Abstract
Background
The atlantoaxial and intracranial segments of vertebral artery (V3–4) are winding around their peripheral structures. Their panorama is not easy to be observed in surgery. CT angiography (CTA) shows some advantages in this aspect. So, the aim of this study is to reveal the three-dimensional (3D) anatomy related to V3–4 and prepare ground for clinical diagnosis and treatment.
Methods
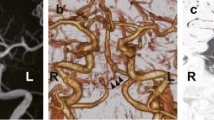
Ninety-eight cases without the pathologies of V3–4 were selected from the head–neck CTA examination. All the 3D images were formed with multiplanar reconstruction, volume rendering and volume rendering together with separating, fusing, opacifying and false-coloring. On the 3D images, the courses and branch of V3–4 were observed and measured, as well as their peripheral venous vascular plexus (VVP).
Results
V3–4 with typical five curves was found in 85 cases and with variations in 13. The left V3–4 is larger than right (P < 0.05). The branch shown on the 3D image is the posterior inferior cerebellar artery at V4, at most two on either side. VVP are at the back of the atlantoaxial joints and around the V3, each on either side. There is no significant difference in size and shape between left and right (P > 0.05).
Conclusions
The anatomy and variations of V3–4 can be clearly and directly shown by 3DCTA. The understanding of vertebral artery and bony structures around there can provide anatomic basis for surgery and radiological diagnosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett ES, Walters TD, Symons SP et al (2006) Diagnosing carotid stenosis near-occlusion by using CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:632–637
Bash S, Villablanca JP, Jahan R et al (2005) Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusive disease: evaluation with CT angiography, MR angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1012–1021
Brinjikji W, Cloft H, Kallmes DF (2009) Anatomy of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery: relevance for C1–C2 puncture procedures. Clin Anat 22:319–323
Bruneau M, Cornelius JF, George B (2006) Antero-lateral approach to the V3 segment of the vertebral artery. Neurosurgery 58:29–35
Cacciola F, Phalke U, Goel A (2004) Vertebral artery in relationship to C1–C2 vertebrae: an anatomical study. Neurol India 52:178–184
Duan SY, Ye F, Kang JH (2007) Three-dimensional CT study on normal anatomical features of atlanto-axial joints. Surg Radiol Anat 29:83–88
Gaillard F (2008) Title of subordinate document. In: Anatomy and vertebral artery. Toshiba (Australia) Medical Division. Available via DIALOG. http://radiopaedia.org/articles/vertebral-artery. Accessed 26 Oct 2008
Goel A, Desai KI, Muzumdar DP (2002) Atlantoaxial fixation using plate and screw method: a report of 160 treated patients. Neurosurgery 51:1351–1357
Harms J, Melcher RP (2001) Posterior C1–C2 fusion with polyaxial screw and rod fixation. Spine 26:2467–2471
Hong JT, Lee SW, Son BC et al (2008) Analysis of anatomical variations of bone and vascular structures around the posterior atlantal arch using three-dimensional computed tomography angiography. J Neurosurg Spine 8:230–236
Huynh-Le P, Matsushima T, Miyazono M et al (2004) Three-dimensional CT angiography for the surgical management of the vertebral artery-posterior inferior cerebellar artery aneurysms. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:329–335
Khan S, Cloud GC, Kerry S et al (2007) Imaging of vertebral artery stenosis: a systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:1218–1225
Lell MM, Ditt H, Panknin C et al (2008) Cervical CT angiography comparing routine noncontrast and a late venous scan as masks for automated bone subtraction: feasibility study and examination of the influence of patient motion on image quality. Invest Radiol 43:27–32
Lesley WS (2008) Fenestration of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery. Cerebellum 7:240–241
Levy C, Laissy JP, Raveau V et al (1994) Carotid and vertebral artery dissections: three dimensional time of flight MR angiography and MR imaging versus conventional angiography. Radiology 190:97–103
Macchi V, Porzionato A, Parenti A et al (2004) The course of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery may be related to its level of origin. Surg Radiol Anat 26:60–65
Malhotra AK, Camacho M, Ivatury RR et al (2007) Computed tomographic angiography for the diagnosis of blunt carotid/vertebral artery injury: a note of caution. Ann Surg 246:632–643
Moftakhar P, Gonzalez NR, Khoo LT et al (2008) Osseous and vascular anatomical variations within the C1–C2 complex: a radiographical study using computed tomography angiography. Int J Med Robot 4:158–164
Petridis AK, Barth H, Buhl R et al (2008) Vertebral artery decompression in a patient with rotational occlusion. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 150:391–394
Peng CW, Chou BT, Bendo JA (2009) Vertebral artery injury in cervical spine surgery-anatomical considerations, management, and preventive measures. Spine J 9:70–76
Plumb AA, Herwadkar A, Laitt R (2009) Double origin of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery with findings on conventional and CT angiography. Surg Radiol Anat 31:393–395
Puchner S, Haumer M, Rand T et al (2007) CTA in the detection and quantification of vertebral artery pathologies: a correlation with color Doppler sonography. Neuroradiology 49:645–650
Pugliese F, Crusco F, Cardaioli G et al (2007) CT angiography versus colour-Doppler US in acute dissection of the vertebral artery. Radiol Med (Torino) 112:435–443
Ren X, Wang W, Zhang X et al (2007) Clinical study and comparison of magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and angiography diagnosis of blunt vertebral artery injury. J Trauma 63:1249–1253
Sanelli PC, Tong S, Gonzalez RG et al (2002) Normal variation of vertebral artery on CT angiography and its implications for diagnosis of acquired pathology. J Comput Assist Tomogr 26:462–670
Senoglu M, Safavi-Abbasi S, Theodore N et al (2007) The frequency and clinical significance of congenital defects of the posterior and anterior arch of the atlas. J Neurosurg Spine 7:399–402
Siclari F, Burger IM, Fasel JH et al (2007) Developmental anatomy of the distal vertebral artery in relationship to variants of the posterior and lateral spinal arterial systems. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1185–1190
Sparacia G, Bencivinni F, Banco A et al (2007) Imaging processing for CT angiography of the cervicocranial arteries: evaluation of reformatting technique. Radiol Med (Torino) 112:224–238
Sylaja PN, Puetz V, Dzialowski I et al (2008) Prognostic value of CT angiography in patients with suspected vertebrobasilar ischemia. J Neuroimaging 18:46–49
Tay KY, U-King-Im JM, Trivedi RA et al (2005) Imaging the vertebral artery. Eur Radiol 15:1329–1343
Utter GH, Hollingworth W, Hallam DK et al (2006) Sixteen-slice CT angiography in patients with suspected blunt carotid and vertebral artery injuries. J Am Coll Surg 203:838–848
Yamazaki M, Okawa A, Hashimoto M et al (2008) Abnormal course of the vertebral artery at the craniovertebral junction in patients with Down syndrome visualized by three-dimensional CT angiography. Neuroradiology 50:485–490
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the support from the fund of Xiamen City’s Scientific & Technical Program (3502Z 20064008) and Xiamen board of health’s Medical Research Program (WSK 0622), Xiamen, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, S., He, H., Lv, S. et al. Three-dimensional CT study on the anatomy of vertebral artery at atlantoaxial and intracranial segment. Surg Radiol Anat 32, 39–44 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-009-0552-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-009-0552-5