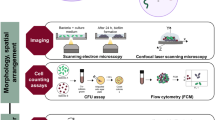
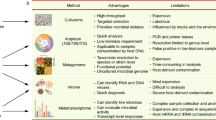
Abstract
During the past decade, there has been an explosion in the quantity of sequencing data that has come out of the studies of microbiomes. This has resulted primarily from new technological developments to interrogating any environment of choice. Additional downstream applications to interrogating these datasets include “omics” studies such as transcriptomics and proteomics, all leading to a deeper understanding of microbial diversity and the multitude of species that remain uncultured. Metagenomic studies are now being performed routinely on a wide range of environments including soils, oceans, air, plants, and various animal species. They are being used to identify novel microbial species, new pathways, and to elucidate the roles of viruses and phage in the environment. In this review, we get a perspective on where the science is headed and what we expect to learn as additional studies unfold.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J, Yang L et al (2011) Oral microbiome profiles: 16S rRNA pyrosequencing and microarray assay comparison. PloS One 6(7):e22788
Brulc JM, Antonopoulos DA et al (2009) Gene-centric metagenomics of the fiber-adherent bovine rumen microbiome reveals forage specific glycoside hydrolases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(6):1948–1953
Castellarin M, Warren RL et al (2012) Fusobacterium nucleatum infection is prevalent in human colorectal carcinoma. Genome Res 22(2):299–306
Cheng KJ, Costerton JW (1981) Adherent rumen bacteria: their role in the digestion of plant material, urea, and epithelial cells. In: Ruchebusch Y, Thivend P (eds) Digestive physiology and metabolism in ruminants. MTP Press, Lancaster, United Kingdom, p 227–250
Chung EJ, Lim HK et al (2008) Forest soil metagenome gene cluster involved in antifungal activity expression in Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 74(3):723–730
Delmont TO, Prestat E et al (2012) Structure, fluctuation and magnitude of a natural grassland soil metagenome. ISME J 6(9):1677–1687
Fouts DE, Pieper R et al (2012) Integrated next-generation sequencing of 16S rDNA and metaproteomics differentiate the healthy urine microbiome from asymptomatic bacteriuria in neuropathic bladder associated with spinal cord injury. J Transl Med 10:174
Fouts DE, Szpakowski S et al (2012) Next generation sequencing to define prokaryotic and fungal diversity in the bovine rumen. PloS One 7(11):e48289
Gevers D, Knight R et al (2012) The human microbiome project: a community resource for the healthy human microbiome. PLoS Biol 10(8):e1001377
Gilbert JA, Field D et al (2008) Detection of large numbers of novel sequences in the metatranscriptomes of complex marine microbial communities. PLoS One 3(8):e3042
Human Microbiome Project Consortium (2012) A framework for human microbiome research. Nature 486(7402):215–221
Human Microbiome Project Consortium (2012) Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 486(7402):207–214
Iverson V, Morris RM et al (2012) Untangling genomes from metagenomes: revealing an uncultured class of marine Euryarchaeota. Science 335(6068):587–590
Lavery TJ, Roudnew B et al (2012) High nutrient transport and cycling potential revealed in the microbial metagenome of Australian sea lion (Neophoca cinerea) faeces. PloS One 7(5):e36478
Martinez-Garcia M, Brazel D et al (2012) Unveiling in situ interactions between marine protists and bacteria through single cell sequencing. ISME J 6(3):703–707
Mason OU, Hazen TC et al (2012) Metagenome, metatranscriptome and single-cell sequencing reveal microbial response to Deepwater Horizon oil spill. ISME J 6(9):1715–1727
McLean JS, Fansler SJ et al (2012) Identifying low pH active and lactate-utilizing taxa within oral microbiome communities from healthy children using stable isotope probing techniques. PloS One 7(3):e32219
Pace NR (2009) Mapping the tree of life: progress and prospects. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 73(4):565–576
Pace NR, Olsen GJ et al (1986) Ribosomal RNA phylogeny and the primary lines of evolutionary descent. Cell 45(3):325–326
Pope PB, Denman SE et al (2010) Adaptation to herbivory by the tammar wallaby includes bacterial and glycoside hydrolase profiles different from other herbivores. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(33):14793–14798
Pope PB, Mackenzie AK et al (2012) Metagenomics of the Svalbard reindeer rumen microbiome reveals abundance of polysaccharide utilization loci. PloS One 7(6):e38571
Qu A, Brulc JM et al (2008) Comparative metagenomics reveals host specific metavirulomes and horizontal gene transfer elements in the chicken cecum microbiome. PloS One 3(8):e2945
Rusch DB, Halpern AL et al (2007) The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling expedition: northwest Atlantic through eastern tropical Pacific. PLoS Biol 5(3):e77
Sharon I, Tzahor S et al (2007) Viral photosynthetic reaction center genes and transcripts in the marine environment. ISME J 1(6):492–501
Stepanauskas R (2012) Single cell genomics: an individual look at microbes. Curr Opin Microbiol 15(5):613–620
Swanson KS, Dowd SE et al (2011) Phylogenetic and gene-centric metagenomics of the canine intestinal microbiome reveals similarities with humans and mice. ISME J 5(4):639–649
Uhlik O, Leewis MC et al (2012) Stable isotope probing in the metagenomics era: a bridge towards improved bioremediation. Biotechnol Adv 31(2):154–165
Venter JC, Remington K et al (2004) Environmental genome shotgun sequencing of the Sargasso Sea. Science 304(5667):66–74
Virk B, Correia G et al (2012) Excessive folate synthesis limits lifespan in the C. elegans: E. coli aging model. BMC Biol 10:67
Wang Z, Klipfell E et al (2011) Gut flora metabolism of phosphatidylcholine promotes cardiovascular disease. Nature 472(7341):57–63
Williamson SJ, Rusch DB et al (2008) The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling Expedition: metagenomic characterization of viruses within aquatic microbial samples. PloS One 3(1):e1456
Wu D, Wu M et al (2011) Stalking the fourth domain in metagenomic data: searching for, discovering, and interpreting novel, deep branches in marker gene phylogenetic trees. PloS One 6(3):e18011
Yooseph S, Sutton G et al (2007) The Sorcerer II Global Ocean Sampling expedition: expanding the universe of protein families. PLoS Biol 5(3):e16
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelson, K.E. Microbiomes. Microb Ecol 65, 916–919 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0227-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-013-0227-y