Abstract
Purpose
Although specific positron emission tomography (PET) scanners have been developed for small animals, spatial resolution remains one of the most critical technical limitations, particularly in the evaluation of the rodent brain. The purpose of the present study was to examine the reliability of voxel-based statistical analysis (Statistical Parametric Mapping, SPM) applied to 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) PET images of the rat brain, acquired on a small animal PET not specifically designed for rodents. The gold standard for the validation of the PET results was the autoradiography of the same animals acquired under the same physiological conditions, reconstructed as a 3-D volume and analysed using SPM.
Methods
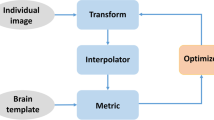
Eleven rats were studied under two different conditions: conscious or under inhalatory anaesthesia during 18F-FDG uptake. All animals were studied in vivo under both conditions in a dedicated small animal Philips MOSAIC PET scanner and magnetic resonance images were obtained for subsequent spatial processing. Then, rats were randomly assigned to a conscious or anaesthetized group for postmortem autoradiography, and slices from each animal were aligned and stacked to create a 3-D autoradiographic volume. Finally, differences in 18F-FDG uptake between conscious and anaesthetized states were assessed from PET and autoradiography data by SPM analysis and results were compared.
Results
SPM results of PET and 3-D autoradiography are in good agreement and led to the detection of consistent cortical differences between the conscious and anaesthetized groups, particularly in the bilateral somatosensory cortices. However, SPM analysis of 3-D autoradiography also highlighted differences in the thalamus that were not detected with PET.
Conclusion
This study demonstrates that any difference detected with SPM analysis of MOSAIC PET images of rat brain is detected also by the gold standard autoradiographic technique, confirming that this methodology provides reliable results, although partial volume effects might make it difficult to detect slight differences in small regions.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eidelberg D. Metabolic brain networks in neurodegenerative disorders: a functional imaging approach. Trends Neurosci 2009;32:548–57.
Blesa J, Juri C, Collantes M, Peñuelas I, Prieto E, Iglesias E, et al. Progression of dopaminergic depletion in a model of MPTP-induced Parkinsonism in non-human primates. An (18)F-DOPA and (11)C-DTBZ PET study. Neurobiol Dis 2010;38:456–63.
Casteels C, Lauwers E, Bormans G, Baekelandt V, Van Laere K. Metabolic-dopaminergic mapping of the 6-hydroxydopamine rat model for Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2008;35:124–34.
Maeda J, Ji B, Irie T, Tomiyama T, Maruyama M, Okauchi T, et al. Longitudinal, quantitative assessment of amyloid, neuroinflammation, and anti-amyloid treatment in a living mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease enabled by positron emission tomography. J Neurosci 2007;27:10957–68.
Goffin K, Van Paesschen W, Dupont P, Van Laere K. Longitudinal microPET imaging of brain glucose metabolism in rat lithium-pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Exp Neurol 2009;217:205–9.
Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline J, Frith CD, Frackowiak RSJ. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp 1994;2:189–210.
Casteels C, Martinez E, Bormans G, Camon L, de Vera N, Baekelandt V, et al. Type 1 cannabinoid receptor mapping with [18F]MK-9470 PET in the rat brain after quinolinic acid lesion: a comparison to dopamine receptors and glucose metabolism. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2010;37:2354–63.
Frumberg DB, Fernando MS, Lee DE, Biegon A, Schiffer WK. Metabolic and behavioral deficits following a routine surgical procedure in rats. Brain Res 2007;1144:209–18.
Casteels C, Vermaelen P, Nuyts J, Van Der Linden A, Baekelandt V, Mortelmans L, et al. Construction and evaluation of multitracer small-animal PET probabilistic atlases for voxel-based functional mapping of the rat brain. J Nucl Med 2006;47:1858–66.
Schweinhardt P, Fransson P, Olson L, Spenger C, Andersson JLR. A template for spatial normalisation of MR images of the rat brain. J Neurosci Methods 2003;129:105–13.
Schmidt KC, Smith CB. Resolution, sensitivity and precision with autoradiography and small animal positron emission tomography: implications for functional brain imaging in animal research. Nucl Med Biol 2005;32:719–25.
Nikolaus S, Larisch R, Beu M, Vosberg H, Müller-Gärtner HW. Imaging of striatal dopamine D(2) receptors with a PET system for small laboratory animals in comparison with storage phosphor autoradiography: a validation study with (18)F-(N-methyl)benperidol. J Nucl Med 2001;42:1691–6.
Toyama H, Ichise M, Liow JS, Modell KJ, Vines DC, Esaki T, et al. Absolute quantification of regional cerebral glucose utilization in mice by 18F-FDG small animal PET scanning and 2-14C-DG autoradiography. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1398–405.
Strome EM, Cepeda IL, Sossi V, Doudet DJ. Evaluation of the integrity of the dopamine system in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease: small animal positron emission tomography compared to behavioral assessment and autoradiography. Mol Imaging Biol 2006;8:292–9.
Wang JL, Oya S, Parhi AK, Lieberman BP, Ploessl K, Hou C, et al. In vivo studies of the SERT-selective [18F]FPBM and VMAT2-selective [18F]AV-133 radiotracers in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Nucl Med Biol 2010;37:479–86.
Ravasi L, Shimoji K, Soto-Montenegro ML, Esaki T, Seidel J, Sokoloff L, et al. Use of [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose and the ATLAS small animal PET scanner to examine cerebral functional activation by whisker stimulation in unanesthetized rats. Nucl Med Commun 2011;32:336–42.
Nguyen P, Holschneider D, Maarek J, Yang J, Mandelkern M. Statistical parametric mapping applied to an autoradiographic study of cerebral activation during treadmill walking in rats. Neuroimage 2004;23:252–9.
Lee JS, Ahn SH, Lee DS, Oh SH, Kim CS, Jeong JM, et al. Voxel-based statistical analysis of cerebral glucose metabolism in the rat cortical deafness model by 3D reconstruction of brain from autoradiographic images. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:696–701.
Dubois A, Dauguet J, Herard A, Besret L, Duchesnay E, Frouin V, et al. Automated three-dimensional analysis of histological and autoradiographic rat brain sections: application to an activation study. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2007;27:1742–55.
Dubois A, Hérard A, Delatour B, Hantraye P, Bonvento G, Dhenain M, et al. Detection by voxel-wise statistical analysis of significant changes in regional cerebral glucose uptake in an APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroimage 2010;51:586–98.
Nguyen PT, Selley DE, Sim-Selley LJ. Statistical Parametric Mapping reveals ligand and region-specific activation of G-proteins by CB1 receptors and non-CB1 sites in the 3D reconstructed mouse brain. Neuroimage 2010;52:1243–51.
Shimoji K, Ravasi L, Schmidt K, Soto-Montenegro ML, Esaki T, Seidel J, et al. Measurement of cerebral glucose metabolic rates in the anesthetized rat by dynamic scanning with 18F-FDG, the ATLAS small animal PET scanner, and arterial blood sampling. J Nucl Med 2004;45:665–72.
Huisman MC, Reder S, Weber AW, Ziegler SI, Schwaiger M. Performance evaluation of the Philips MOSAIC small animal PET scanner. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2007;34:532–40.
Collantes M, Prieto E, Peñuelas I, Blesa J, Juri C, Martí-Climent J, et al. New MRI, 18F-DOPA and 11C-(+)-α-dihydrotetrabenazine templates for Macaca fascicularis neuroimaging: advantages to improve PET quantification. Neuroimage 2009;47:533–9.
Surti S, Karp JS, Perkins AE, Cardi CA, Daube-Witherspoon ME, Kuhn A, et al. Imaging performance of A-PET: a small animal PET camera. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 2005;24:844–52.
Paxinos G, Watson C. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. San Diego, Elsevier; 2007.
Hooker JM, Patel V, Kothari S, Schiffer WK. Metabolic changes in the rodent brain after acute administration of salvinorin A. Mol Imaging Biol 2009;11:137–43.
Ahn SH, Oh SH, Lee JS, Jeong JM, Lim D, Lee DS, et al. Changes of 2-deoxyglucose uptake in the rat auditory pathway after bilateral ablation of the cochlea. Hear Res 2004;196:33–8.
Sung KK, Jang DP, Lee S, Kim M, Lee SY, Kim YB, et al. Neural responses in rat brain during acute immobilization stress: a [F-18]FDG micro PET imaging study. Neuroimage 2009;44:1074–80.
Mizuma H, Shukuri M, Hayashi T, Watanabe Y, Onoe H. Establishment of in vivo brain imaging method in conscious mice. J Nucl Med 2010;51:1068–75.
Kung MP, Kung HF. Mass effect of injected dose in small rodent imaging by SPECT and PET. Nucl Med Biol 2005;32:673–8.
Kessler RM, Ellis Jr JR, Eden M. Analysis of emission tomographic scan data: limitations imposed by resolution and background. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1984;8:514–22.
D’Ambrosio D, Marengo M, Boschi S, Fanti S,Spinelli AE. Post-reconstruction partial volume correction of PET images using iterative deconvolution algorithm and anatomical priors. IFMBE Proc 2010;25:257–60.
Rousset OG, Collins DL, Rahmim A, Wong DF. Design and implementation of an automated partial volume correction in PET: application to dopamine receptor quantification in the normal human striatum. J Nucl Med 2008;49:1097–106.
Tohka J, Reilhac A. Deconvolution-based partial volume correction in raclopride-PET and Monte Carlo comparison to MR-based method. Neuroimage 2008;39:1570–84.
Collantes M, Peñuelas I, Álvarez-Erviti L, Blesa J, Martí-Climent JM, Quincoces G, et al. Use of 11C-(+)-α-dihydrotetrabenazine for the assessment of dopaminergic innervation in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Rev Esp Med Nucl 2008;27:103–11.
Sossi V, Dinelle K, Topping GJ, Holden JE, Doudet D, Schulzer M, et al. Dopamine transporter relation to levodopa–derived synaptic dopamine in a rat model of Parkinson’s: an in vivo imaging study. J Neurochem 2009;109:85–92.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Margarita Ecay and Izaskun Bilbao for their excellent work in the animal preparation and acquisition of the PET studies, and also the cyclotron staff of the Nuclear Medicine Department of Clínica Universidad de Navarra for the radiotracer production.
The authors are also grateful to Ana Vegas and Rubén Fernández de la Rosa, from the FINNOVA program of the Community of Madrid for their assistance in the performance of the autoradiographic images, the Cyclotron Unit and Instituto Tecnológico PET (ITP).
This research was supported in part by Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación grants SAF 2009–09020 and CENIT MIND. CJ is supported by the ALBAN Programme, the European Union Programme of High Level Scholarships for Latin America, scholarship No.E07D403507CL.
Dr. Michael Paterson kindly corrected and edited the article.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prieto, E., Collantes, M., Delgado, M. et al. Statistical parametric maps of 18F-FDG PET and 3-D autoradiography in the rat brain: a cross-validation study. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 38, 2228–2237 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1905-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-011-1905-y