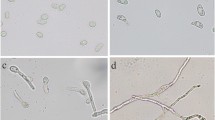
Abstract
When fungi interact with plants as pathogens or as symbionts, there are often changes in fungal cell morphology and nuclear state. This study establishes the use of cDNA microarrays to detect gene expression changes in Ustilago maydis cells that differ in structure and nuclear content. Categorizing differentially expressed genes on the basis of function indicated that U. maydis cell types vary most in the expression of genes related to metabolism. We also observed that more genes are up-regulated in the filamentous dikaryon than in the filamentous diploid, relative to non-pathogenic budding cells. Our comparison of pathogenic development indicated that the dikaryon is more virulent than the diploid. Other identified expression patterns suggest a cell-specific difference in nutrient acquisition, cell metabolism and signal transduction. The relevance of gene expression change to cell type biology is discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agrios GN (1997) Plant pathology, 4th edn. Academic, New York
Aign V, Hoheisel JD (2003) Analysis of nutrient-dependent transcript variations in Neurospora crassa. Fungal Genet Biol 40:225–233
Akopyants NS, Matlib RS, Bukanova EN, Smeds MR, Brownstein BH, Stormo GD, Beverley SM (2004) Expression profiling using random genomic DNA microarrays identifies differentially expressed genes associated with three major developmental stages of the protozoan parasite Leishmania major. Mol Biochem Parasitol 136:71–86
Austin R, Provart N, Sacadura NT, Nugent KG, Babu M, Saville BJ (2004) A comparative genomic analysis of ESTs from Ustilago maydis. Funct Integr Genomics 4:207–218
Banuett F (1995) Genetics of Ustilago maydis, a fungal pathogen that induces tumors in maize. Annu Rev Genet 29:179–208
Banuett F, Herskowitz I (1989) Different a alleles of Ustilago maydis are necessary for maintenance of filamentous growth but not for meiosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:5878–5882
Banuett F, Herskowitz I (1996) Discrete developmental stages during teliospore formation in the corn smut fungus, Ustilago maydis. Development 122:2965–2976
Basse CW, Steinberg G (2004) Ustilago maydis, model system for analysis of the molecular basis of fungal pathogenicity. Mol Plant Pathol 5:83–92
Basse CW, Stumpferl S, Kahmann R (2000) Characterization of a Ustilago maydis gene specifically induced during the biotrophic phase: evidence for negative as well as positive regulation. Mol Cell Biol 20:321–329
Belhumeur P, Lee A, Tam R, DiPaolo T, Fortin N, Clark MW (1993) GSP1 and GSP2, genetic suppressors of the prp20-1 mutant in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: GTP-binding proteins involved in the maintenance of nuclear organization. Mol Cell Biol 13:2152–2161
Bortfeld M, Auffarth K, Kahmann R, Basse CW (2004) The Ustilago maydis a2 mating-type locus genes iga2 and rga2 compromise pathogenicity in the absence of the mitochondrial p32 family protein Mrb1. Plant Cell 16:2233–2248
Boyd ML, Carris LM (1997) Enhancement of teliospore germination in wheat- and wild grass-infecting species of Tilletia on activated charcoal medium. Phytopathology 88:260–264
Brachmann A, Weinzierl G, Kämper J, Kahmann R (2001) Identification of genes in the bW/bE regulatory cascade in Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 42:1047–1063
Cano-Canchola C, Acevedo L, Ponce-Noyola P, Flores-Martinez A, Flores-Carreon A, Leal-Morales CA (2000) Induction of lytic enzymes by the interaction of Ustilago maydis with Zea mays tissues. Fungal Genet Biol 29:145–151
Chambergo FS, Bonaccorsi ED, Ferriera AJ, Ramos AS, Ferriera JJ Jr, Abrahao-Neto J, Farah JP, El-Dorry H (2002) Elucidation of the metabolic fate of glucose in filamentous fungus Trichoderma reesei using expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis and cDNA microarrays. J Biol Chem 277:13983–13988
Chigira Y, Abe K, Gomi K, Nakajima T (2002) ChsZ, a gene for a novel class of chitin synthase from Aspergillus oryzae. Curr Genet 41:261–267
Cho RJ, Campbell MJ, Winzeler EA, Steinmetz L, Conway A, Wodicka L, Wolfsberg TG, Gabriellan AE, Landsman D, Lockhart DJ, Davis RW (1998) A genomic-wide transcriptional analysis of the mitotic cell cycle. Mol Cell 2:65–73
Christensen JJ (1931) Studies on the genetics of Ustilago zeae. Phytopathology 4:124–188
Chu S, DeRisi J, Eisen M, Mulholland J, Botstein D, Brown PO, Herskowitz I (1998) The transcriptional program of sporulation in budding yeast. Science 282:699–705
Clark IA, Alleva LM, Mills AC, Cowden WB (2004) Pathogenesis of malaria and clinically similar conditions. Clin Microbiol Rev 2004 17:509–539
Day PR, Anagnostakis SL (1971) Corn smut sikaryon in culture. Nat New Biol 231:19–20
DeRisi J, Penland L, Brown PO, Bittner ML, Meltzer PS, Ray M, Chen Y, Su YA, Trent JM (1996) Use of cDNA microarray to analyse gene expression patterns in human cancer. Nat Genet 14:457–460
DeRisi JL, Iyer VR, Brown PO (1997) Exploring the metabolic and genetic control of gene expression on a genomic scale. Science 278:680–686
Dutta S, Gerhold DL, Rice M, Germann M, Kmiec EB (1997) The cloning and overexpression of a cruciform binding protein from Ustilago maydis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1352:258–266
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO, Botstein D (1998) Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:14863–14868
Gagiano M, Bauer FF, Pretorius IS (2002) The sensing of nutritional status and the relationship to filamentous growth in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 2:433–470
Gold SE, Brogdon SM, Mayroga ME, Kronstad JW (1997) The Ustilago maydis regulatory subunit of a cAMP-dependent protein kinase is required for gall formation in maize. Plant Cell 9:1585–1594
Herrmann S, Oelmuller R, Buscot F (2004) Manipulation of the onset of ectomycorrhiza formation by indole-3-acetic acid, activated charcoal or relative humidity in the association between oak microcuttings and Piloderma croceum: influence on plant development and photosynthesis. J Plant Physiol 161:509–517
Heyer LJ, Kruglyak S, Yooseph S (1999) Exploring expression data: identification and analysis of co-expressed genes. Genome Res 9:1106–1115
Holliday R (1961) Induced mitotic crossing-over in Ustilago maydis. Genet Res 2:231–248
Holliday R (1974) Ustilago maydis. In: King RC (ed) Handbook of genetics, vol 1. Plenum, New York, pp 575–595
Huber SMFE, Lottspeich F, Kämper J (2002) A gene that encodes a product with similarity to dioxygenases is highly expressed in teliospores of Ustilago maydis. Mol Genet Genomics 267:757–771
Kadowaki T, Goldfarb D, Spitz LM, Tartakoff AM, Ohno M (1993) Regulation of RNA processing and transport by a nuclear guanine nucleotide release protein and members of the Ras superfamily. EMBO J 12:2929–2937
Kojic M, Kostrub CF, Buchman AR, Holloman WK (2002) BRCA2 homolog required for proficiency in DNA repair, recombination, and genome stability in Ustilago maydis. Mol Cell 10:683–691
Kronstad JW, Leong SA (1989) Isolation of two alleles of the b locus of Ustilago maydis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:978–982
Kronstad JW, Leong SA (1990) The b mating- type locus of Ustilago maydis contains variable and constant regions. Genes Dev 4:1384–1395
Madhani HD, Fink GR (1998) The control of filamentous differentiation and virulence in fungi. Trends Cell Biol 8:348–353
Martínez-Espinoza AD, Garcia-Pedrajas MD, Gold SE (2002) The ustilaginales as plant pests and model systems. Fungal Genet Biol 35:1–20
Mews HW, Albermann K, Bahr M, Frishman D, Gleissner A, Hani J, Heumann K, Kliene K, Maierl A, Oliver SG, Pfeiffer F, Zollner A. (1997) Overview of the yeast genome. Nature 387 [Suppl]:7–8
Neal SJ, Gibson M, Anthony KC, Westwood JT (2003) Construction of a cDNA-based microarray for Drosophila melanogaster: a comparison of gene transcription profiles from SL2 and Kc167 cells. Genome 46:879–892
Nugent KG, Choffe K, Saville BJ (2004) Gene expression during Ustilago maydis diploid filamentous growth: EST library creation and analyses. Fungal Genet Biol 41:349–360
O’Donnell KL, McLaughlin DJ (1984) Ultrastructure of meiosis in Ustilago maydis. Mycologia 76:468–485
Quadbeck-Seeger C, Wanner G, Huber S, Kahmann R, Kämper J (2000) A protein with similarity to the human retinoblastoma binding protein 2 acts specifically as a repressor for genes regulated by the b mating-type locus in Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 38:154–166
van de Rhee MD, Mendes O, Werten MWT, Huizing HJ, Mooibroek H (1996) Highly efficient homologous integration via tandem exo-b-1,3,-glucanase genes in common mushroom, Agaricus bisporus. Curr Genet 30:166–173
Romeis T, Brachmann A, Kahmann R, Kämper J (2000) Identification of a target gene for bE-bW homeodomain protein complex in Ustilago maydis. Mol Microbiol 37:54–66
Ross DT, Scherf U, Eisen MB, Perou CM, Rees C, Spellman P, Iyer V, Jeffrey SS, Van de Rijn M, Waltham M, Pergamenschikov A, Lee JCF, Lashkari D, Shalon D, Myers TG, Weinstein JN, Botstein D, Brown PO (2000) Systematic variation in gene expression patterns in human cancer cell lines. Nat Genet 24:227–235
Sacadura NT, Saville BJ (2003) Gene expression and EST analyses of Ustilago maydis germinating teliospores. Fungal Genet Biol 40:47–64
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y., pp 7.27–7.30
Saville BJ, Leong SA (1992) The molecular biology of pathogenesis in Ustilago maydis. In: Setlow JK (ed) Genetic engineering: principles and methods, vol 14. Plenum, New York
Schauwecker F, Wanner G, Kahmann R (1995) Filament-specific expression of a cellulose gene in the dimorphic fungus Ustilago maydis. Biol Chem Hoppe-Seyler 376:617–625
Sims AH, Robson GD, Hoyle DC, Oliver SG, Turner G, Prade RA, Russell HH, Dunn-Coleman NS, Gent ME (2004) Use of expressed sequence tag analysis and cDNA microarrays of the filamentous fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Fungal Genet Biol 41:199–212
Snetselaar KM, Mims CW (1992) Sporidial fusion and infection of maize seedlings by the smut fungus Ustilago maydis. Mycologia 84:193–203
Snetselaar KM, Mims CW (1994) Light and electron microscopy of Ustilago maydis hyphae in maize. Mycol Res 98:347–355
Spellman PT, Sherlock G, Zhang MQ, Iyer VR, Anders K, Eisen MB, Brown PO, Botstein D, Futcher B (1998) Comprehensive identification of cell cycle regulated genes of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae by microarray hybridization. Mol Biol Cell 9:3273–3297
Takano Y, Choi W, Mitchell TK, Okuno T, Dean RA (2003) Large scale parallel analysis of gene expression during infection-related morphogenesis of Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Plant Pathol 4:337–346
Taniguchi M, Miura K, Iwao H, Yamanaka S (2001) Quantitative assessment of DNA microarrays—comparison with northern blot analyses. Genomics 71:34–39
Wen X, Furham S, Michaels GS, Carr DB, Smith S, Barker JL, Somogyi R (1998) Large-scale temporal gene expression mapping of central nervous system development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:334–339
Yao B, Rakhade SN, Li Q, Ahmed S, Krauss R, Draghici S, Loeb JA (2004) Accuracy of cDNA microarray methods to detect small gene expression changes induced by neuregulin on breast epithelial cells. BMC Bioinformatics 5:1–16
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. F. Banuett for providing us with U. maydis strains. We acknowledge and thank Dr. Timothy J. Westwood, Director of the Canadian Drosophila Microarray Centre, and Dr. Jianming Pei and Scott J. Neal, Department of Biology, University of Toronto at Mississauga, for their discussion and assistance on printing the cDNA microarray slides. We thank Ali Zahiri, Eric Ho and Matthew Cahill for their comments on the manuscript. This work was supported by a Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council grant to B.J.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by U. Kück
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, M.R., Choffe, K. & Saville, B.J. Differential gene expression in filamentous cells of Ustilago maydis. Curr Genet 47, 316–333 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0574-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-005-0574-4