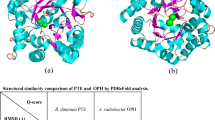
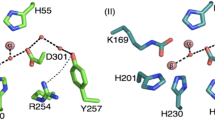
Abstract
There are classes of microbial enzymes that have the ability to degrade harmful organophosphorus (OP) compounds that are present in some pesticides and nerve agents. To date, the most studied and potentially important OP-degrading enzymes are organophosphorus hydrolase (OPH) and organophosphorus acid anhydrolase (OPAA), which have both been characterized from a number of organisms. Here we provide an update of what is experimentally known about OPH and OPAA to include their structures, substrate specificity, and catalytic properties. Current and future potential applications of these enzymes in the hydrolysis of OP compounds are also addressed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RS, Durst HD, Landis WG (1988) Organofluorophosphate-hydrolyzing activity in an estuarine clam, Rangia cuneata. Comp Biochem Physiol C 91:575–578
Attaway H, Nelson JO, Baya AM, Voll MJ, White WE, Grimes DJ, Colwell RR (1987) Bacterial detoxification of diisopropyl fluorophosphate. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:1685–1689
Benning MM, Kuo JM, Raushel FM, Holden HM (1994) Three-dimensional structure of phosphotriesterase: an enzyme capable of detoxifying organophosphate nerve agents. Biochemistry 33:15001–15007
Benning MM, Kuo JM, Raushel FM, Holden HM (1995) Three-dimensional structure of the binuclear metal center of phosphotriesterase. Biochemistry 34:7973–7978
Benning MM, Shim H, Raushel FM, Holden HM (2001) High resolution X-ray structures of different metal-substituted forms of phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Biochemistry 40:2712–2722
Bird SB, Sutherland TD, Gresham C, Oakeshott J, Scott C, Eddleston M (2008) OpdA, a bacterial organophosphorus hydrolase, prevents lethality in rats after poisoning with highly toxic organophosphorus pesticides. Toxicology 247:88–92
Caldwell SR, Raushel FM (1991a) Detoxification of organophosphate pesticides using a nylon based immobilized phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 31:59–73
Caldwell SR, Raushel FM (1991b) Detoxification of organophosphate pesticides using an immobilized phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Biotechnol Bioeng 37:103–109
Chen W, Mulchandani A (1998) The use of live biocatalysts for pesticide detoxification. Trends Biotechnol 16:71–76
Chen W, Richins RD, Mulchandani P, Kaneva I, Mulchandani A (2000) Biodegradation of organophosphorus nerve agents by surface expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. In: Zwanenburg B, Mikolajczyk M, Kielbasinski P (eds) Enzymes in action green solutions for chemical problems, vol 33. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 211–221
Cheng TC, DeFrank JJ (2000) Hydrolysis of Organophosphorus Compounds by Bacterial Prolidases. In: Zwanenburg B, Mikolajczyk M, Kielbasinski P (eds) Enzymes in action green solutions for chemical problems, vol 33. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 243–261
Cheng TC, Harvey SP, Stroup AN (1993) Purification and properties of a highly active organophosphorus acid anhydrolase from Alteromonas undina. Appl Environ Microbiol 59:3138–3140
Cheng TC, Harvey SP, Chen GL (1996) Cloning and expression of a gene encoding a bacterial enzyme for decontamination of organophosphorus nerve agents and nucleotide sequence of the enzyme. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1636–1641
Cheng T, Liu L, Wang B, Wu J, DeFrank JJ, Anderson DM, Rastogi VK, Hamilton AB (1997) Nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding an organophosphorus nerve agent degrading enzyme from Alteromonas haloplanktis. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 18:49–55
Cheng TC, Rastogi VK, DeFrank JJ, Sawiris GP (1998) G-type nerve agent decontamination by Alteromonas prolidase. Ann N Y Acad Sci 864:253–258
Cheng TC, DeFrank JJ, Rastogi VK (1999) Alteromonas prolidase for organophosphorus G-agent decontamination. Chem Biol Interact 119–120:455–462
Chungjatupornchai W, Fa-Aroonsawat S (2008) Biodegradation of organophosphate pesticide using recombinant Cyanobacteria with surface- and intracellular-expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:946–951
Defense Threat Reduction Agency (2008) Joint Science and Technology Office for Chemical and Biological Defense FY 10/11-new initiatives. Defense Threat Reduction Agency, Fort Belvoir, pp 1–53
DeFrank JJ, White WE (2002) Phosphofluoridates: Biological Activity and Biodegradation. In: Neilson AH (ed) The handbook of environmental chemistry organofluorines, vol 3N. Springer, Berlin, pp 295–343
DeFrank JJ, Beaudry WT, Cheng TC, Harvey SP, Stroup AN, Szafraniec LL (1993) Screening of halophilic bacteria and Alteromonas species for organophosphorus hydrolyzing enzyme activity. Chem Biol Interact 87:141–148
DeFrank JJ, Guelta M, Harvey S, Fry IJ, Earley JP, Lupton FS (2000) Biodegradation of hydrolyzed chemical warfare agents by bacterial consortia. In: Zwanenburg B, Mikolajczyk M, Kielbasinski P (eds) Enzymes in action green solutions for chemical problems, vol 33. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 193–209
Ditargiani RC, Chandrasekaran L, Belinskaya T, Saxena A (2010) In search of a catalytic bioscavenger for the prophylaxis of nerve agent toxicity. Chem Biol Interact 187:349–354
Dumas DP, Caldwell SR, Wild JR, Raushel FM (1989) Purification and properties of the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. J Biol Chem 264:19659–19665
Dumas DP, Durst HD, Landis WG, Raushel FM, Wild JR (1990) Inactivation of organophosphorus nerve agents by the phosphotriesterase from Pseudomonas diminuta. Arch Biochem Biophys 277:155–159
Ghanem E, Raushel FM (2005) Detoxification of organophosphate nerve agents by bacterial phosphotriesterase. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 207:459–470
Ghosh M, Grunden AM, Dunn DM, Weiss R, Adams MW (1998) Characterization of native and recombinant forms of an unusual cobalt-dependent proline dipeptidase (prolidase) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. J Bacteriol 180:4781–4789
Graham SC, Lilley PE, Lee M, Schaeffer PM, Kralicek AV, Dixon NE, Guss JM (2006) Kinetic and crystallographic analysis of mutant Escherichia coli aminopeptidase P: insights into substrate recognition and the mechanism of catalysis. Biochemistry 45:964–975
Grimsley JK, Disioudi BD, Holton TR, Sacchettini JC, Wild JR (2000) Active site modifications of organophosphorus hydrolase for improved detoxification of organophosphorus neurotoxins. In: Zwanenburg B, Mikolajczyk M, Kielbasinski P (eds) Enzymes in action green solutions for chemical problems, vol 33. Kluwer Academic, Dordrecht, pp 223–242
Grunden AM, Comfort DA, Malotky EL, Kelly RM (2004) Expression of Extremophilic Proteins. In: Baneyx F (ed) Expression technologies: current status and future trends. Horizon Scientific, Norfolk, pp 1–84
Holm L, Sander C (1997) An evolutionary treasure: unification of a broad set of amidohydrolases related to urease. Proteins 28:72–82
Hoskin FC, Roush AH (1982) Hydrolysis of nerve gas by squid-type diisopropyl phosphorofluoridate hydrolyzing enzyme on agarose resin. Science 215:1255–1257
Jaenicke R, Bohm G (1998) The stability of proteins in extreme environments. Curr Opin Struct Biol 8:738–748
Jeyaratnam J (1990) Acute pesticide poisoning: a major global health problem. World Health Stat Q 43:139–144
Karns J, Haperman C, Mulbry W, Ahrens E, Shelton D (1998) Biotechnology for the elimination of agrochemical wastes. Hort Sci 33:626–631
Lai K, Stolowich NJ, Wild JR (1995) Characterization of P–S bond hydrolysis in organophosphorothioate pesticides by organophosphorus hydrolase. Arch Biochem Biophys 318:59–64
Lai K, Grimsley JK, Kuhlmann BD, Scapozza L, Harvey SP, DeFrank JJ, Kolalowski JE, Wild JR (1996) Rational enzyme design: computer modeling and site-directed mutagenesis for the modification of catalytic specificity in organophosphorus hydrolase. Chimia 50:430–431
Landis WG, Haley DM, Haley MV, Johnson DW, Durst HD, Savage RE Jr (1987) Discovery of multiple organofluorophosphate hydrolyzing activities in the protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila. J Appl Toxicol 7:35–41
LeJeune KE, Russell AJ (1999) Biocatalytic nerve agent detoxification in fire fighting foams. Biotechnol Bioeng 62:659–665
LeJeune KE, Wild JR, Russell AJ (1998) Nerve agents degraded by enzymatic foams. Nature 395:27–28
Little JS, Broomfield CA, Fox-Talbot MK, Boucher LJ, MacIver B, Lenz DE (1989) Partial characterization of an enzyme that hydrolyzes sarin, soman, tabun, and diisopropyl phosphorofluoridate (DFP). Biochem Pharmacol 38:23–29
Lowther WT, Matthews BW (2002) Metalloaminopeptidases: common functional themes in disparate structural surroundings. Chem Rev 102:4581–4608
Lupi A, Della Torre S, Campari E, Tenni R, Cetta G, Rossi A, Forlino A (2006) Human recombinant prolidase from eukaryotic and prokaryotic sources. Expression, purification, characterization and long-term stability studies. Febs J 273:5466–5478
Mazur A (1946) An enzyme in animal tissues capable of hydrolyzing the phosphorus–fluorine bond of alkyl fluorophosphates. J Biol Chem 164:271–289
Merone L, Mandrich L, Rossi M, Manco G (2005) A thermostable phosphotriesterase from the archaeon Sulfolobus solfataricus: cloning, overexpression and properties. Extremophiles 9:297–305
Mulbry WW, Karns JS, Kearney PC, Nelson JO, McDaniel CS, Wild JR (1986) Identification of a plasmid-borne parathion hydrolase gene from Flavobacterium sp. by southern hybridization with opd from Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:926–930
Mulchandani A, Mulchandani P, Kaneva I, Chen W (1998a) Biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate nerve agents using recombinant Escherichia coli with surface-expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. 1. Potentiometric microbial electrode. Anal Chem 70:4140–4145
Mulchandani A, Kaneva I, Chen W (1998b) Biosensor for direct determination of organophosphate nerve agents using recombinant Escherichia coli with surface-expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. 2. Fiber-optic microbial biosensor. Anal Chem 70:5042–5046
Mulchandani A, Kaneva I, Chen W (1999) Detoxification of organophosphate nerve agents by immobilized Escherichia coli with surface-expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. Biotechnol Bioeng 63:216–223
Niehaus F, Bertoldo C, Kahler M, Antranikian G (1999) Extremophiles as a source of novel enzymes for industrial application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 51:711–729
Omburo GA, Kuo JM, Mullins LS, Raushel FM (1992) Characterization of the zinc binding site of bacterial phosphotriesterase. J Biol Chem 267:13278–13283
Omburo GA, Mullins LS, Raushel FM (1993) Structural characterization of the divalent cation sites of bacterial phosphotriesterase by 113Cd NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 32:9148–9155
Pei L, Petrikovics I, Way JL (1995) Antagonism of the lethal effects of paraoxon by carrier erythrocytes containing phosphotriesterase. Fundam Appl Toxicol 28:209–214
Petrikovics I, Hong K, Omburo G, Hu QZ, Pei L, McGuinn WD, Sylvester D, Tamulinas C, Papahadjopoulos D, Jaszberenyi JC, Way JL (1999) Antagonism of paraoxon intoxication by recombinant phosphotriesterase encapsulated within sterically stabilized liposomes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 156:56–63
Porzio E, Merone L, Mandrich L, Rossi M, Manco G (2007) A new phosphotriesterase from Sulfolobus acidocaldarius and its comparison with the homologue from Sulfolobus solfataricus. Biochimie 89:625–636
Rainina EI, Efremenco EN, Varfolomeyev SD, Simonian AL, Wild JR (1996) The development of a new biosensor based on recombinant E. coli for the direct detection of organophosphorus neurotoxins. Biosens Bioelectron 11:991–1000
Raushel FM (2002) Bacterial detoxification of organophosphate nerve agents. Curr Opin Microbiol 5:288–295
Rastogi VK, DeFrank JJ, Cheng TC, Wild JR (1997) Enzymatic hydrolysis of Russian-VX by organophosphorus hydrolase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 241:294–296
Richins RD, Kaneva I, Mulchandani A, Chen W (1997) Biodegradation of organophosphorus pesticides by surface-expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. Nat Biotechnol 15:984–987
Serdar CM, Gibson DT, Munnecke DM, Lancaster JH (1982) Plasmid involvement in parathion hydrolysis by Pseudomonas diminuta. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:246–249
Sethunathan N, Yoshida T (1973) A Flavobacterium sp. that degrades diazinon and parathion. Can J Microbiol 19:873–875
Shimazu M, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2001) Simultaneous degradation of organophosphorus pesticides and p-nitrophenol by a genetically engineered Moraxella sp. with surface-expressed organophosphorus hydrolase. Biotechnol Bioeng 76:318–324
Singh BK (2009) Organophosphorus-degrading bacteria: ecology and industrial applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:156–164
Singh BK, Walker A (2006) Microbial degradation of organophosphorus compounds. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:428–471
Takayama K, Suye S, Kuroda K, Ueda M, Kitaguchi T, Tsuchiyama K, Fukuda T, Chen W, Mulchandani A (2006) Surface display of organophosphorus hydrolase on Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Prog 22:939–943
Theriot CM, Tove SR, Grunden AM (2010a) Characterization of two proline dipeptidases (prolidases) from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:177–188
Theriot CM, Du X, Tove SR, Grunden AM (2010b) Improving the catalytic activity of hyperthermophilic Pyrococcus prolidases for detoxification of organophosphorus nerve agents over a broad range of temperatures. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1715–1726
Tuovinen K, Kaliste-Korhonen E, Raushel FM, Hanninen O (1994) Phosphotriesterase—a promising candidate for use in detoxification of organophosphates. Fundam Appl Toxicol 23:578–584
Tuovinen K, Kaliste-Korhonen E, Raushel FM, Hanninen O (1996) Protection of organophosphate-inactivated esterases with phosphotriesterase. Fundam Appl Toxicol 31:210–217
Vanhooke JL, Benning MM, Raushel FM, Holden HM (1996) Three-dimensional structure of the zinc-containing phosphotriesterase with the bound substrate analog diethyl 4-methylbenzylphosphonate. Biochemistry 35:6020–6025
Vyas NK, Nickitenko A, Rastogi VK, Shah SS, Quiocho FA (2010) Structural insights into the dual activities of the nerve agent degrading organophosphate anhydrolase/prolidase. Biochemistry 49:547–559
Wang AA, Mulchandani A, Chen W (2002) Specific adhesion to cellulose and hydrolysis of organophosphate nerve agents by a genetically engineered Escherichia coli strain with a surface-expressed cellulose-binding domain and organophosphorus hydrolase. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:1684–1689
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Sherry Tove for her helpful comments on the manuscript. We also thank Dr. Joseph DeFrank and Saumil Shah from the US Army, Edgewood Chemical Biological Center, for helpful discussion on the use of OP compound-degrading enzymes for CWA decontamination. Support for some of the studies described in this review was provided by the Army Research Office (contract number 44258LSSR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Theriot, C.M., Grunden, A.M. Hydrolysis of organophosphorus compounds by microbial enzymes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 89, 35–43 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2807-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2807-9