Abstract
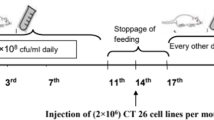
The synergistic effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and bovine colostrums on the immunity of mice in vivo and in vitro were investigated. Eight- to ten-week-old mice were used for two series experiments; one part of mice were immunocompromised by intraperitoneal injections of cyclophosphamide. In series I, immunocompromised mice were continuously fed with diet A (L. rhamnosus ZDY114 5 × 107 CFU/kg), B (bovine colostrums 0.5 g/kg), C (combination of diet A and B), and D (sterile saline) for 4 weeks and killed. Thereof, phagocytosis ratio and index of macrophage to chicken red blood cells in abdominal cavity and lymphocyte transformation rate were determined. In series II, both normal and immunocompromised mice were used to investigate the in vitro stimulation of lymphocyte proliferation by substances from the overnight culture of L. rhamnosus ZDY114 by the MTT colorimetric method. Compared with diet D, in the diet A, B, and C groups, the phagocytosis ratio of macrophages increased by 1.63, 1.54, and 2.3-fold, respectively, and the lymphocyte transformation ratio by 1.78, 2.08, and 2.35-fold, respectively. In vitro test with MTT showed that 3, 10, 50 kD substances from the overnight culture of L. rhamnosus ZDY114 significantly increased the growth of lymphocyte by 1.63, 1.53, and 1.34-fold, respectively. In conclusion, L. rhamnosus and bovine colostrums can enhance the functions of immune system supported by lymphocytes and peritoneal macrophages either in vivo or in vitro.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alander M, Korpela R, Saxelin M, Vilpponen-Salmela T, Mattila-Sandholm T, von Wright A (1997) Recovery of L. rhamnosus GG from human colonic biopsies. Lett Appl Microbiol 24:361–364
Davidkova G, Popova P, Guencheva G, Bogdanov A, Pacelli E, Auteri A, Mincheva V (1992) Endogenous production of tumor necrosis factor in normal mice orally treated with Deodan—a preparation from Lactobacillus bulgaricus LB51. Int J Immunopharmacol 14:1355–1362
Davidson GP, Tam J, Kirubakaran C (1994) Passive protection against symptomatic hospital acquired rotavirus infection in India and Hong Kong. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 19:351
de Ambrosini VM, Gonzalez S, Perdigon G, de Ruiz Holgado AP, Oliver G (1996) Chemical composition of the cell wall of lactic acid bacteria and related species. Chem Pharm Bull 44:2263–2267
Dividson GP (1996) Passive protection against diarrhea disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 23:207–212
Donohue DC, Salminen S, Marteau P (1998) Safety of probiotic bacteria. In: Salminen S, von Wright A (eds) Lactic acid bacteria: microbiology and functional aspects. Marcel Dekker, New York, NY, pp 369–383
Elo S, Saxelin M, Salminen S (1991) Attachment of L. casei strain GG to human colon carcinoma cell line Caco-2: comparison with other dairy strains. Lett Appl Microbiol 13:154–156
Forrest BD (1988) Identification of an intestinal immune response using peripheral blood lymphocytes. Lancet 1:81–83
Freedman DJ, Tacket CO, Delehanty A, Maneval DR, Nataro J, Crabb JH (1998) Milk immunoglobulin with specific activity against purified colonization factor antigens can protect against oral challenge with enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis 177:662–667
Gill HS, Ruthfurd KJ (2001) Viability and dose-response studies on the effects of the immunoenhancing lactic acid bacterium Lactobacillus rhamnosus in mice. Br J Nutr 86:285–289
Hammarstr L, Gardulf A, Hammarstr V, Janson A, Lindberg K, Smith CIE (1994) Systemic and topical immunoglobulin treatment in immunocompromised patients. Immunol Rev 139:43–47
He D, Liu F, Guo Z (2002) The immune function injury and its mechanism in drug abuser. Chin J Clin Rehab 6:2966–2967
Kato I, Endo K, Yokokura T (1994) Effects of oral administration of Lactobacillus casei on antitumor responses induced by tumor resection in mice. Int J Immunopharmacol 16:29–36
Kirjavainen PV, El-Nezami HS, Salminen SJ, Ahokas JT, Wright PF (1999) Effects of orally administered viable Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG and Propionibacterium freudenreichii subsp. shermanii JS on mouse lymphocyte proliferation. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 6:799–802
Korhonen H, Marnila P, Gill HS (2000) Bovine milk antibodies for health. Br J Nutr 84(Suppl 1):S135–S146
Kuisma J, Mentula S, Jarvinen H, Kahri A, Saxelin M, Farkkila M (2003) Effect of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on ileal pouch inflammation and microbial flora. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 17:509–515
Leblanc J, Fliss I, Matar C (2004) Induction of a humoral immune response following an Escherichia coli O157:H7 infection with an immunomodulatory peptidic fraction derived from L. helveticus-fermented milk. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 11:1171–1181
Loimaranta V, Nuutila J, Marnila P, Tenovuo J, Korhonen H, Lilius E (1999) Colostral proteins from cows immunised with Streptococcus mutans/S. sobrinus support the phagocytosis and killing of mutans Streptococci by human leukocytes. J Med Microbiol 48:1–10
Majamaa H, Isolauri E, Saxelin M, Vesikari T (1995) Lactic acid bacteria in the treatment of acute rotavirus gastroenteritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 20:333–338
Malin M, Verronen P, Korhonen H, Syvaja EL, Salminen S, Mykkien H, Arvilommi H, Eerola E, Isolauri E (1997) Dietary therapy with Lactobacillus GG, bovine colostrum or bovine immune colostrum in patients with juvenile chronic arthritis: evaluation of effect on gut defense mechanisms. Inflammopharmacology 5:219–236
Marnila P, Rokka S, Rehnberg-Laiho L, Karkkainen P, Kosunen TU, Rautelin H, Hanninen ML, Syvaoja EL, Korhonen H (2003) Prevention and suppression of Helicobacter felis infection in mice using colostral preparation with specific antibodies. Helicobacter 8:192–201
Marteau P, Verman JP, Dehennin JP, Bord S, Brassart D, Pochart P, Desjeux JF, Rambaud JC (1997) Effects of intrajejunal perfusion and chronic ingestion of Lactobacillus johusonii strain La l on serum concentration and jejunal secretions of immunoglobulins and serum proteins in healthy humans. Gastroenterol Clin Biol 21:293–298
Marteau PR, de Vrese M, Cellier CJ, Schrezenmeir J (2001) Protection from gastrointestinal diseases with the use of probiotics. Am J Clin Nutr 73(Suppl 2):430–436
Pakkanen R, Aalto J (1997) Growth factors and antimicrobial factors of bovine colostrum. Int Dairy J 7:285–297
Perdigon G, de Marcias MEN, Alvarez S, Oliver G, de Ruiz Holgado AP (1986) Effect of perorally administered lactobacilli on macrophage activation in mice. Infect Immun 53:404–410
Perdigon G, Alvarez S, Rachid M, Aguero G, Gobbato N (1995) Immune system stimulation by probiotics. J Dairy Sci 78:1597–1606
Ruiz LP (1994) Antibodies from milk for the prevention and treatment of diarrhea disease. Processing of the IDF seminar indigenous antimicrobial agents of milk: recent developments. IDF Special Issue 9404:108–121
Sasaki T, Fukami S, Namioka S (1994) Enhancement of cytotoxic activity of lymphocytes in mice by oral administration of peptidoglycan derived from Bifidobacterium thermophilum. J Vet Med Sci 56:1129–1133
Schiffrin EJ, Rochat F, Link-Amster H, Aeschlimann JM, Donnet-Hughes A (1995) Immunomodulation of human blood cells following the ingestion of lactic acid bacteria. J Dairy Sci 78:491–497
Solis-Pereyra B, Aattouri N, Lemonnier D (1997) Role of food in the stimulation of cytokine production. Am J Clin Nutr 66:521–525
Strobel S, Mowat AM (1998) Immune responses to dietary antigens: oral tolerance. Immunol Today 19:173–181
Tacket CO, Binion SB, Bostwick E, Losonsky G, Roy MJ, Edelman R (1992) Efficacy of bovine milk immunoglobulin concentrate in preventing illness after Shigella flexneri challenge. Am J Trop Med Hyg 47:276–283
Viljanen M, Savilahti E, Haahtela T, Juntunen-Backman K, Korpela R, Poussa T, Tuure T, Kuitunen M (2005) Probiotics in the treatment of atopic eczema/dermatitis syndrome in infants: a double-blind placebo-controlled trial. Allergy 60:494–500
Wei H, Marnila P, Korhonen H (2002a) Effects of anti-caries antibodies on Lactobacillus GG in its fermentation and storage periods. Biomed Environ Sci 15:153–165
Wei H, Loimaranta V, Tenovuo J, Rokka S, Syvaoja EL, Korhonen H, Joutsjoki V, Marnila P (2002b) Stability and activity of specific antibodies against Streptococcus mutans and Streptococcus sobrinus in bovine milk fermented with L. rhamnosus strain GG or treated at ultra-high temperature. Oral Microbiol Immunol 17:9–15
Acknowledgment
This research project was supported by the CSC (Chinese Scholar Committee) and CIMO (The Centre for International Mobility CIMO, Finland).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, H., Xu, Y., Cheng, B. et al. Synergistic effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus ZDY114 and bovine colostrums on the immunological function of mouse in vivo and in vitro. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75, 427–434 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0818-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0818-3