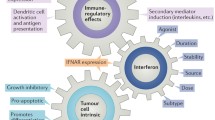
Abstract
Interferon α (IFN-α) has been widely used in the treatment of human solid and haematologic malignancies. Although the antitumour activity of IFN-α is well recognised at present, no major advances have been achieved in the last few years. Recent findings have provided new information on the molecular mechanisms of the antitumour activity of the cytokine. In fact, IFN-α appears to block cell proliferation, at least in part, through the induction of apoptotic effects. This cytokine can also regulate the progression of tumour cells through the different phases of the cell cycle inducing an increase of the expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21 and p27. However, it must be considered that IFN-α is a physiologic molecule with ubiquitously expressed receptors that is likely to activate survival mechanisms in the cell. We have recently identified an epidermal growth factor (EGF) Ras-dependent protective response to the apoptosis induced by IFN-α in epidermoid cancer cells. The identification of tissue- and/or tumour-specific survival pathways and their selective targeting might provide a new approach to improve the efficacy of IFN-α–based treatment of human cancer. Moreover, new pegylated species of IFN-α are now available with a more favourable pharmacokinetic profile. We will review these achievements, and we will specifically address the topic of IFN-α–based molecularly targeted combinatory antitumour approaches.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad S, Alsayed Y, Druker BJ, Platanias LC (1997) The type I interferon receptor mediates tyrosine phosphorylation of the CrkL adaptor protein. J Biol Chem 272:29991–29994
Allan NC, Richards SM, Shepherd PC (1995) UK Medical Research Council randomised, multicentre trial of interferon-alpha n1 for chronic myeloid leukaemia: improved survival irrespective of cytogenetic response. The UK Medical Research Council’s working parties for therapeutic trials in adult leukaemia. Lancet 345:1392–1397
Atzpodien J, Hoffmann R, Franzke M, Stief C, Wandert T, Reitz M (2002) Thirteen-year, long-term efficacy of interferon 2-alpha and interleukin 2-based home therapy in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. Cancer 95:1045–1050
Berg WJ, Nanus DM, Leung A, Brown KT, Hutchinson B, Mazumdar M, Xu XC, Lotan R, Reuter VE, Motzer RJ (1999) Up-regulation of retinoic acid receptor beta expression in renal cancers in vivo correlates with response to 13-cis-retinoic acid and interferon-alpha-2a. Clin Cancer Res 5:1671–1675
Biron CA (2001) Interferons alpha and beta as immune regulators—a new look. Immunity 14:661–664
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96:857–868
Budillon A, Tagliaferri P, Caraglia M, Torrisi MR, Normanno N, Iacobelli S, Palmieri G, Stoppelli MP, Frati L, Bianco AR (1991) Upregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor induced by alpha-interferon in human epidermoid cancer cells. Cancer Res 51:1294–1299
Buechner S, Wernli M, Hass T, Hahn S, Itin P, Erb P (1997) Regression of basal carcinoma by intralesional interferon-alpha treatment is mediated by CD95 (Apo-1/Fas)-CD95 ligand-induced suicide. J Clin Invest 100:2691–2696
Bukowski R, Ernstoff MS, Gore ME, Nemunaitis JJ, Amato R, Gupta SK, Tendler CL (2002) Pegylated interferon alfa-2b treatment for patients with solid tumours: a phase I/II study. J Clin Oncol 20:3841–3849
Bukowski RM, Tendler C, Cutler D, Rose E, Laughlin MM, Statkevich P (2002) Treating cancer with PEG intron: pharmacokinetic profile and dosing guidelines for an improved interferon-alpha-2b formulation. Cancer 95:389–396
Caraglia M, Leardi A, Corradino S, Ciardiello F, Budillon A, Guarrasi R, Bianco AR, Tagliaferri P (1995) Alpha-interferon potentiates epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated effects on human epidermoid carcinoma KB cells. Int J Cancer 61:342–347
Caraglia M, Abbruzzese A, Leardi A, Pepe S, Budillon A, Baldassare G, Selleri C, Lorenzo SD, Fabbrocini A, Giuberti G, Vitale G, Lupoli G, Bianco AR, Tagliaferri P (1999) Interferon-alpha induces apoptosis in human KB cells through a stress-dependent mitogen activated protein kinase pathway that is antagonized by epidermal growth factor. Cell Death Differ 6:773–780
Caraglia M, Tagliaferri P, Marra M, Giuberti G, Budillon A, Gennaro ED, Pepe S, Vitale G, Improta S, Tassone P, Venuta S, Bianco AR, Abbruzzese A (2003) EGF activates an inducible survival response via the Ras→ERK-1/2 pathway to counteract interferon-alpha-mediated apoptosis in epidermoid cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 10:218–229
Caraglia M, Marra M, Giuberti G, D’Alessandro AM, Baldi A, Tassone P, Venuta S, Tagliaferri P, Abbruzzese A (2003) The eukaryotic initiation factor 5A is involved in the regulation of proliferation and apoptosis induced by interferon-alpha and EGF in human cancer cells. J Biochem (Tokyo) 133:757
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S, Reed JC (1998) Regulation of cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science 282:1318–1321
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, Franklin RA, McCubrey JA (2003) Involvement of PI3 K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression, apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: a target for cancer chemotherapy. Leukemia 17:590–603
Chawla-Sarkar M, Leaman DW, Borden EC (2001) Preferential induction of apoptosis by interferon (IFN)-beta compared with IFN-alpha2: correlation with TRAIL/Apo2L induction in melanoma cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 7:1821–1831
Chawla-Sarkar M, Lindner DJ, Liu YF, Williams BR, Sen GC, Silverman RH, Borden EC (2003) Apoptosis and interferons: role of interferon-stimulated genes as mediators of apoptosis. Apoptosis 8:237–249
Cohen B, Novick D, Barak S, Rubinstein M (1995) Ligand-induced association of the type I interferon receptor components. Mol Cell Biol 15:4208–4214
Colamonici O, Yan H, Domanski P, Handa R, Smalley D, Mullersman J, Witte M, Krishnan K, Krolewski J (1994) Direct binding to and tyrosine phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of the type I interferon receptor by p135tyk2 tyrosine kinase. Mol Cell Biol 14:8133–8142
Costelli P, Aoki P, Zingaro B, Carbo N, Reffo P, Lopez-Soriano FJ, Bonelli G, Argiles JM, Baccino FM (2003) Mice lacking TNFalpha receptors 1 and 2 are resistant to death and fulminant liver injury induced by agonistic anti-Fas antibody. Cell Death Differ 10:997–1004
Croze E, Russell-Harde D, Wagner TC, Pu H, Pfeffer LM, Perez HD (1996) Reconstitution of a high affinity binding site for type I interferons. J Biol Chem 271:33165–33168
Darnell JE Jr, Kerr IM, Stark GR (1994) Jak-STAT pathways and transcriptional activation in response to IFNs and other extracellular signaling proteins. Science 264:1415–1421
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME (1997) Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell Oct 91:231–241
David M, Petricoin E III, Larner AC (1996) Activation of protein Kinase A inhibits interferon induction of the Jak/Stat pathway in U266 cells. J Biol Chem 271:4585–4588
Dijkers PF, Medema RH, Pals C, Banerji L, Thomas NS, Lam EW, Burgering BM, Raaijmakers JA, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ (2000) Forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1 modulates cytokine-dependent transcriptional regulation of p27(KIP1). Mol Cell Biol 20:9138–9148
Dijkers PF, Medema RH, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ (2000) Expression of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member Bim is regulated by the forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1. Curr Biol 10:1201–1204
Dijkers PF, Birkenkamp KU, Lam EW, Thomas NS, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ (2002) FKHR-L1 can act as a critical effector of cell death induced by cytokine withdrawal: protein kinase B-enhanced cell survival through maintenance of mitochondrial integrity. J Cell Biol 156:531–542
Ezekowitz RA, Mulliken JB, Folkman J (1992) Interferon alfa-2a therapy for life-threatening hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med 326:1456–1463
Fritz E, Ludwin H (2000) Interferon alpha treatment in multiple myeloma: meta-analysis of 30 randomized trials among 3948 patients. Ann Oncol 11:1427–1436
Fu X, Kessler DS, Veals SA, Levy DE, Darnell JE (1990) The transcriptional activator induced by interferon α, consists of multiple interacting polypeptide chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:8555–8559
Gil J, Esteban M (2000) Induction of apoptosis by the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR): mechanism of action. Apoptosis 5:107–114
Gisslinger H, Kurzrock R, Gisslinger B, Jiang S, Li S, Virgolini I, Woloszczuk W, Andreeff M, Talpaz M (2001) Autocrine cell suicide in a Burkitt lymphoma cell line (Daudi) induced by interferon alpha: involvement of tumour necrosis factor as ligand for the CD95 receptor. Blood 97:2791–2797
Gray RJ, Pockaj BA, Kirkwood JM (2002) An update on adjuvant interferon for melanoma. Cancer Control 9:16–21
Herberman RB (2002) Cancer immunotherapy with natural killer cells. Semin Oncol 29(Suppl 7):27–30
Italian Cooperative Study Group on chronic myeloid leukemia (1994) Interferon alfa-2a as compared with conventional chemotherapy for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 330:820–825
Jagus R, Joshi B, Barber GN (1999) PKR, apoptosis and cancer. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 31:123–138
Jonasch E, Haluska FG (2001) Interferon in oncological practice: review of interferon biology, clinical applications, and toxicities. Oncologist 34–55
Khan J (2003) Genomic and Proteomic technological advances in cancer research. Pharmacogenomics 4:245–249
Kim SH, Gunnery S, Choe JK, Mathews MB (2002) Neoplastic progression in melanoma and colon cancer is associated with increased expression and activity of the interferon-inducible protein kinase, PKR. Oncogene 21:8741–8748
Kirkwood JM, Strawderman MH, Ernstoff MS, Smith TJ, Borden EC, Blum RH (1996) Interferon alfa-2b adjuvant therapy of high-risk resected cutaneous melanoma in the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group trial EST 1684. J Clin Oncol 14:7–17
Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim JG, Sondak VK, Richards J, Flaherty LE, Ernstoff MS, Smith TJ, Rao U, Steele M, Blum RH (2000) High- and low-dose interferon alfa-2b in high-risk melanoma: first analysis of intergroup trial E1690/S9111/C9190. J Clin Oncol 18:2444–2458
Kirkwood JM, Ibrahim J, Lawson DH, Atkins MB, Agarwala SS, Collins K, Mascari R, Morrissey DM, Chapman PB (2001) High-dose interferon alfa-2b does not diminish antibody response to GM2 vaccination in patients with resected melanoma: results of the Multicenter Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Phase II Trial E2696. J Clin Oncol 19:1430–1436
Kirkwood JM, Richards T, Zarour HM, Sosman J, Ernstoff M, Whiteside TL, Ibrahim J, Blum R, Wieand S, Mascari R (2002) Immunomodulatory effects of high-dose and low-dose interferon alpha2b in patients with high-risk resected melanoma: the E2690 laboratory corollary of intergroup adjuvant trial E1690. Cancer 95:1101–1112
Klampfer L, Huang J, Corner G, Mariadason J, Arango D, Sasazuki T, Shirasawa S, Augenlicht L (2003) Oncogenic k-ras inhibits the expression of IFN-responsive genes through inhibition of STAT1 and STAT2 expression. J Biol Chem 278:46278–46287
Koch CA, Anderson D, Moran MF, Ellis C, Pawson T (1991) SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signalling proteins. Science 252:668–674
Lawen A (2003) Apoptosis-an introduction. Bioessays 25:888–896
Lesinski GB, Anghelina M, Zimmerer J, Bakalakos T, Badgwell B, Parihar R, Hu Y, Becknell B, Abood G, Chaudhury AR, Magro C, Durbin J, Carson WE III (2003) The antitumour effects of IFN-alpha are abrogated in a STAT1-deficient mouse. J Clin Invest 112:170–180
Lipowsky G, Bischoff FR, Schwarzmaier P, Kraft R, Kostka S, Hartmann E, Kutay U, Gorlich D (2000) Exportin 4: a mediator of a novel nuclear export pathway in higher eukaryotes. EMBO J 19:4362–4371
Liu B, Liao J, Rao X, Kushner SA, Chung CD, Chang DD, Shuai K (1998) Inhibition of Stat1-mediated gene activation by PIAS1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:10626–10631
Lutfalla G, Holland SJ, Cinato E, Monneron D, Reboul J, Rogers NC, Smith JM, Stark GR, Gardiner K, Morgensen KE, Kerr IM, Uzé G (1995) Mutant U5A cells are complemented by an interferon-alpha beta receptor subunit generated by alternative processing of a new member of a cytokine receptor gene cluster. EMBO J 14:5100–5108
Israel LG, Israel ED (1999) Apoptosis. The Oncologist 4:332–339
Mayer IA, Verma A, Grumbach IM, Uddin S, Lekmine F, Ravandi F, Majchrzak B, Fujita S, Fish EN, Platanias LC (2001) The p38 MAPK pathway mediates the growth inhibitory effects of interferon-alpha in BCR-ABL-expressing cells. J Biol Chem 276:28570–28577
Medical Research Council Renal Cancer Collaborators (1999) Interferon-alpha and survival in metastatic renal carcinoma: early results of a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 353:14–17
Mitsiades CS, Poulaki V, Mitsiades N (2003) The role of apoptosis-inducing receptors of the tumour necrosis factor family in thyroid cancer. J Endocrinol 178:205–216
Motzer RJ, Schwartz L, Law TM, Murphy BA, Hoffman AD, Albino AP, Vlamis V, Nanus DM (1995) Interferon alfa-2a and 13-cis-retinoic acid in renal cell carcinoma: antitumour activity in a phase II trial and interactions in vitro. J Clin Oncol 13:1950–1957
Motzer RJ, Rakhit A, Ginsberg M, Rittweger K, Vuky J, Yu R, Fettner S, Hooftman L (2001) Phase I trial of 40-kd branched pegylated interferon alfa-2a for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 19:1312–1319
Myeloma Trialists’ Collaborative Group (2001) Interferon as therapy for multiple myeloma: an individual patient data overview of 24 randomized trials and 4012 patients. Br J Haematol 113:1020–1034
Nadeau O, Domanski P, Usacheva A, Uddin S, Platanias LC, Pitha P, Raz R, Levy D, Majchrzak B, Fish E, Colamonici OR (1999) A Region of the subunit of the interferon receptor different from box 1 interacts with Jak1 and is sufficient to activate the Jak–Stat pathway and induce an antiviral state. J Biol Chem 274:4045–4052
Navarro S, Colamonici OR, Llombart-Bosch A (1996) Immunohistochemical detection of the type I interferon receptor in human fetal, adult, and neoplastic tissues. Mod Pathol 9:150–156
Novick D, Cohen B, Rubinstein M (1994) The human interferon alpha/beta receptor-Characterization and molecular cloning. Cell 77:391–400
Nyman TA, Matikainen S, Sareneva T, Julkunen I, Kalkkinen N (2000) Proteome analysis reveals ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes to be a new family of interferon-alpha-regulated genes. Eur J Biochem 267:4011–4011
Pestka S (1997) The human interferon-alpha species and hybrid proteins. Semin Oncol 24:S9-4–S9-17
Pyrhonen S, Salminen E, Ruutu M, Lehtonen T, Nurmi M, Tammela T, Juusela H, Rintala E, Hietanen P, Kellokumpu-Lehtinen PL (1999) Prospective randomized trial of interferon alfa-2a plus vinblastine versus vinblastine alone in patients with advanced renal cell cancer. J Clin Oncol 17:2859–2867
Rodriguez-Villanueva J, McDonnell TJ (1995) Induction of apoptotic cell death in non-melanoma skin cancer by interferon-alpha. Int J Cancer 61:110–114
Sacchi S, Federico M, Vitolo U, Boccomini C, Vallisa D, Baldini L, Petrini M, Rupoli S, Di Raimondo F, Merli F, Liso V, Tabilio A, Saglio G, Vinci G, Brugiatelli M, Dastoli G, Gis L (2001) Clinical activity and safety of combination immunotherapy with IFN-alpha 2a and rituximab in patients with relapsed low grade non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Haematologica 86:951–958
Sangfelt O, Erickson S, Castro J, Heiden T, Gustafsson A, Einhorn S, Grander D (1999) Molecular mechanisms underlying interferon-alpha-induced G0/G1 arrest: CKI-mediated regulation of G1 Cdk-complexes and activation of pocket proteins. Oncogene 18:2798–2810
Schindler C, Darnell JE (1995) Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: the JAK-STAT pathway. Annu Rev Biochem 64:621–651
Selleri C, Sato T, Del Vecchio L, Luciano L, Barrett AJ, Rotoli B, Neal S Young, Maciejewski JP (1997) Involvement of Fas-mediated apoptosis in the inhibitory effects of interferon-α in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 89:957–964
Slaton JW, Perrotte P, Inoue K, Dinney CP, Fidler IJ (1999) Interferon-alpha-mediated down-regulation of angiogenesis-related genes and therapy of bladder cancer are dependent on optimization of biological dose and schedule. Clin Cancer Res 5:2726–2734
Song MM, Shuai K (1998) The suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) 1 and SOCS3 but not SOCS2 proteins inhibit interferon-mediated antiviral and antiproliferative activities. J Biol Chem 273:35056–35062
Stahl N, Farruggella TJ, Boulton TG, Zhong Z, Darnell JE Jr, Yancopoulos GD (1995) Choice of STATs and other substrates specified by modular tyrosine-based motifs in cytokine receptors. Science 267:1349–1353
Takaoka A, Hayakawa S, Yanai H, Stoiber D, Negishi H, Kikuchi H, Sasaki S, Imai K, Shibue T, Honda K, Taniguchi T (2003) Integration of interferon-alpha/beta signalling to p53 responses in tumour suppression and antiviral defence. Nature 424:516–523
Thiesing JT, Ohno-Jones S, Kolibaba KS, Druker BJ (2000) Efficacy of STI571, an abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor, in conjunction with other antileukemic agents against bcr-abl-positive cells. Blood 96:3195–3199
Uddin S, Sassano A, Deb DK, Verma A, Majchrzak B, Rahman A, Malik AB, Fish EN, Platanias LC (2002) Protein kinase C-delta (PKC-delta) is activated by type I interferons and mediates phosphorylation of Stat1 on serine 727. J Biol Chem 277:14408–14416
Vitale G, Tagliaferri P, Caraglia M, Rampone E, Ciccarelli A, Bianco AR, Abbruzzese A, Lupoli G (2000) Slow release lanreotide in combination with interferon-alpha2b in the treatment of symptomatic advanced medullary thyroid carcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:983–988
Vitale G, Caraglia M, Ciccarelli A, Lupoli G, Abbruzzese A, Tagliaferri P, Lupoli G (2001) Current approaches and perspectives in the therapy of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer 91:1797–1808
Wadler S, Schwartz EL (1997) New advances in interferon therapy of cancer. Oncologist 2:254
Wadler S, Schwartz EL, Haynes H, Rameau R, Quish A, Mandeli J, Gallagher R, Hallam S, Fields A, Goldberg G, McGill F, Jennings S, Wallach RC, Runowicz CD (1997) All-trans retinoic acid and interferon-alpha-2a in patients with metastatic or recurrent carcinoma of the uterine cervix: clinical and pharmacokinetic studies. New York Gynecologic Oncology Group. Cancer 79:1574–1580
Wagner TC, Velichko S, Vogel D, ani MR, Leung S, Ransohoff RM, Stark GR, Perez HD, Croze E (2002) Interferon signaling is dependent on specific tyrosines located within the intracellular domain of IFNAR2c. J Biol Chem 277:1493–1499
Weisberg E, Griffin JD (2003) Resistance to imatinib (Glivec): update on clinical mechanisms. Drug Resist Updat 6:231–238
Wills RJ (1990) Clinical pharmacokinetics of interferons. Clin Pharmacokinet 19:390–399
Yan H, Krishman H, Greenlund AC, Gupta S, Lim J, Schreiber RD, Schlinder CW, Krolewski JJ (1996) STAT3 activation by type I interferons is dependent on specific tyrosines located in the cytoplasmic domain of interferon receptor chain 2c. EMBO J 15:1064–1074
Yan H, Krishnan K, Lim JT, Contillo LG, Krolewski JJ (1996) Molecular characterization of an alpha interferon receptor 1 subunit (IFNAR1) domain required for TYK2 binding and signal transduction. Mol Cell Biol 16:2074–2082
Yang B, Jung D, Motto D, Meyer J, Koretzky G, Campbell KP (1995) SH3 Domain-mediated interaction of dystroglycan and Grb2. J Biol Chem 270:11711–11714
Yang C-H, Murti A, Lawrence MP (1998) STAT3 complements defects in an interferon-resistant cell line: evidence for an essential role for STAT3 in interferon signaling and biological activities. Proc Nat Acad Sci U S A 95:5568–5572
Yang C-H, Murti A, Pfeffer SR, Kim JG, Donner DB, Pfeffer LM (2001) Interferon promotes cell survival by activating nuclear factorβ/α through phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt. J Biol Chem 276:13756–13761
Yee KW, Keating A (2003) Advances in targeted therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 3:295–310
You M, Yu DH, Feng GS (1999) Shp-2 tyrosine phosphatase functions as a negative regulator of the interferon-stimulated Jak/STAT pathway. Mol Cell Biol 19:2416–2424
Zella D, Barabitskaja O, Casareto L, Romerio F, Secchiero P, Reitz MS Jr, Gallo RC, Weichold FF (1999) Recombinant IFN-alpha (2b) increases the expression of apoptosis receptor CD95 and chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR3 in monocytoid cells. J Immunol 163:3169–3175
Zhang K, Kumar R (1994) Interferon-alpha inhibits cyclin E- and cyclin D1-dependent CDK-2 kinase activity associated with RB protein and E2F in Daudi cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 200:522–528
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tagliaferri, P., Caraglia, M., Budillon, A. et al. New pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic tools for interferon-alpha (IFN-α) treatment of human cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54, 1–10 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-004-0549-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-004-0549-1