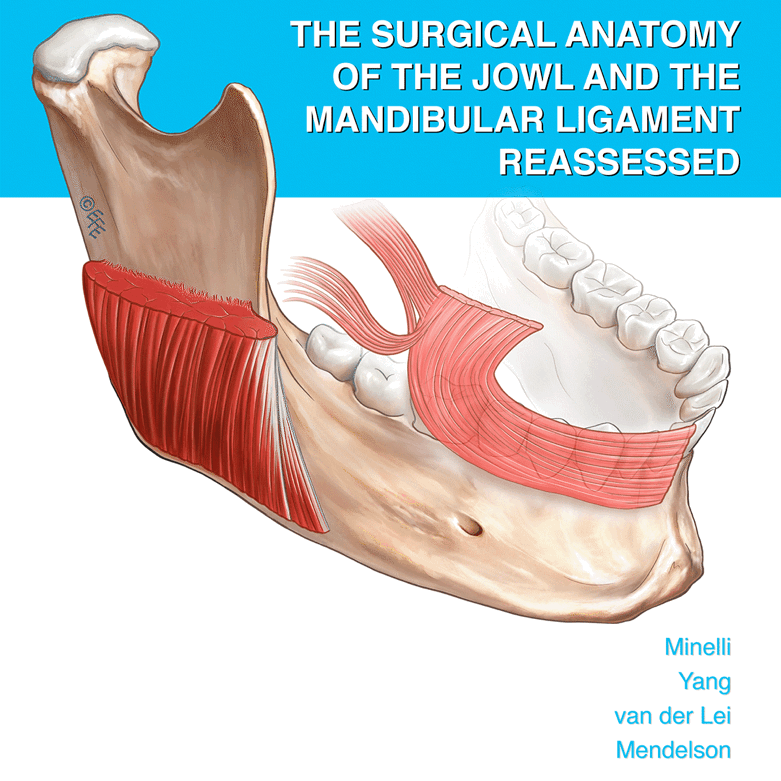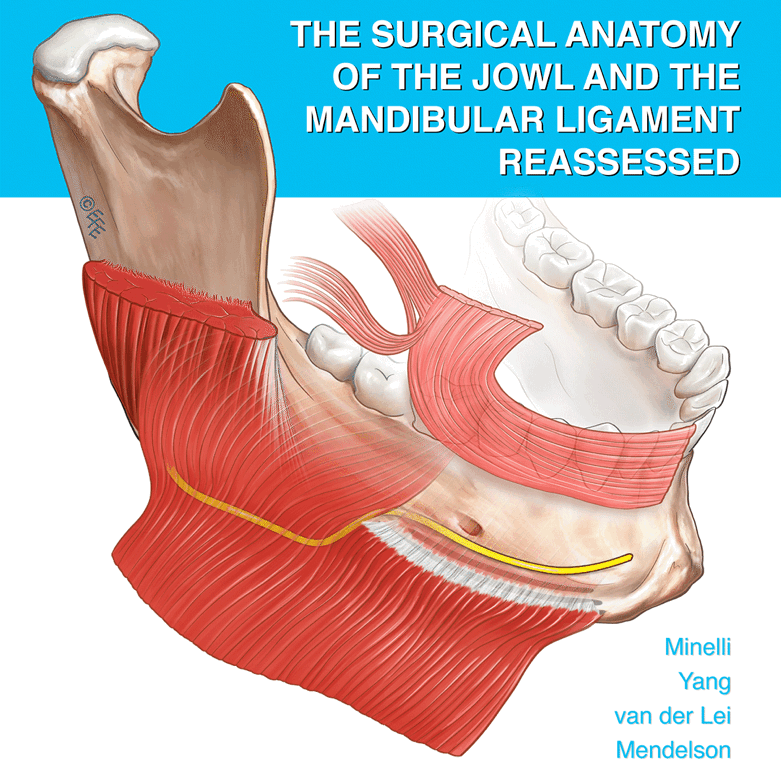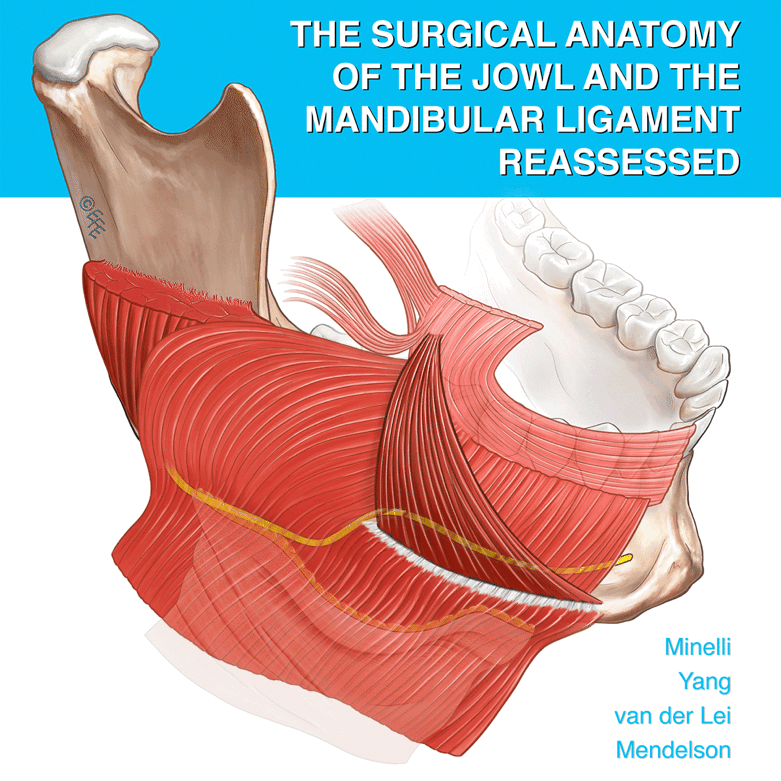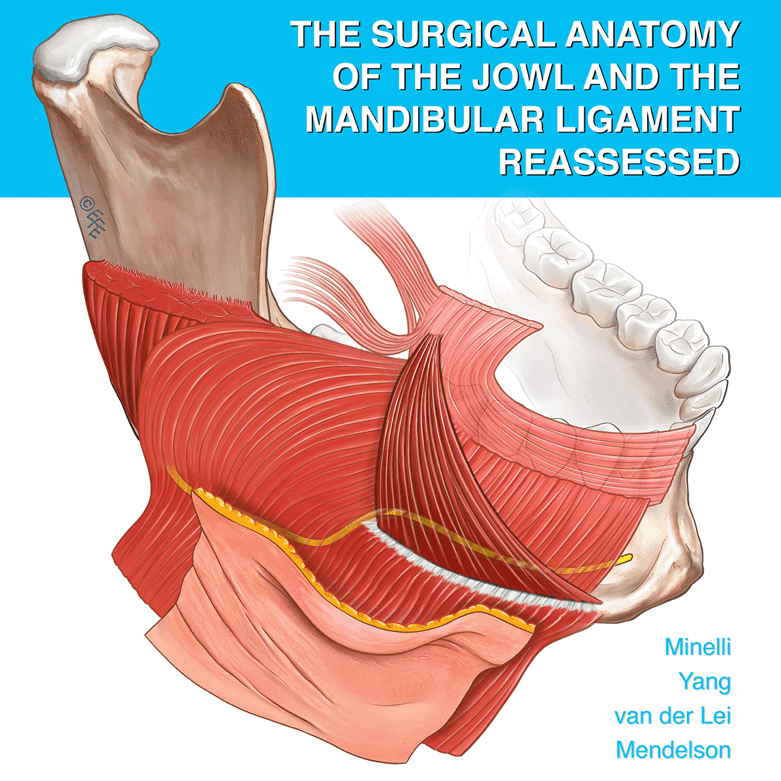
Abstract
Background
Minimally invasive procedures for aesthetic surgery have become widely popular, and facial soft tissue augmentation is one of the most common procedures. Various kinds of fillers have been used, and recently the use of calcium hydroxylapatite was extended to cosmetic facial procedures. This article presents the authors’ experience with primary and secondary nasal bridge correction using calcium hydroxylapatite (Radiesse).
Methods
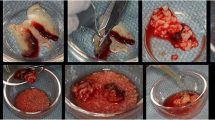
This preliminary prospective study investigated the use of commercially available calcium hydroxylapatite (Radiesse) for correction of nasal bridge deformities. Calcium hydroxylapatite was injected on the plane of the periosteum in a retrograde fashion using a linear, threading, fanning, or crosshatching technique. The patients were followed for several months, with the outcome and side effects assessed both subjectively and objectively.
Results
Patients showed a persistence of benefit up to 1 year during the follow-up period, with pleasing long-term results.
Conclusion
Calcium hydroxylapatite (Radiesse) is a useful injectable filler for correction of nasal bridge deformities. Further efficacy studies seem justified.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Busso M, Karlsberg PL (2006) Check augmentation and rejuvenation using injectable calcium hydroxylapatite (Radiesse). Cosmet Dermatol 19:583
Carruthers A, Liebeskind B, Carruthers J, Forster BB (2008) Radiographic and computed tomographic studies of calcium hydroxylapatite for treatment of HIV-associated facial lipoatrophy and correction of nasolabial folds. Dermatol Surg 34(Suppl 1):S78–S84
Felderman LI (2005) Radiesse for facial rejuvenation. Cosmet Dermatol 18:823
Goldberg DJ (2006) Calcium hydroxylapatite: fillers in cosmetic dermatology. Informa UK Ltd, Abingdon, England
Graivier MH, Bass LS, Busso M, Jasin ME, Narins RS, Tzikas TL (2007) Calcium hydroxylapatite (Radiesse) for correction of the mid- and lower face: consensus recommendations. Plast Reconstr Surg 120(Suppl):55S–66S
Hubbard W (2002) BioForm implants: durability. Bioform, Inc, Franksville
Hubbard W (2003) BioForm implants: biocompatibility. Bioform, Inc, Franksville
Jansen DA, Graivier MH (2006) Evaluation of a calcium hydroxylapatite-based implant (Radiesse) for facial soft tissue augmentation. Plast Reconstr Surg 118(Suppl.):22S
Jones JK (2006) Patient safety considerations regarding dermal filler injections. Plast Surg Nurs 26:156
Marmur ES, Phelps R, Goldberg DJ (2004) Clinical, histologic, and electron microscopic findings after injection of a calcium hydroxylapatite filler. J Cosmet Laser Ther 6:223
Tzikas TL (2004) Evaluation of Radiance FN soft tissue filler for facial soft tissue augmentation. Arch Facial Plast Surg 6:234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siclovan, H.R., Jomah, J.A. Injectable Calcium Hydroxylapatite for Correction of Nasal Bridge Deformities. Aesth Plast Surg 33, 544–548 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9281-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-008-9281-0