Abstract
Background
Lipocalin-2 is a multifaceted modulator in cancer progression. Its clinical significance is not clear in pancreatic cancer. The purpose of this study was to investigate whether lipocalin-2 is associated with good prognosis by reversing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in pancreatic cancer.
Methods
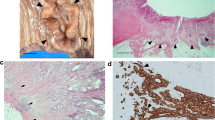
Lipocalin-2, E-cadherin, or vimentin expression was detected in 60 pancreatic adenocarcinoma specimens. Correlations between lipocalin-2 expression and EMT, the clinicopathologic characteristics, and prognosis were investigated. Whether pancreatic cancer cells’ migration and invasion (some characteristics of EMT) were affected by lipocalin-2 was also explored.
Results
High lipocalin-2 expression was significantly associated with a good prognosis in pancreatic cancer (p < 0.05). Overexpression of lipocalin-2 correlated with a lower extent of EMT (p < 0.05), increased E-cadherin expression (p < 0.05), decreased vimentin expression (p < 0.05), and reduced cancer cell migration and invasion in pancreatic cancer.
Conclusions
Lipocalin-2 may be considered an epithelial inducer, which may reverse EMT and predict a good prognosis in pancreatic cancer.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J et al (2010) Cancer statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin 60:277–300
Gounaris I, Zaki K, Corrie P (2010) Options for the treatment of gemcitabine-resistant advanced pancreatic cancer. JOP 11:113–123
Yu X, Zhang Y, Chen C et al (2010) Targeted drug delivery in pancreatic cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 1805:97–104
Bhutia YD, Hung SW, Patel B et al (2011) CNT1 expression influences proliferation and chemosensitivity in drug-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res 71:1825–1835
Roy LD, Sahraei M, Subramani DB et al (2011) MUC1 enhances invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells by inducing epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Oncogene 30:1449–1459
Kikuta K, Masamune A, Watanabe T et al (2010) Pancreatic stellate cells promote epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 403:380–384
Iwatsuki M, Mimori K, Yokobori T et al (2010) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer development and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci 101:293–299
Dubois-Marshall S, Thomas JS, Faratian D et al (2011) Two possible mechanisms of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in invasive ductal breast cancer. Clin Exp Metastasis 28:811–818
Yilmaz M, Christofori G (2009) EMT, the cytoskeleton, and cancer cell invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 28:15–33
Al Saleh S, Sharaf LH, Luqmani YA (2011) Signalling pathways involved in endocrine resistance in breast cancer and associations with epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Int J Oncol 38:1197–1217
Yori JL, Johnson E, Zhou GJ et al (2010) Kruppel-like factor 4 inhibits epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through regulation of E-cadherin gene expression. J Biol Chem 285:16854–16863
Grandclement C, Pallandre JR, Valmary Degano S et al (2011) Neuropilin-2 expression promotes TGF-beta1-mediated epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells. PLoS One 6:e20444
Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F, Cano A (2008) Transcriptional regulation of cell polarity in EMT and cancer. Oncogene 27:6958–6969
Peinado H, Olmeda D, Cano A (2007) Snail, ZEB and bHLH factors in tumour progression: an alliance against the epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer 7:415–428
Lander R, Nordin K, LaBonne C (2011) The F-box protein Ppa is a common regulator of core EMT factors Twist, Snail, Slug, and Sip1. J Cell Biol 194:17–25
Hanai JI (2005) Reversing EMT. Kidney Int 68:1970–1970
Vaid M, Singh T, Katiyar SK (2011) Grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit melanoma cell invasiveness by reduction of PGE2 synthesis and reversal of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One 6:e21539
Hanai J, Mammoto T, Seth P et al (2005) Lipocalin 2 diminishes invasiveness and metastasis of Ras-transformed cells. J Biol Chem 280:13641–13647
Gwira JA, Wei F, Ishibe S et al (2005) Expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin regulates epithelial morphogenesis in vitro. J Biol Chem 280:7875–7882
Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S et al (2004) Lipocalin 2 mediates an innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating iron. Nature 432:917–921
Lee HJ, Lee EK, Lee KJ et al (2006) Ectopic expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin suppresses the invasion and liver metastasis of colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer 118:2490–2497
Hiromoto T, Noguchi K, Yamamura M et al (2011) Up-regulation of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in oral squamous cell carcinoma: relation to cell differentiation. Oncol Rep 26:1415–1421
Tong Z, Chakraborty S, Sung B et al (2011) Epidermal growth factor down-regulates the expression of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) through E-cadherin in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer 117:2408–2418
Zhou XH (2007) Analysis of prognostic factors and roles of EMT in human pancreatic cancers. Chinese master thesis, Fudan University, p 9
Xu B, Zheng WY, Jin DY et al (2012) Treatment of pancreatic cancer using an oncolytic virus harboring the lipocalin-2 gene. Cancer 118:5217–5226
Saad AG, Yeap BY, Thunnissen FB et al (2008) Immunohistochemical markers associated with brain metastases in patients with nonsmall cell lung carcinoma. Cancer 113:2129–2138
Kowalski PJ, Rubin MA, Kleer CG (2003) E-cadherin expression in primary carcinomas of the breast and its distant metastases. Breast Cancer Res 5:R217–R222
Rubin MA, Mucci NR, Figurski J et al (2001) E-cadherin expression in prostate cancer: a broad survey using high-density tissue microarray technology. Hum Pathol 32:690–697
Brzozowska A, Sodolski T, Duma D et al (2012) Evaluation of prognostic parameters of E-cadherin status in breast cancer treatment. Ann Agric Environ Med 19:541–546
Liu X, Wang C, Chen Z et al (2011) MicroRNA-138 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Biochem J 440:23–31
Fernandez CA, Yan L, Louis G et al (2005) The matrix metalloproteinase-9/neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin complex plays a role in breast tumor growth and is present in the urine of breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 11:5390–5395
Yang J, Moses MA (2009) Lipocalin 2: a multifaceted modulator of human cancer. Cell Cycle 8:2347–2352
Kehrer JP (2010) Lipocalin-2: pro- or anti-apoptotic? Cell Biol Toxicol 26:83–89
Bolignano D, Donato V, Lacquaniti A et al (2010) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in human neoplasias: a new protein enters the scene. Cancer Lett 288:10–16
Carlson SK, Classic KL, Hadac EM et al (2009) Quantitative molecular imaging of viral therapy for pancreatic cancer using an engineered measles virus expressing the sodium-iodide symporter reporter gene. AJR Am J Roentgenol 192:279–287
Ramirez PJ, Vickers SM, Ono HA et al (2008) Optimization of conditionally replicative adenovirus for pancreatic cancer and its evaluation in an orthotopic murine xenograft model. Am J Surg 195:481–490
Watanabe I, Kasuya H, Nomura N et al (2008) Effects of tumor selective replication-competent herpes viruses in combination with gemcitabine on pancreatic cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 61:875–882
Venkatesha S, Hanai J, Seth P et al (2006) Lipocalin 2 antagonizes the proangiogenic action of ras in transformed cells. Mol Cancer Res 4:821–829
Robstad KA, Choate JD, Sheehan CE et al (2010) Prognostic implications of cytoplasmic and nuclear overexpression of lipocalin-2/NGAL in colorectal adenocarcinoma (CRC). Lab Invest 90:722
Liao CJ, Huang YH, Au HK et al (2012) The cancer marker neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is highly expressed in human endometrial hyperplasia. Mol Biol Rep 39:1029–1036
Cavalcante RB, Lopes FF, Ferreira AS et al (2007) Immunohistochemical expression of vimentin, calponin and HHF-35 in salivary gland tumors. Braz Dent J 18:192–197
Gao YF, Li T, Chang Y et al (2011) Cdk1-phosphorylated CUEDC2 promotes spindle checkpoint inactivation and chromosomal instability. Nat Cell Biol 13:924–933
Hidalgo M (2010) Pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 362:1605–1617
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81001007), the Program for Young Excellent Talents in Tongji University (2008KJ060), and Youth Fund of the Shanghai 10th People’s Hospital (10RQ105).
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, B., Jin, DY., Lou, WH. et al. Lipocalin-2 is Associated With a Good Prognosis and Reversing Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic Cancer. World J Surg 37, 1892–1900 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-013-2009-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-013-2009-6