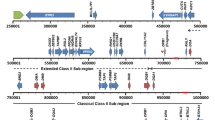
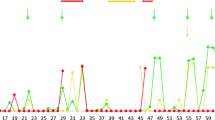
Abstract
Genes of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) play a pivotal role in the vertebrate immune system and are attractive markers for functional, fitness-related, genetic variation. Although bats (Chiroptera) represent the second largest mammalian order and are prone to various emerging infectious diseases, little is known about MHC evolution in bats. In the present study, we examined expressed MHC class II DRB sequences (exons 1 to 4) of New World bat species, Saccopteryx bilineata, Carollia perspicillata, Noctilio albiventris and Noctilio leporinus (only exon 2). We found a wide range of copy number variation of DRB loci with one locus detected in the genus Noctilio and up to ten functional loci observed in S. bilineata. Sequence variation between alleles of the same taxa was high with evidence for positive selection. We found statistical support for recombination or gene conversion events among sequences within the same but not between bat species. Phylogenetic relationships among DRB alleles provided strong evidence for independent evolution of the functional MHC class II DRB genes in the three investigated species, either by recent gene duplication, or homogenization of duplicated loci by frequent gene conversion events. Phylogenetic analysis of all available chiropteran DRB exon 2 sequences confirmed their monophyletic origin within families, but revealed a possible trans-species mode of evolution pattern in congeneric bat species, e.g. within the genera Noctilio and Myotis. This is the first study investigating phylogenetic relationships of MHC genes within bats and therefore contributes to a better understanding of MHC evolution in one of the most dominant mammalian order.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisimova M, Nielsen R, Yang Z (2003) Effect of recombination on the accuracy of the likelihood method for detecting positive selection at amino acid sites. Genetics 164:1229–1236
Axtner J, Sommer S (2011) Heligmosoides polygyrus infection is associated with lower MHC class II gene expression in Apodemys flavicolis: indication for immune suppression? Inf Gen Evol 2063–2071
Babik W, Radwan J (2007) Sequence diversity of MHC class II DRB genes in the bank vole Myodes glareolus. Acta Theriol 52(3):227–235
Baker ML, Tachedjian M, Wang LF (2010) Immunoglobulin heavy chain diversity in Pteropid bats: evidence for a diverse and highly specific antigen binding reservoir. Immunogenetics 62:173–184
Bollmer JL, Dunn PO, Whittingham LA, Wimpee C (2010) Extensive MHC class II B gene duplication in a passerine, the common yellowthroat (Geothlypis trichas). J Hered 101(4):448–460
Bouchard S (2001) Sex discrimination and roost mate recognition by olfactory cues in the African bats, Mops condylurus and Chaerephon pumilus (Chiroptera: Molossidae). J Zool 254(1):109–117
Bowen L, Aldridge BM, Gulland F, Woo J, Van Bonn W, DeLong R, Stott JL, Johnson ML (2002) Molecular characterization of expressed DQA and DQB genes in the California sea lion (Zalophus californianus). Immunogenetics 54:332–347
Bowen L, Aldridge BM, Gulland F, Van Bonn W, DeLong R, Melin S, Lowenstein LJ, Stott JL, Johnson ML (2004) Class II multiformity generated by variable MHC-DRB region configurations in the California sea lion (Zalophus californianus). Immunogenetics 56:12–27
Brown JH, Jardetzky TS, Gorga JC, Stern LJ, Urban RG, Strominger JL et al (1993) Three-dimensional structure of the human class II histocompatibility antigen HLA DR1. Nature 364:33–39
Bryja J, Galan M, Charbonnel N, Cosson J-F (2006) Duplication, balancing selection and trans-species evolution explain the high levels of polymorphism of DQA MHC class II gene in voles (Arvicolinae). Immunogenetics 58:191–202
Burri R, Hirzel HN, Salamin N, Roulin A, Fumagalli L (2008) Evolutionary patterns of MHC class II B in owls and their implication for the understanding of avian MHC evolution. Mol Biol Evol 25(6):1180–1191
Burri R, Salamin N, Studer RA, Roulin A, Fumagalli L (2010) Adaptive divergence of ancient duplicates in the avian MHC class II β. Mol Biol Evol 27(10):2360–2374
Calisher CH, Childs JE, Field HE, Holmes KV, Schountz T (2006) Bats: important reservoir hosts of emerging viruses. Clin Microbiol Rev 19(3):531–545
Dobson AP (2005) What links bats to emerging infectious diseases? Science 310:628–629
Doxiadis GGM, de Groot N, de Groot NG, Rotmans G, deVos-Reouweler AJM, Bontrop RE (2010) Extensive DRB region diversity in cynomolgus macaques: recombination as a driving force. Immunogenetics 62:137–147
Ellis SA, Bontrop RE, Antczak DF, Ballingall K, Davies CJ, Kaufman J et al (2006) ISAG/IUIS-VIC Comparative MHC Nomenclature Committee report, 2005. Immunogenetics 57:953–958
Field HE (2009) Bats and emerging zoonoses: henipaviruses and SARS. Zoonoses Public Hlth 56(6–7):278–284
Figuroa F, Günther G, Klein J (1988) MHC polymorphism predating speciation. Nature 335:265–67
Gannon WL, Sikes RS (2007) Guidelines of the American Society of Mammalogists for the use of wild mammals in research. J Mammal 88:809
Goüy de Bellocq J, Suchentrunk F, Baird SEB, Schaschl H (2009) Evolutionary history of an MHC gene in two leporid species: characterisation of Mhc-DQA in the European brown hare and comparison with European rabbit. Immunogenetics 61:131–144
Hess CM, Edwards SV (2002) The evolution of the major histocompatibility complex in birds. Bioscience 52(5):423–431
Hughes AL (1994) The evolution of functionally novel proteins after gene duplications. Proc R Soc Lond B 256:119–124
Hughes AL (1999) Adaptive evolution of genes and genomes. Oxford University Press, New York
Hughes AL (2000) Evolution of introns and exons of class II major histocompatibility complex genes of vertebrates. Immunogenetics 51:473–486
Hughes AL (2007) Looking for Darwin in all the wrong places: the misguided quest for positive selection at the nucleotide sequence level. Heredity 99:364–373
Hughes AL, Nei M (1988) Pattern of nucleotide substitution at major histocompatibility complex class I loci reveals overdominant selection. Nature 335:167–170
Hughes AL, Yeager M (1998) Natural selection at major histocompatibility complex loci of vertebrates. Annu Rev Genet 32:415–435
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munroe HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism. Academic, New York, pp 21–132
Kennedy LJ, Ryvar R, Gaskell RM, Addie DD, Willoughby K, Carter SD et al (2002) Sequence analyses of MHC DRB alleles in domestic cats from the United Kingdom. Immunogenetics 54:348–352
Kikkawa EF, Tsuda TT, Sumiyama D, Naruse TK, Fukuda M, Kurita M, Wilson RP, LeMaho Y, Miller GD, Tsuda M, Murata K, Kulski JK, Inoko H (2009) Trans-species polymorphism of the MHC class II DRB-like gene in banded penguins (genus Spheniscus). Immunogenetics 61:341–352
Klein J (1986) Natural history of the major histocompatibility complex. Wiley, New York
Klein J (1987) Origin of major histocompatibility complex polymorphism: the trans-species hypothesis. Human Immunol 19:155–162
Klein J, Sato A, Nikolaides N (2007) MHC, TSP, and the origin of species: from immunogenetics to evolutionary genetics. Annu Rev Genet 41:281–304
Kriener K, O’hUigin C, Tichy H, Klein J (2000) Convergent evolution of major histocompatibility complex molecules in humans and New World monkeys. Immunogenetics 51:69–178
Kriener K, O’hUigin C, Klein J (2001) Independent origin of functional MHC class II genes in humans and new world monkeys. Hum Immun 62:1–14
Kumanovics A, Takada T, Fischer Lindahl K (2003) Genomic organization of the mammalian MHC. Annu Rev Immunol 21:629–657
Kunz TH, Braun de Torres E, Bauer D, Lobova T, Fleming TH (2011) Ecosystem services provided by bats. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1223:1–3
Kupfermann H, Satta Y, Takahata N, Tichy H, Klein J (1999) Evolution of MHC-DRB introns: implication for the origin of primates. J Mol Evol 48:663–674
Kwak J, Opiekun MC, Matsumura K, Preti G, Yamazaki K, Beauchamp GK (2009) Major histocompatibility complex-regulated odortypes: peptide-free urinary volatile signals. Phys Behav 96:184–188
Lewis-Oritt N, Van den Busche RA, Baker RJ (2001) Molecular evidence for evolution of piscivory in Noctilio (Chiroptera: Noctilionidae). J Mammal 82:748–759
Librado P, Rozas J (2009) DnaSP v5: a software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 25:1451–1452
Mansai SP, Innan H (2010) The power of the methods for detecting interlocus gene conversion. Genetics 184:517–572
Mayer F, Brunner A (2007) Non-neutral evolution of the major histocompatibility complex class II gene DRB1 in the sac-winged bat Saccopteryx bilineata. Heredity 99:257–264
Mayer WE, Jonker M, Klein D, Ivanyi P, van Seventer G, Klein J (1988) Nucleotide sequences of chimpanzee MHC class I alleles: evidence for trans-species mode of evolution. EMBO 7(9):2765–2774
Mikko S, Roed K, Schmutz S, Andersson L (1999) Monomorphism and polymorphism at MHC DRB loci in domestic and wild ruminants. Immunol Rev 167:169–178
Musolf K, Meyer-Lucht Y, Sommer S (2004) Evolution of MHC-DRB class II polymorphism in the genus Apodemus and a comparison of DRB sequences within the family Muridae (Mammalia: Rodentia). Immunogenetics 56(6):420–426
Nemeth E, Baird AW, O’Farrelly C (2009) Microanatomy of the liver immune system. Semin Immunopathol 31:333–343
Nei M, Gojobori T (1986) Simple methods for estimating the numbers of synonymous and nonsynonymous nucleotide substitutions. Mol Biol Evol 3(5):418–426
Nei M, Hughes AL (1992) Balanced polymorphism and evolution by the birth-and-death process in the MHC loci. In: Tsuij K, Aizawa M, Sasazuki T (eds) 11th Histocompatibility Workshop and Conference. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, New York
Nei M, Rooney AP (2005) Concerted and birth-and-death evolution of multigene families. Annu Rev Genet 39:121–152
O’hUigin C (1995) Quantifying the degree of convergence in primate MHC-DRB genes. Immunol Rev 143:123–140
Otha T (1999) Effect of gene conversion on polymorphic patterns at major histocompatibility complex loci. Immunol Rev 167:319–325
Penn DJ, Potts WK (1998) How do major histocompatibility complex genes influence odour and mating preference? Adv Immunol 69:411–436
Penn DJ, Potts WK (1999) The evolution of mating preferences and major histocompatibility complex genes. Am Nat 153:145–164
Piertney SB, Oliver MK (2006) The evolutionary ecology of the major histocompatibility complex. Heredity 96:7–21
Posada D (2002) Evaluation of methods for detecting recombination from DNA sequences: empirical data. Mol Biol Evol 19(5):708–717
Posada D (2008) jModelTest: phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:1253–1256
Reusch TBH, Langefors A (2005) Inter- and intralocus recombination drive MHC class II B gene diversification in a teleost, three-spined stickleback Gasterosteus aculeatus. J Mol Evol 61:531–545
Richman AD, Herrera LG, Nash D, Schierup HM (2003) Relative roles of mutation and recombination in generating allelic polymorphism at a MHC class II locus in Peromyscus maniculatus. Genet Res Camb 82:89–99
Richman AD, Herrera LG, Ortega-Garcia S, Flores-Martinez JJ, Arroyo-Cabrales J, Morales-Malacara JB (2010) Class II DRB polymorphism and sequence diversity in two vesper bats in the genus Myotis. Immunogenetics 37(5):401–405
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Santos PSC, Kellermann T, Uchanska-Ziegler B, Ziegler A (2010) Genomic architecture of MHC linked odorant receptor gene repertoires among 16 vertebrate species. Immunogenetics 62(9):569–584
Sawyer SA (1999) GENECONV: a computer package for the statistical detection of gene conversion. Distribution by the author, Dept of Mathematics, Washington University, St Louis (http://www.math.wustl.edu/-sawyer)
Schad J, Sommer S, Ganzhorn J (2004) MHC variability of a small lemur in the littoral forest fragments of south-eastern Madagascar. Conserv Genet 5:299–309
Schad J, Dechmann DKN, Voigt CC, Sommer S (2011) MHC class II DRB diversity, selection pattern and population structure in a neotropical bat species, Noctilio albiventris. Heredity 107:115–126
Schaschl H, Suchentrunk F, Hammer S, Goodman SJ (2005) Recombination and the origin of sequence diversity in the MHC class II DRB in chamois (Rupicapra spp.). Immunogenetics 57:108–115
Schaschl H, Wandeler P, Suchentrunk F, Obexer-Ruff G, Goodman SJ (2006) Selection and recombination drive evolution of MHC class II DRB diversity in ungulates. Heredity 97:427–437
Spurgin LG, Richardson DS (2010) How pathogens drive genetic diversity: MHC, mechanisms and misunderstandings. Proc R Soc Lond B 277:979–988
Srithayakumar V, Castillo S, Mainguy J, Kyle CJ (2012) Evidence for evolutionary convergence at MHC in two broadly distributed mesocarnivores. Immunogenetics. doi:10.1007/s00251.011-0588-7
Stern LJ, Brown JH, Jardetzky JCG, Urban RG, Strominger JL, Wiley DC (1994) Crystal structure of the human class II MHC protein HLA-DR1 complexed with an influenza virus peptide. Nature 368:215–221
Studier EH, Lavoie KH (1984) Microbial involvement in scent production in noctilionid bats. J Mammal 65:711–714
Suárez CF, Patarroyo ME, Trujillo E, Estupiñán M, Baquero JE, Parra C, Rodriguez R (2006) Owl monkey MHC DRB exon 2 reveals high similarity with several HLA-DRB lineages. Immunogenetics 58:542–558
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Trowsdale J (1995) Both man & bird & beast: comparative organization of MHC genes. Immunogenetics 41:1–17
Vilamiu RP, Correa MM, Pessoa LM, Oliveira JA, Oliveira LFB (2010) The karyotype of Noctilio albiventris (Chiroptera: Noctilionidae) from Brazil and its taxonomic implications. Mastozool Neotrop 17(1):219–224
Virtue ER, Marsh GA, Baker ML, Wang LF (2011) Interferon production and signalling pathways are antagonized during Henipavirus infection in fruit bat cell lines. Plos One 6(7):e22488
Voigt CC, van Helversen O (1999) Storage and display of odour by male Saccopteryx bilineata (Chiroptera, Emballonuridae). Behav Ecol Sociobiol 47:29–40
Wei K, Zhang Z, Wang X, Zhang W, Xu X, Shen F, Yue B (2010) Lineage pattern, trans-species polymorphism, and selection pressure among the major lineages of feline MHC-DRB peptide-binding region. Immunogenetics 62:307–317
Wibbelt G, Moore M, Schountz T, Voigt CC (2010) Emerging diseases in Chiroptera: why bats? Biol Lett 6:438–440
Worthington-Wilmer J, Baratt E (1996) A non-lethal method of tissue-sampling for genetic studies of chiropterans. Bat Res News 37:1–3
Xu SX, Chen BY, Zhou KY, Yang G (2008) High sequence similarity at three MHC loci between baiji and finless porpoise: trans-species or convergent evolution? Mol Phylogenet Evol 47:36–44
Xu SX, Ren WH, Li SZ, Wei FW, Zhou KY, Yang G (2009) Sequence polymorphism and evolution of three Cetacean MHC genes. J Mol Evol 69:260–275
Yang ZH (2007) PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol 24:1586–1591
Yang ZH, Bielawski JP (2000) Statistical methods for detecting molecular adaptation. Trends Ecol Evol 15:496–503
Yang ZH, Wong WSW, Nielsen R (2005) Bayes empirical Bayes inference of amino acid sites under positive selection. Mol Biol Evol 22:1107–1118
Yeager M, Hughes AL (1999) Evolution of the mammalian MHC: natural selection, recombination and convergent evolution. Immun Rev 167:45–58
Yuhki N, Beck T, Stephens R, Neelam B, O’Brien ST (2007) Comparative genomic structure of human, dog and cat MHC: HLA, DLA, and FLA. J Hered 98(5):390–399
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank PD Dr. Karl-Heinz Esser of the Tierärztliche Hochschule Hannover, Germany for providing a specimen of C. perspicillata for our cDNA analyses. We thank Anke Schmidt for technical laboratory assistance and Aines Castro-Prieto and Pablo Santos for helpful comments on earlier versions of the manuscript. We further thank Charles Gunn for linguistic advice as well as an anonymous reviewer for the constructive scientific comments on the former version of the manuscript. All capture and handling of animals as well as collection and export of samples was done in concordance with national laws. Field work and animal handling was carried out according to the protocol approved by the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute—Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (STRI-IUCAC). Permits were issued from the Panamanian authority Autoridad National del Ambiente (ANAM, SE/A 98-08, SEX/A78-08, SEX/A-138-08) and from the Ministerio del Ambiente y Energia, Costa Rica (MINAE, Permit Number: No 183-2008-SINAC). This work was supported by the Leibniz Institute for Zoo and Wildlife Research (IZW), Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 123 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schad, J., Voigt, C.C., Greiner, S. et al. Independent evolution of functional MHC class II DRB genes in New World bat species. Immunogenetics 64, 535–547 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-012-0609-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-012-0609-1