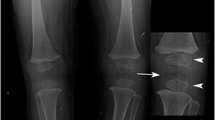
Summary.
Five cases of multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) were treated from 1985–1996 at the Orthopaedics and Trauma Department of SSK İzmir Educational Hospital. Four patients were female and one was male. The pedigrees of the first two female patients had the same features of inter-related marriages. The patients have been followed up for 5.5–11 years (average of 7.5 years). Surgical operations were mostly required in the lower limbs. Problems in the hips required adductor myotomy, the Soutter procedure, total hip replacement, and pertrochanteric extension osteotomy. Management of the knees required supracondylar shortening and extension osteotomy of the femur, high tibial extension osteotomy, debridement of the knee joint with removal of osteophytes, ogleotomy of the patellar lengthening of the knee flexors and posterior capsulotomy. Interphalangeal arthrodesis for hammer toes, extension osteotomy of the head of the first metatarsals, and Kellers operation were carried out in the foot. In the upper limb decompression and anterior transposition of the ulnar nerve, debridement of the elbow joint, extension and valgus osteotomy of the distal radius, and extension osteotomy of the head of the first metacarpal were required.
Résumé.
Cinq cas de dysplasie multi-épiphysaire ont été traités pendant la période 1985–1996 dans le département d’Orthopédie et Traumatologie de l’Hôpital Universitaire SSK İzmir. Il y avait 5 femmes et un homme. L’arbre généalogique des deux premiers patients montre des particularités tel que le mariage entre proches parents. Les patients ont été observés pendant un délai de 5,5 à 11 années (7,5 en moyenne). La plupart des interventions chirurgicales ont été faites sur les membres inférieurs. Au niveau de la hanche ont été pratiquées: la ténotomie des adducteurs, l’opération de Soutter, arthroplastie totale, et l’ostéotomie d’extension pertrochantérienne. Au niveau des genoux, ont été faits: ostéotomie supracondylienne de récurvatum et raccourcissement, ostéotomie d’extension tibiale, débridement articulaire avec ablation des ostéophytes, amincissement rotulien, allongement des fléchisseurs du genou et capsulotomie postérieure. Au niveau des pieds, ont été réalisées l’arthrodèse inter-phalangienne pour orteils en marteau, l’ostéotomie d’extension de la tête du premier métatarsien et l’opération de Keller. Au niveau du membre supérieur ont été réalisés: transposition antérieure du nerf cubital, débridement du coude, ostéotomie de valgus extension du radius distal et ostéotomie d’extension de la tête du premier métacarpien.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted: 30 November 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sebik, A., Sebik, F., Kutluay, E. et al. The orthopaedic aspects of multiple epiphyseal dysplasia. International Orthopaedics SICOT 22, 417–421 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002640050291
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002640050291