Knowlton S, Lin W, Mauvais J (1988) Properties of an isolated transcription stimulating sequence derived from the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter. Plant Mol Biol 10:263–272
Pang S-Z, Jan F-J, Gonsalves D (1997) Nontarget DNA sequences reduce the transgene length necessary for RNA-mediated tospovirus resistance in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:8261–8266
Parkhurst SM, Harrison DA, Remington MP, Spana C, Kelley RL, Coyne RS, Corces VG (1988) The Drosophila su(Hw) gene, which controls the phenotypic effect of the gypsy transposable element, encodes a putative DNA-binding protein. Genes Dev 2:1205–1215
Petersen K, Leah R, Knudsen S, Cameron-Mills V (2002) Matrix attachment regions (MARs) enhance transformation frequencies and reduce variance of transgene expression in barley. Plant Mol Biol 49:45–58
Rosso MG, Li Y, Strizhov N, Reiss B, Dekker K, Weisshaar B (2003) An Arabidopsis thaliana T-DNA mutagenized population (GABI-Kat) for flanking sequence tag-based reverse genetics. Plant Mol Biol 53:247–259
Saitoh N, Bell AC, Recillas-Targa F, West AG, Simpson M, Pikaart M, Felsenfeld G (2000) Structural and functional conservation at the boundaries of the chicken β-globin domain. EMBO J 19:2315–2322
Sidorenko L, Bruce W, Maddock S, Tagliani L, Li X, Daniels M, Peterson T (2003) Functional analysis of two matrix attachment region (MAR) elements in transgenic maize plants. Transgenic Res 12:137–154
Sieburth LE, Meyerowitz EM (1997) Molecular dissection of the AGAMOUS control region shows that cis elements for spatial regulation are located intragenically. Plant Cell 9:355–365
Smith PA, Corces VG (1995) The suppressor of Hairy-wing protein regulates the tissue-specific expression of the Drosophila gypsy retrotransposon. Genetics 139:215–228
Stief A, Winter DM, Strätling WH, Sippel AE (1989) A nuclear DNA attachment element mediates elevated and position-independent gene activity. Nature 341:343–345
Tikhonov AP, Bennetzen JL, Avramova ZV (2000) Structural domains and matrix attachment regions along collinear chromosomal segments of maize and sorghum. Plant Cell 12:249–264
Torney F, Partier A, Says-Lesage V, Nadaud I, Barret P, Beckert M (2004) Heritable transgene expression pattern imposed onto maize ubiquitin promoter by maize adh-1 matrix attachment regions: tissue and developmental specificity in maize transgenic plants. Plant Cell Rep 22:931–938
Ülker B, Allen GC, Thompson WF, Spiker S, Weissinger AK (1999) A tobacco matrix attachment region reduces the loss of transgene expression in the progeny of transgenic tobacco plants. Plant J 18:253–263
Van der Geest AHM, Hall TC (1997) The β-phaseolin 5′ matrix attachment region acts as an enhancer facilitator. Plant Mol Biol 33:553–557
Van der Geest AHM, Hall GE Jr, Spiker S, Hall TC (1994) The β-phaseolin gene is flanked by matrix attachment regions. Plant J 6:413–423
Van Leeuwen W, Mlynárová L, Nap JP, van der Plas LH, van der Krol AR (2001) The effect of MAR elements on variation in spatial and temporal regulation of transgene expression. Plant Mol Biol 47:543–554
Verma D, Verma M, Dey M, Jain RK, Wu R (2005) Molecular dissection of the tobacco Rb7 matrix attachment region (MAR): effect of 5′ half on gene expression in rice. Plant Sci 169:704–711
Yoo SY, Bomblies K, Yoo SK, Yang JW, Choi MS, Lee JS, Weigel D, Ahn JH (2005) The 35S promoter used in a selectable marker gene of a plant transformation vector affects the expression of the transgene. Planta 221:523–530
Yusufzai TM, Tagami H, Nakatani Y, Felsenfeld G (2004) CTCF tethers an insulator to subnuclear sites, suggesting shared insulator mechanisms across species. Mol Cell 13:291–298
Zhang M-M, Ji L-S, Xue H, Yang Y-T, Wu C-A, Zheng C-C (2007) High transformation frequency of tobacco and rice via Agrobacterium-mediated gene transfer by flanking a tobacco matrix attachment region. Physiol Plantarum 129:644–651
Zheng X, Deng W, Luo K, Duan H, Chen Y, McAvoy R, Song S, Pei Y, Li Y (2007) The cauliflower mosaic virus (CaMV) 35S promoter sequence alters the level and patterns of activity of adjacent tissue- and organ-specific gene promoters. Plant Cell Rep 26:1195–1203
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Mr. Dennis Bennett (USDA-ARS, Kearneysville, WV) for his technical assistance, and Dr. Ann Callahan (USDA-ARS, Kearneysville, WV) for critical reading of the manuscript. This study was funded by the USDA-ARS Headquarter 2005 and 2007 classes of postdoctoral grants and a USDA CSREES BRAG grant (2006-03701).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D. Somers.
Accession numbers: TBS from Petunia hybrida cultivar V26, GenBank accession number EU864306.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hily, JM., Singer, S.D., Yang, Y. et al. A transformation booster sequence (TBS) from Petunia hybrida functions as an enhancer-blocking insulator in Arabidopsis thaliana . Plant Cell Rep 28, 1095–1104 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0700-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-009-0700-8