Abstract
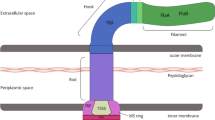
The opportunistic human pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa produces an extracellular polysaccharide called alginate. This is especially relevant in pulmonary infection of cystic fibrosis patients where it protects the bacteria from the hosts’ immune system and the diffusion of antibiotics. Here a connection between the stability of a proposed alginate polymerisation/secretion complex and the regulation of the operon encoding these proteins was assessed. Experimental evidence was provided for a periplasmic multiprotein complex composed of AlgX, AlgK, and the regulatory protein MucD. Disruption of the alginate machinery in a mucoid strain, either by removal, or over production of various essential proteins resulted in an at least 2-fold increase in transcription of a lacZ reporter under the control of the algD promoter. Instability of the complex was indicated by an increase in secretion of alginate degradation products. This increase in transcription was found to be dependent on the negative regulatory protein MucD. Surprisingly, over production of MucD leads to a 3.3-fold increase in transcription from the alginate promoter and a 1.7-fold increase in the levels of alginate produced, suggesting an additional positive regulatory role for MucD in mucoid strains. Overall, this study provided experimental evidence for the proposed periplasmic multiprotein complex and established a link of a constituent of this complex, MucD, to transcriptional regulation of alginate biosynthesis genes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becher A, Schweizer HP (2000) Integration-proficient Pseudomonas aeruginosa vectors for isolation of single-copy chromosomal lacZ and lux gene fusions. Biotechniques 29(5):948–950, 952
Blumenkrantz N, Asboe-Hansen G (1973) New method for quantitative determination of uronic acids. Anal Biochem 54(2):484–489
Boucher JC, Martinez-Salazar J, Schurr MJ, Mudd MH, Yu H, Deretic V (1996) Two distinct loci affecting conversion to mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis encode homologs of the serine protease HtrA. J Bacteriol 178(2):511–523
Boucher JC, Yu H, Mudd MH, Deretic V (1997) Mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis: characterization of muc mutations in clinical isolates and analysis of clearance in a mouse model of respiratory infection. Infect Immun 65(9):3838–3846
Boucher JC, Schurr MJ, Deretic V (2000) Dual regulation of mucoidy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and sigma factor antagonism. Mol Microbiol 36(2):341–351
Cezairliyan BO, Sauer RT (2009) Control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa AlgW protease cleavage of MucA by peptide signals and MucB. Mol Microbiol 72(2):368–379
Chitnis CE, Ohman DE (1993) Genetic analysis of the alginate biosynthetic gene cluster of Pseudomonas aeruginosa shows evidence of an operonic structure. Mol Microbiol 8(3):583–593
Choi KH, Kumar A, Schweizer HP (2006) A 10-min method for preparation of highly electrocompetent Pseudomonas aeruginosa cells: application for DNA fragment transfer between chromosomes and plasmid transformation. J Microbiol Methods 64(3):391–397
Ciofu O, Lee B, Johannesson M, Hermansen NO, Meyer P, Hoiby N (2008) Investigation of the algT operon sequence in mucoid and non-mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolates from 115 Scandinavian patients with cystic fibrosis and in 88 in vitro non-mucoid revertants. Microbiology 154(Pt 1):103–113
Damron FH, Yu HD (2011) Pseudomonas aeruginosa MucD regulates the alginate pathway through activation of MucA degradation via MucP proteolytic activity. J Bacteriol 193(1):286–291
Deretic V, Schurr MJ, Boucher JC, Martin DW (1994) Conversion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to mucoidy in cystic fibrosis: environmental stress and regulation of bacterial virulence by alternative sigma factors. J Bacteriol 176(10):2773–2780
Firoved AM, Deretic V (2003) Microarray analysis of global gene expression in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 185(3):1071–1081
Franklin MJ, Ohman DE (2002) Mutant analysis and cellular localization of the AlgI, AlgJ, and AlgF proteins required for O acetylation of alginate in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 184(11):3000–3007
Franklin MJ, Chitnis CE, Gacesa P, Sonesson A, White DC, Ohman DE (1994) Pseudomonas aeruginosa AlgG is a polymer level alginate C5-mannuronan epimerase. J Bacteriol 176(7):1821–1830
Gutsche J, Remminghorst U, Rehm BH (2006) Biochemical analysis of alginate biosynthesis protein AlgX from Pseudomonas aeruginosa: purification of an AlgX–MucD (AlgY) protein complex. Biochimie 88(3–4):245–251
Hay ID, Remminghorst U, Rehm BH (2009) MucR, a novel membrane-associated regulator of alginate biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 75(4):1110–1120
Hay ID, Rehman ZU, Ghafoor A, Rehm BHA (2010a) Bacterial biosynthesis of alginates. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85(6):752–759
Hay ID, Rehman ZU, Rehm BH (2010b) Membrane topology of the outer membrane protein AlgE which is required for alginate production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(6):1806–1812
Hoang TT, Karkhoff-Schweizer RR, Kutchma AJ, Schweizer HP (1998) A broad-host-range Flp-FRT recombination system for site-specific excision of chromosomally-located DNA sequences: application for isolation of unmarked Pseudomonas aeruginosa mutants. Gene 212(1):77–86
Hoang TT, Kutchma AJ, Becher A, Schweizer HP (2000) Integration-proficient plasmids for Pseudomonas aeruginosa: site-specific integration and use for engineering of reporter and expression strains. Plasmid 43(1):59–72
Jain S, Ohman DE (1998) Deletion of algK in mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa blocks alginate polymer formation and results in uronic acid secretion. J Bacteriol 180(3):634–641
Keiski CL, Harwich M, Jain S, Neculai AM, Yip P, Robinson H, Whitney JC, Riley L, Burrows LL, Ohman DE, Howell PL (2010) AlgK is a TPR-containing protein and the periplasmic component of a novel exopolysaccharide secretin. Structure 18(2):265–273
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM 2nd, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166(1):175–176
Martin DW, Schurr MJ, Mudd MH, Deretic V (1993) Differentiation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa into the alginate-producing form: inactivation of mucB causes conversion to mucoidy. Mol Microbiol 9(3):497–506
Mathee K, McPherson CJ, Ohman DE (1997) Posttranslational control of the algT (algU)-encoded sigma22 for expression of the alginate regulon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and localization of its antagonist proteins MucA and MucB (AlgN). J Bacteriol 179(11):3711–3720
Mathee K, Sternberg C, Ciofu O, Jensen P, Campbell J, Givskov M, Ohman DE, Hoiby N, Molin S, Kharazmi A (1999) Mucoid conversion of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by hydrogen peroxide: a mechanism for virulence activation in the cystic fibrosis lung. Microbiol 145:1349–1357
Miller JH (1972a) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Miller JH (1972b) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Pier GB, Coleman F, Grout M, Franklin M, Ohman DE (2001) Role of alginate O acetylation in resistance of mucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa to opsonic phagocytosis. Infect Immun 69(3):1895–1901
Qiu D, Eisinger VM, Rowen DW, Yu HD (2007) Regulated proteolysis controls mucoid conversion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104(19):8107–8112
Qiu D, Damron FH, Mima T, Schweizer HP, Yu HD (2008a) PBAD-based shuttle vectors for functional analysis of toxic and highly regulated genes in Pseudomonas and Burkholderia spp. and other bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(23):7422–7426
Qiu D, Eisinger VM, Head NE, Pier GB, Yu HD (2008b) ClpXP proteases positively regulate alginate overexpression and mucoid conversion in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microbiology 154(Pt 7):2119–2130
Ramsey DM, Wozniak DJ (2005) Understanding the control of Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate synthesis and the prospects for management of chronic infections in cystic fibrosis. Mol Microbiol 56(2):309–322
Rehm BH (2010) Bacterial polymers: biosynthesis, modifications and applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 8(8):578–592
Rehm BH, Boheim G, Tommassen J, Winkler UK (1994) Overexpression of algE in Escherichia coli: subcellular localization, purification, and ion channel properties. J Bacteriol 176:5639–5647
Remminghorst U, Rehm BH (2006a) Alg44, a unique protein required for alginate biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. FEBS Lett 580(16):3883–3888
Remminghorst U, Rehm BH (2006b) Bacterial alginates: from biosynthesis to applications. Biotechnol Lett 28(21):1701–1712
Remminghorst U, Rehm BHA (2006c) In vitro alginate polymerization and the functional role of Alg8 in alginate production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(1):298–305
Remminghorst U, Hay ID, Rehm BH (2009) Molecular characterization of Alg8, a putative glycosyltransferase, involved in alginate polymerisation. J Biotechnol 140(3–4):176–183
Robles-Price A, Wong TY, Sletta H, Valla S, Schiller NL (2004) AlgX is a periplasmic protein required for alginate biosynthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 186(21):7369–7377
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Plainview
Schiller NL, Monday SR, Boyd CM, Keen NT, Ohman DE (1993) Characterization of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate lyase gene (algL): cloning, sequencing, and expression in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 175(15):4780–4789
Schlegel HG, Kaltwasser H, Gottschalk G (1961) [A submersion method for culture of hydrogen-oxidizing bacteria: growth physiological studies] article in German. Arch Mikrobiol 38:209–222
Schurr MJ, Yu H, Martinez-Salazar JM, Boucher JC, Deretic V (1996) Control of AlgU, a member of the sigma E-like family of stress sigma factors, by the negative regulators MucA and MucB and Pseudomonas aeruginosa conversion to mucoidy in cystic fibrosis. J Bacteriol 178(16):4997–5004
Schweizer HP, Chuanchuen R (2001) Small broad-host-range lacZ operon fusion vector with low background activity. Biotechniques 31(6):1258, 1260, 1262
Simpson JA, Smith SE, Dean RT (1988) Alginate inhibition of the uptake of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by macrophages. J Gen Microbiol 134(1):29–36
Simpson JA, Smith SE, Dean RT (1989) Scavenging by alginate of free radicals released by macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med 6(4):347–353
Slack MP, Nichols WW (1981) The penetration of antibiotics through sodium alginate and through the exopolysaccharide of a mucoid strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Lancet 2(8245):502–503
Song Z, Wu H, Ciofu O, Kong KF, Hoiby N, Rygaard J, Kharazmi A, Mathee K (2003) Pseudomonas aeruginosa alginate is refractory to Th1 immune response and impedes host immune clearance in a mouse model of acute lung infection. J Med Microbiol 52(Pt 9):731–740
Wood LF, Ohman DE (2006) Independent regulation of MucD, an HtrA-like protease in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and the role of its proteolytic motif in alginate gene regulation. J Bacteriol 188(8):3134–3137
Wood LF, Ohman DE (2009) Use of cell wall stress to characterize sigma 22 (AlgT/U) activation by regulated proteolysis and its regulon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 72(1):183–201
Wood LF, Leech AJ, Ohman DE (2006) Cell wall-inhibitory antibiotics activate the alginate biosynthesis operon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: roles of sigma (AlgT) and the AlgW and Prc proteases. Mol Microbiol 62(2):412–426
Yorgey P, Rahme LG, Tan MW, Ausubel FM (2001) The roles of mucD and alginate in the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in plants, nematodes and mice. Mol Microbiol 41(5):1063–1076
Zhang X, Bremer H (1995) Control of the Escherichia coli rrnB P1 promoter strength by ppGpp. J Biol Chem 270(19):11181–11189
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by research grants to B.H.A.R. from Massey University. I.D.H was funded by a Massey University Doctoral scholarship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 214 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hay, I.D., Schmidt, O., Filitcheva, J. et al. Identification of a periplasmic AlgK–AlgX–MucD multiprotein complex in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in biosynthesis and regulation of alginate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 215–227 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3430-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3430-0