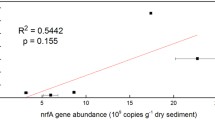
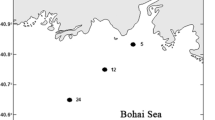
Abstract
Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) has recently been recognized as a pathway for the removal of fixed N from aquatic ecosystems. However, the quantitative significance of anammox in estuarine sediments is variable, and measurements have been limited to a few estuaries. We measured anammox and conventional denitrification activities in sediments along salinity gradients in the Chesapeake Bay and two of its sub-estuaries, the Choptank River and Patuxent River. Homogenized sediments were incubated with 14/15N amendments of \( {\text{NH}}^{ + }_{4} \), \( {\text{NO}}^{ - }_{3} \), and \( {\text{NO}}^{ - }_{2} \) to determine relative activities of anammox and denitrification. The percent of N2 production due to anammox (ra%) ranged from 0 to 22% in the Chesapeake system, with the highest ra% in the freshwater portion of the main stem of upper Chesapeake Bay, where water column \( {\text{NO}}^{ - }_{3} \) concentrations are consistently high. Intermediate levels of relative anammox (10%) were detected at locations corresponding to tidal freshwater and mesohaline locations in the Choptank River, whereas anammox was not detected in the tidal freshwater location in the Patuxent River. Anammox activity was also not detected in the seaward end of Chesapeake Bay, where water column \( {\text{NO}}^{ - }_{3} \) concentrations are consistently low. The ra% did not correlate with \( {\text{NH}}^{ + }_{4} \) accumulation rate in anoxic sediment incubations, but ra% was related to water column \( {\text{NO}}^{ - }_{3} \) concentrations and salinity. Anammox bacterial communities were also examined by amplifying DNA extracted from the upper Chesapeake Bay sediment with polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers that are specific for 16S rRNA genes of anammox organisms. A total of 35 anammox-like sequences were detected, and phylogenetic analysis grouped the sequences in two distinct clusters belonging to the Candidatus “Scalindua” genus.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender, M, Jahnke, R, Weiss, R, Martin, W, Heggie, DT, Orchardo, J, Sowers, T (1989) Organic-carbon oxidation and benthic nitrogen and silica dynamics in San-Clemente Basin, a continental borderland site. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 53: 685–697
Broda, E (1977) Two kinds of lithotrophs missing in nature. Zeitschrift fur Allgemeine Mikrobiologie 17: 491–493
Cowan, JLW, Boynton, WR (1996) Sediment-water oxygen and nutrient exchanges along the longitudinal axis of Chesapeake Bay: seasonal patterns, controlling factors and ecological significance. Estuaries 19: 562–580
Dalsgaard, T, Thamdrup, B (2002) Factors controlling anaerobic ammonium oxidation with nitrite in marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 3802–3808
Dalsgaard, T, Canfield, DE, Petersen, J, Thamdrup, B, Acuna-Gonzalez, J (2003) N2 production by the anammox reaction in the anoxic water column of Golfo Dulce, Costa Rica. Nature 422: 606–608
Dalsgaard, T, Thamdrup, B, Canfield, DE (2005) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) in the marine environment. Res Microbiol 156: 457–464
Egli, K, Fanger, U, Alvarez, PJJ, Siegrist, H, van der Meer, JR, Zehnder, AJB (2001) Enrichment and characterization of an anammox bacterium from a rotating biological contactor treating ammonium-rich leachate. Arch Microbiol 175: 198–207
Engström, P, Dalsgaard, T, Hulth, S, Aller, RC (2005) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation by nitrite (anammox): implications for N2 production in coastal marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 69: 2057–2065
Ferris, M, Muyzer, G, Ward, D (1996) Denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis profiles of 16S rRNA-defined populations inhabiting a hot spring microbial mat community. Appl Environ Microbiol 62: 340–346
Francis, CA, O’Mullan, GD, Ward, BB (2003) Diversity of ammonia monooxygenase (amoA) genes across environmental gradients in Chesapeake Bay sediments. Geobiology 1: 129–140
Fujii, T, Sugino, H, Rouse, JD, Furukawa, K (2002) Characterization of the microbial community in an anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing biofilm cultured on a nonwoven biomass carrier. J Biosci Bioeng 94: 412–418
Galloway, JN, Dentener, FJ, Capone, DG, Boyer, EW, Howarth, RW, Seitzinger, SP, Asner, GP, Cleveland, CC, Green, PA, Holland, EA, Karl, DM, Michaels, AF, Porter, JH, Townsend, AR, Vorosmarty, CJ (2004) Nitrogen cycles: past, present, and future. Biogeochemistry 70: 153–226
Güven, D, Dapena, A, Kartal, B, Schmid, MC, Maas, B, van de Pas-Schoonen, K, Sozen, S, Mendez, R, Op den Camp, HJM, Jetten, MSM, Strous, M, Schmidt, I (2005) Propionate oxidation by and methanol inhibition of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 1066–1071
Howarth, RW, Boyer, EW, Pabich, WJ, Galloway, JN (2002) Nitrogen use in the United States from 1961–2000 and potential future trends. Ambio 31: 88–96
Hulth, S, Aller, RC, Gilbert, F (1999) Coupled anoxic nitrification manganese reduction in marine sediments. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 63: 49–66
Jetten, M, Schmid, M, van de Pas-Schoonen, K, Sinninghe Damsté, J, Strous, M (2005) Anammox organisms: enrichment, cultivation, and environmental analysis. Methods Enzymol 397: 34–57
Jones, MN (1984) Nitrate reduction by shaking with Cd. Water Res 18: 643–646
Kartal, B, van Niftrik, L, Sliekers, O, Schmid, MC, Schmidt, I, van de Pas-Schoonen, K, Cirpus, I, van der Star, W, van Loosdrecht, M, Abma, W, Kuenen, GJ, Mulder, J-W, Jetten, MSM, Strous, M. , van de Vossenberg, J (2004) Application, eco-physiology and biodiversity of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria. Rev Environ Sci Biotechnol 3: 255–264
Kartal, B, Rattray, J, van Niftrik, LA, van de Vossenberg, J, Schmid, MC, Webb, RI, Schouten, S, Fuerst, JA, Damste, JS, Jetten, MSM, Strous, M (2007) Candidatus “Anammoxoglobus propionicus” a new propionate oxidizing species of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 30: 39–49
Kirkpatrick, J, Oakley, B, Fuchsman, C, Srinivasan, S, Staley, JT, Murray, JW (2006) Diversity and distribution of Planctomycetes and related Bacteria in the suboxic zone of the Black Sea. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 3079–3083
Koroleff, F (1983) Determination of nutrients. In: Grasshoff K (Ed.) Methods of Seawater Analysis. Verlag Chemie
Kuypers, MMM, Sliekers, AO, Lavik, G, Schmid, M, Jorgensen, BB, Kuenen, JG, Damste, JSS, Strous, M, Jetten, MSM (2003) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation by anammox bacteria in the Black Sea. Nature 422: 608–611
Kuypers, MMM, Lavik, G, Woebken, D, Schmid, M, Fuchs, BM, Amann, R, Jorgensen, BB, Jetten, MSM (2005) Massive nitrogen loss from the Benguela upwelling system through anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 6478–6483
Laima, MCJ (1994) Is KCl a reliable extractant of \( ^{{{\text{15}}}} {\text{NH}}^{ + }_{4} \) added to coastal marine sediments? Biogeochemistry 27: 83–95
Li, L, Kato, C, Horikoshi, K (1999) Bacterial diversity in deep-sea sediments from different depths. Biodivers Conserv 8: 659–677
Liesack, W, Stackebrandt, E (1992) Occurrence of novel groups of the domain Bacteria as revealed by analysis of genetic material isolated from an Australian terrestrial environment. J Bacteriol 174: 5072–5078
Luther, GW, Sundby, B, Lewis, BL, Brendel, PJ, Silverberg, N (1997) Interactions of manganese with the nitrogen cycle: alternative pathways to dinitrogen. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 61: 4043–4052
Meyer, RL, Risgaard-Petersen, N, Allen, DE (2005) Correlation between anammox activity and microscale distribution of nitrite in a subtropical mangrove sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 6142–6149
Mulder, A, van de Graaf, AA, Robertson, LA, Kuenen, JG (1995) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation discovered in a denitrifying fluidized-bed reactor. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 16: 177–183
Neef, A, Amann, R, Schlesner, H, Schleifer, K (1998) Monitoring a widespread bacterial group: in situ detection of planctomycetes with 16S rRNA-targeted probes. Microbiology 144: 3257–3266
Penton, CR, Devol, AH, Tiedje, JM (2006) Molecular evidence for the broad distribution of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria in freshwater and marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 6829–6832
Richards, FA (1965) Anoxic basins and fjords. In: Riley JP, Skirrow G (Eds.) Chemical Oceanography. Academic Press, vol 1, pp 611–645
Risgaard-Petersen, N, Meyer, RL, Schmid, M, Jetten, MSM, Enrich-Prast, A, Rysgaard, S, Revsbech, NP (2004) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in an estuarine sediment. Aquat Microb Ecol 36: 293–304
Risgaard-Petersen, N, Meyer, RL, Revsbech, NP (2005) Denitrification and anaerobic ammonium oxidation in sediments: effects of microphytobenthos and \( {\text{NO}}^{ - }_{3} \). Aquat Microb Ecol 40: 67–76
Rysgaard, S, Thastum, P, Dalsgaard, T, Christensen, PB, Sloth, NP (1999) Effects of salinity on \( {\text{NH}}^{ + }_{4} \) adsorption capacity, nitrification, and denitrification in Danish estuarine sediments. Estuaries 22: 21–30
Rysgaard, S, Glud, RN, Risgaard-Petersen, N, Dalsgaard, T (2004) Denitrification and anammox activity in Arctic marine sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 49: 1493–1502
Schmid, M, Twachtmann, U, Klein, M, Strous, M, Juretschko, S, Jetten, M, Metzger, JW, Schleifer, KH, Wagner, M (2000) Molecular evidence for genus level diversity of bacteria capable of catalyzing anaerobic ammonium oxidation. Syst Appl Microbiol 23: 93–106
Schmid, M, Schmitz-Esser, S, Jetten, M, Wagner, M (2001) 16S-23S rDNA intergenic spacer and 23S rDNA of anaerobic ammonium-oxidizing bacteria: implications for phylogeny and in situ detection. Environ Microbiol 3: 450–459
Schmid, M, Walsh, K, Webb, R, Rijpstra, WIC, van de Pas-Schoonen, K, Verbruggen, MJ, Hill, T, Moffett, B, Fuerst, J, Schouten, S, Damste, JSS, Harris, J, Shaw, P, Jetten, M, Strous, M (2003) Candidatus “Scalindua brodae”, sp nov., Candidatus “Scalindua wagneri”, sp nov., two new species of anaerobic ammonium oxidizing bacteria. Syst Appl Microbiol 26: 529–538
Schubert, CJ, Durisch-Kaiser, E, Wehrli, B, Thamdrup, B, Lam, P, Kuypers, M (2006) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in a tropical freshwater system (Lake Tanganyika). Environ Microbiol DOI 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2006.001074.x
Strickland, JD, Parsons, TR (1972) A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Fish Res Board Can 167: 1–311
Strous, M, Fuerst, JA, Kramer, EHM, Logemann, S, Muyzer, G, van de Pas-Schoonen, KT, Webb, R, Kuenen, JG, Jetten, MSM (1999) Missing lithotroph identified as new planctomycete. Nature 400: 446–449
Strous, M (2006) Deciphering the evolution and metabolism of an anammox bacterium from a community genome. Nature 440: 790–794
Swofford, DL (2002) PAUP*: Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony, Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Tal, Y, Watts, JEM, Schreier, HJ (2005) Anaerobic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and related activity in Baltimore inner Harbor sediment. Appl Environ Microbiol 71: 1816–1821
Tal, Y, Watts, JEM, Schreier, HJ (2006) Characterization and abundance of anaerobic ammonia oxidizing (anammox) bacteria in biofilters of recirculating aquaculture systems. Appl Environ Microbiol 72: 2896–2904
Thamdrup, B, Dalsgaard, T (2000) The fate of ammonium in anoxic manganese oxide-rich marine sediment. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 64: 4157–4164
Thamdrup, B, Dalsgaard, T (2002) Production of N2 through anaerobic ammonium oxidation coupled to nitrate reduction in marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 68: 1312–1318
Thamdrup, B, Dalsgaard, T, Jensen, MM, Ulloa, O, Farias, L, Escribano, R (2006) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation in the oxygen-deficient waters off northern Chile. Limnol Oceanogr 51: 2145–2156
Trimmer, M, Nicholls, JC, Deflandre, B (2003) Anaerobic ammonium oxidation measured in sediments along the Thames estuary, United Kingdom. Appl Environ Microbiol 69: 6447–6454
Trimmer, M, Risgaard-Petersen, N, Nicholls, JC, Engström, P (2006) Direct measurement of anaerobic ammonium oxidation (anammox) and denitrification in intact sediment cores. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 326: 37–47
van de Graaf, AA, Mulder, A, Debruijn, P, Jetten, MSM, Robertson, LA, Kuenen, JG (1995) Anaerobic oxidation of ammonium is a biologically mediated process. Appl Environ Microbiol 61: 1246–1251
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the NSF Microbial Biology Fellowship program (DBI-0301308 to JJR) and the NSF Biocomplexity program (OCE 99-81482 to BBW). We thank the Biocomplexity team for shiptime, supplying some of the nutrient data, and assistance, particularly J. Alexander, J. Cornwell, and M. Owens. We are also indebted to D. A. Bronk, R. Mason, and T. Jordan for shiptime; T. Jordan provided nutrient data for the Patuxent River, as well. We thank T. Dalsgaard, N. Risgaard-Petersen, L. Nielsen, B. Thamdrup, M. Jensen, J. Nicholls, C. Davies, and M. Trimmer for methodological advice and helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rich, J.J., Dale, O.R., Song, B. et al. Anaerobic Ammonium Oxidation (Anammox) in Chesapeake Bay Sediments. Microb Ecol 55, 311–320 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-007-9277-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-007-9277-3