Abstract
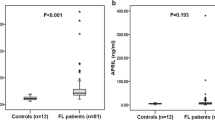
The prognosis of follicular lymphoma could vary with the tumor immune microenvironment. We evaluated the prognostic value of serum levels of ten cytokines. Our study cohort included 60 follicular lymphoma patients and 20 controls. Serum was available at diagnosis in 31 patients, at first relapse in 18, and complete remission in 11. Bioplex technology was used for determination of nine cytokines [interleukin (IL)-1Ra, IL-6, IL-7, IL-10, IL-13, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), and basic fibroblast growth factor (b-FGF)]. Transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) was measured by sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. IL-1Ra, IL-6, IL-7, IL-10, IL-13, TNF-α, VEGF, and PDGF levels were found increased in follicular lymphoma patients compared to controls. Multivariate analysis identified early stage and high TGF-β levels as independent predictors of overall survival associated with improved outcome. High lactate dehydrogenase and VEGF levels were independently associated with poorer progression-free survival. These results show the prognostic value of TGF-β and VEGF in follicular lymphoma and suggest their contribution to tumor microenvironment alterations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armitage JO, Weinsenburger DD (1998) New approach to classifying non-Hodgkin's lymphomas: clinical features of the major histologic subtypes. Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma Classification Project. J Clin Oncol 16:2780–2795
Horning SJ (1993) Natural history of and therapy for the indolent non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Semin Oncol 20:75–88
Liu Q, Fayad L, Cabanillas F, Hagemeister FB, Ayers GD, Hess M et al (2006) Improvement of overall and failure-free survival in stage IV follicular lymphoma: 25 years of treatment experience at The University of Texas M.D. Anderson Cancer Center. J Clin Oncol 24:1582–1589
Coiffier B, Brice P, Delarue R, Haioun C, Souleau B, Mounier N et al (2007) Effect of rituximab and/or high-dose therapy with autotransplant at time of relapse in patients with follicular lymphoma. Blood (ASH annual meeting abstracts) 110, Abstract 386
Solal-Celigny P, Roy P, Colombat P, White J, Armitage JO, Arranz-Saez R et al (2004) Follicular lymphoma international prognostic index. Blood 104:1258–1265
Salles GA (2007) Clinical features, prognosis and treatment of follicular lymphoma. Hematology 2007:216–225
De Jong D (2005) Molecular pathogenesis of follicular lymphoma: a cross talk of genetic and immunologic factors. J Clin Oncol 23:6358–6363
Dave SS, Wright G, Tan B, Rosenwald A, Gascoyne RD, Chan WC et al (2004) Prediction of survival in follicular lymphoma based on molecular features of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. N Engl J Med 351:2159–2169
Carreras J, Lopez-Guillermo A, Fox BC, Colomo L, Martinez A, Roncador G et al (2006) High numbers of tumor-infiltrating FOXP3-positive regulatory T cells are associated with improved overall survival in follicular lymphoma. Blood 108:2957–2964
Lee AM, Clear AJ, Calaminici M, Davies AJ, Jordan S, MacDougall F et al (2006) Number of CD4+ cells and location of forkhead box protein P3-positive cells in diagnostic follicular lymphoma tissue microarrays correlates with outcome. J Clin Oncol 24:5052–5059
Farinha P, Masoudi H, Skinnider BF, Shumansky K, Spinelli JJ, Gill K et al (2005) Analysis of multiple biomarkers shows that lymphoma-associated macrophage (LAM) content is an independent predictor of survival in follicular lymphoma (FL). Blood 106:2169–2174
Canioni D, Salles G, Mounier N, Brousse N, Keuppens M, Morchhauser F et al (2008) High numbers of tumor-associated macrophages have an adverse prognostic value that can be circumvented by rituximab in patients with follicular lymphoma enrolled onto the GELA-GOELAMS FL-2000 trial. J Clin Oncol 26:440–446
Casanovas RO, Mounier N, Brice P, Divine M, Morschhauser F, Gabarre J et al (2007) Plasma cytokine and soluble receptor signature predicts outcome of patients with classical Hodgkin's lymphoma: a study from the Groupe d'Etude des Lymphomes de l'Adulte. J Clin Oncol 25:1732–1740
Blay JY, Burdin N, Rousset F, Lenoir G, Biron P, Philip T et al (1993) Serum interleukin-10 in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a prognostic factor. Blood 82:2169–2174
Pedersen LM, Klausen TW, Davidsen UH, Johnsen HE (2005) Early changes in serum IL-6 and VEGF levels predict clinical outcome following first-line therapy in aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Hematol 84:510–516
Salven P, Orpana A, Teerenhovi L, Joensuu H (2000) Simultaneous elevation in the serum concentrations of the angiogenic growth factors VEGF and bFGF is an independent predictor of poor prognosis in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: a single-institution study of 200 patients. Blood 96:3712–3718
Fayad L, Cabanillas F, Talpaz M, McLaughlin P, Kuzrock R (1998) High serum interleukin-6 levels correlate with a shorter failure-free survival in indolent lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 30:563–571
Ansell SM, Novak AJ, Ziesmer S, LaPlant B, Cerhan JR, Yang ZZ et al (1997) Serum cytokine levels predict time to progression after rituximab as initial therapy in patients with follicular grade 1 non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 110, abstract 3410
Carbone PP, Kaplan HS, Musshoff K, Smithers DW, Tubiana M (1971) Report of the committee on Hodgkin's disease staging classification. Cancer Res 31:1860–1861
Vignali DA (2000) Multiplexed particle-based flow cytometric assays. J Immunol Methods 243:243–255
Kaplan EL, Meier P (1958) Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc 53:457–481
Therneau T, Grambsch P (2000) Modeling survival data: extending the Cox model. Springer, New York
Cerhan JR, Wang S, Maurer MJ, Ansell SM, Geyer SM, Cozen W et al (2007) Prognostic significance of host immune gene polymorphisms in follicular lymphoma survival. Blood 109:5439–5446
Khatri VP, Caligiuri MA (1998) A review of the association between interleukin-10 and human B-cell malignancies. Cancer Immunol Immunother 46:239–244
Levy Y, Brouet JC (1994) Interleukin-10 prevents spontaneous death of germinal center B cells by induction of the bcl-2 protein. J Clin Invest 93:424–428
Lech-Maranda E, Baseggio L, Bienvenu J, Charlot C, Berger F, Rigal D et al (2004) Interleukin-10 gene promoter polymorphisms influence the clinical outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 103:3529–3534
Masood R, Zhang Y, Bond MW, Scadden DT, Moudgil T, Law RE et al (1995) Interleukin-10 is an autocrine growth factor for acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-related B-cell lymphoma. Blood 85:3423–3430
Lebman DA, Edmiston JS (1999) The role of TGF-beta in growth, differentiation, and maturation of B lymphocytes. Microbes Infect 1:1297–1304
Golstein P, Wyllie AH (2001) T cell death and transforming growth factor beta1. J Exp Med 194:F19–F22
Tvrdik D, Dundr P, Povysil G, Pytlik R, Plankova M (2006) Up-regulation of p21WAF1 expression is mediated by Sp1/Sp3 transcription factors in TGFbeta1-arrested malignant B cells. Med Sci Monit 12:BR227–BR234
Tvrdik D (2004) The effect of TGFbeta1 on the expression and phosphorylation of key cell-cycle regulators in malignant B cells. Med Sci Monit 10:BR447–BR454
Husson H, Carideo EG, Neuberg D, Schultze J, Munoz A, Marks PW et al (2002) Gene expression profiling of follicular lymphoma and normal germinal center B cells using cDNA arrays. Blood 99:282–289
Huse K, Bakkebo M, Oksvold M, Smeland EB, Myklebust JH (2007) B cell lymphomas escape bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) induced growth inhibition: downregulation of BMP receptors and upregulation of inhibitory Smads. Blood (American Society of Hematology) 110, Abstract 2605
Ganjoo K (2007) Antiangiogenesis: a new approach to the treatment of lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 48:454–455
Jorgensen JM, Sorensen FB, Bendix K, Nielsen JL, Olsen ML, Funder AM et al (2007) Angiogenesis in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: clinico-pathological correlations and prognostic significance in specific subtypes. Leuk Lymphoma 48:584–595
Stopeck AT, Bellamy W, Unger J, Rimsza L, Lannone M, Fisher RI et al (2005) Phase II trial of single agent bevacizumab (Avastin) in patients with relapsed, aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (NHL): Southwest Oncology Group Study S0108. J Clin Oncol (ASCO Annual Meeting), Abstract 6592
Sorafenib in treating patients with recurrent diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (2008) http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/record/NCT00131937
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Damien Jeantet, Ecole Normale Superieure, Lyon, for technical assistance and Marie Dominique Reynaud, Centre Leon Berard, for editorial assistance.
Declaration of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Financial support
This study was supported in part by research funding from Roche France laboratories.
Authorship
Ghesquières, Blay, and Labidi made the design of the study. Ghesquières obtained funding. Labidi, Gargi, Sebban, and Biron obtained biological and clinical data. Chassagne carried out pathology revision. Labidi and Caux performed serum cytokine dosage. Chabaud made the statistical analysis. Labidi and Ghesquières drafted the manuscript. All authors revised the manuscript and have reviewed and approved the final manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Labidi, S.I., Ménétrier-Caux, C., Chabaud, S. et al. Serum cytokines in follicular lymphoma. Correlation of TGF-β and VEGF with survival. Ann Hematol 89, 25–33 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-009-0777-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-009-0777-8