Abstract
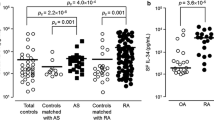
IL-6 plays a key role in local and systemic manifestation of RA. IL-6 is not only a pro-inflammatory cytokine, but also interacts in complex ways with the cells involved in bone remodeling. In RA, IL-6 may indirectly promote osteoclastogenesis by increasing the release of RANK-L by osteoblasts, and it diminishes the proliferation of osteoblasts at late differentiation stages. The aims of this work were to evaluate the level of serum IL-6 and to correlate it with the activity, severity, early development of osteoporosis, and early structural bone damage in RA patients. The following parameters were investigated in 40 RA patients and 20 healthy controls: IL-6 level, BMI, ESR, CRP, CBCs, serum ionized calcium, blood urea, serum creatinine, AST, ALT, anti-CCP, and RF. Bone mineral density was measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry at lumbar spines and femoral neck. Drug history was taken stressing on steroid therapy. Data were processed and analyzed using computer-based program. IL-6 was significantly positively correlated with HAQ1, PTGA, grade of pain, ESR, platelet count, blood urea, AST level, and anti-CCP level; IL-6 showed an inverse significant correlation with T-score. IL-6 was positively correlated with TGC, DAS-28 score, and RF level. No correlation was found between T-score and morning stiffness duration, BMI, CRP, RBC, serum creatinine, and ALT. There was an inverse significant correlation between T-score and HAQ1, SJC, pain grade, DAS-28 score, PTGA, ESR, RF, anti-CCP, and IL-6. Patients with RA on steroid therapy had significantly higher TJC, SJC, and DAS-28 score, anti-CCP, and IL-6 than patients with RA not on steroid therapy. Patients with RA on steroid therapy had significantly lower T-score and lower serum ionized calcium than patients with RA not on steroid therapy. IL-6 has an important role in increasing osteoclastic activity and subsequent bone resorption in the patients with RA. Blocking IL-6 by using IL-6 inhibitors and anti-RANK-L therapy may be effective in inhibiting the inflammatory process and preventing the bone complications of RA disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walsh NC, Crotti TN, Coldring SR, Gravallese EM (2005) Rheumatic diseases: the effects of inflammation on bone. Immunol Rev 208:228–251
Firestern GS (2003) Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 423:356–361
Mikuls TR (2003) Co-morbidity in rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 17:729–752
Young A, Koduri G (2007) Extra-articular manifestations and complications of rheumatoid arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 21:907–927
Forsblad DH, Larsen A, Waltbrand E, Kvist G, Mellstrom D, Saxne T, Ohlsson C, Nordborg E, Carlsten H (2003) Radiographic joint destruction in postmenopausal rheumatoid arthritis is strongly associated with generalized osteoporosis. Ann Rheum Dis 62:617–623
Sinigaglia L, Varenna M, Girasole G, Bianchi G (2006) Epidemiology of osteoporosis in rheumatic diseases. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 32:631–658
Kroger H, Honkanen R, Saarikoski S, Alhava E (1994) Decreased axial bone mineral density in elderly women. The study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. J Bone Miner Res 10:257–263
Lane NE, Pressman AR, Star VL, Cummings SR, Nevitt MC (1995) Rheumatoid arthritis and bone mineral density in elderly women. The study of Osteoporotic Fractures Research Group. J Bone Miner Res 10:257–263
Van Staa TP, Geusens P, Bijlsma JW, Leufkens HG, Cooper C (2006) Clinical assessment of the long-term risk of fracture in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 54:3104–3112
Emery P, Salmon M (1991) The immune response. 2, Systemic mediators of inflammation. Br J Hosp Med 45:164–168
Kwan TS, Padrines M, Theoleyre S, Heymann D, Fortun Y (2004) IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-l: inter relations in bone resorption pathophysiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 15:49–60
Naka T, Nishimoto N, Kishimoto T (2002) The paradigm of IL-6: from basic science to medicine. Arthr Res 4(Suppl 3):S233–S242
De Benedetn F, Rucci N, Del Fattore A, Peruzzi B, Paro R, Longo M, Vivarelli M, Muratori F, Berni S, Ballanti P, Ferrari S, Teti A (2006) Impaired skeletal development in interleukin-6-transgenic mice, a model for the impact of chronic inflammation on the growing skeletal system. Arthr Rheum 54:3551–3563
Ershler WB, Harman SM, Keller ET (1997) Immunologic aspects of osteoporosis. Dev Comp Immunol 21:487–499
Devlin RD, Reddy SV, Savino R, Ciliberto G, Roodman GD (1998) IL-6 mediates the effects of IL-l or TNF, but not PTHrP or 1,25(OH)2D3, on osteoclast-like cell formation in normal human bone marrow cultures. J Bone Miner Res 13:393–399
Nakashima T, Kobayashi Y, Yamasaki S, Kawakami A, Eguchi K, Sasaki H (2000) Protein expression and functional difference of membrane-bound and soluble receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand: modulation of the expression by osteotropic factors and cytokines. Biophys Res Commun 275:768–775
Le Goff B, Blanchard F, Berthelot JM, Heymann D, Maugars Y (2010) Role for interleukin-6 in structural joint damage and systemic bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt Bone Spine 77(3):201–205
Burkhaer F, Haindl P, Maktari A, Nothngal T et al (2007) Diseases activity score-28 values differ considerably depending on patient’s pain perception and sex. J Rheumatol 34:2382–2387
Krishman E, Tugwell F, Fries JF (2004) Percentile benchmarks in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Health Assessment Questionnaire as quality indicator (QI). Arthr Res Ther 6:505–513
Dacie JV, Lewis SM (1994) Basic haematologic techniques. In: Practical haematology, 7th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburg, pp 37–66
Sox HC, Liang MH (1986) The erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Guidelines for rational use. Ann Int Med 104(4):515–523
Ritche D, Boyle JA, Innes JM (1988) Clinical studies with an articular index for assessment of joint tenderness in patient with rheumatoid arthritis. Q J Med 37:393–406
Jones MG et al (1990) Specificity of rheumatoid factor in relation to the disease state in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 49:757–762
Bizzaro N et al (2001) Diagnostic accuracy of anti-citrulline antibody assay for rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chem 47:1089–1093
Ding C, Parameswaran V, Udayan R, Burgess J, Jones G (2008) Circulating levels of inflammatory markers predict change in bone mineral and resorption in older adults: a longitudinal study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93:1952–1958
Kennedy AC, Smith DA, Buchanan WW, Anderson JB, Jasani MK (1937) Bone loss in patients with rheumatoid arthritis 4:73–79
Harris ED Jr (1993) Etiology, pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. In: Kelley WN, Harris ED Jr, Ruddy S, Sledge CB (eds) Textbook of rheumatology, vol 1, 4th edn. WB Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 833–873
Sambrook PN, Eisman JA, Champion GD, Yeates MG, Pocock NA, Eberl S (1987) Determinants of axial bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 30:721–728
Suzki Y, Mizushima Y (1997) Osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoporos Int 7(Suppl 3):S217–S222
Le Goff B, Blanchard F, Berthelot JM, Heymann D, Maugars Y (2010) Role of interleukin-6 in structural and systemic bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt Bone Spine 77(3):201–205
Verstraeten A, Dequeker J (1986) Vertebral and peripheral bone mineral content and fracture incidence in postmenopausal patients with rheumatoid arthritis: effect of low dose corticosteroids. Ann Rheum Dis 45(10):852–857
Sambrook PN, Cohen ML, Eisman JA, Pocock NA, Champion GD, Yeates MG (1989) Effects of low dose corticosteroids on bone mass in rheumatoid arthritis: a longitudinal study. Ann Rheum Dis 48(7):535–538
Kröger H, Laitinen K (1992) Bone mineral density measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry in normal men. Eur J Clin Invest 22(7):454–460
O’Malley M, Kenrick AJ, Sartoris DJ, Hochberg AM, Weisman MH, Ramos E, Zvaifler N, Resnick D (1989) Axial bone density in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison of dual-energy projection radiography and dual-photon absorptiometry. Radiology 170(2):501–505
Als OS, Gotfredsen A, Riis BJ, Christiansen C (1985) Are disease duration and degree of functional impairment determinants of bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis 44(6):406–411
Edwards CJ, Williams E (2010) The role of interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis-associated osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int 21:1287–1293
Giuliani N, Sansoni P, Girasole G, Vescovini R, Passeri G, Passeri M, Padrazzoni M (2010) Serum interleukin-6, soluble interleukin-6 receptor and soluble gp130 exhibit different patterns of age and menopause-related changes. Exp Gerontol 36:547–557
Ferrari SL, Ahn-Luong L, Garnero P, Humphries SE, Greenspan SL (2003) Two promoter polymorphisms regulating interleukin-6 gene expression are associated with circulating levels of c-reactive protein and markers of bone resorption in postmenopausal women. J Endocrinol Metab 88:225–229
Sambrook PN, Eisman JA, Yeates MG, Pocock NA, Eberl S, Champion GD (1986) Osteoporosis in rheumatoid arthritis: safety of low dose corticosteroids. Ann Rheum Dis 45(11):950–953
Hooyman JR, Melton LJ III, Nelson AM, O’Fallon WM, Riggs BL (1984) Fractures after rheumatoid arthritis. A population-based study. Arthr Rheum 27(12):1353–1361
Magaro M, Tricerri A, Piane D, Zoli A, Serra F, Altomonte L, Mirone L (1991) Generalized osteoporosis in non-steroid treated rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 11(2):73–76
Sambrook PN, Eisman JA, Champion GD, Yeates MG, Pocock NA, Eberl S (1987) Determinants of axial bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthr Rheum 30(7):721–728
Reid DM, Kennedy NS, Smith MA, Nicoll J, Brown N, Tothill P, Nuki G (1986) Bone loss in rheumatoid arthritis and primary generalized osteoarthrosis: effects of corticosteroids, suppressive antirheumatic drugs and calcium supplements. Br J Rheumatol 25(3):253–259
Als OS, Gotfredsen A, Christiansen C (1985) The effect of glucocorticoids on bone mass in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Influence of menopausal state. Arthr Rheum 28(4):369–375
McClung MR, Lewiecki EM, Cohen SB, Bolognese MA, Woodsen GC, Moffett AH et al (2006) Denosumab in postmenopausal women with low bone mineral density. N Engl J Med 354:821–831
Cohen SB, Dore RK, Lane NE, Ory PA, Peterfy CG, Sharp JT, and the Denosumab Rheumatoid Arthritis Study Group et al (2008) Denosumab treatment effects on structural damage, bone mineral density, and bone turnover in rheumatoid arthritis: a twelvemonth, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II clinical trial. Arthr Rheum 58:1299–1309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abdel Meguid, M.H., Hamad, Y.H., Swilam, R.S. et al. Relation of interleukin-6 in rheumatoid arthritis patients to systemic bone loss and structural bone damage. Rheumatol Int 33, 697–703 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2375-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2375-7