Abstract
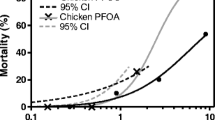
We examined the sensitivity of the wood duck (Aix sponsa) embryo to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) by injecting the toxicant into their eggs. Six groups of wood duck eggs (n = 35 to 211 per trial) were injected with 0 to 4600 pg TCDD/g egg between 2003 and 2005. Injections were made into yolk prior to incubation, and eggs were subsequently incubated and assessed weekly for mortality. Significant TCDD-induced mortality was not observed through day 25 (90% of incubation). Liver, heart, eye, and brain histology were generally unremarkable. Hepatic ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase activity, a biomarker of dioxin-like compound exposure, was induced by 12-fold in the 4600 pg/g treatment relative to controls. The median lethal dose for chicken (Gallus domesticus) eggs we dosed identically to wood duck eggs was about 100 pg/g, similar to other assessments of chickens. Among dioxin-like compound embryo lethality data for 15 avian genera, the wood duck 4600 pg/g no-observed-effect level ranks near the middle. Because no higher doses were tested, wood ducks may be like other waterfowl (order Anseriformes), which are comparatively tolerant to embryo mortality from polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans when exposed by egg injection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allred PM, Strange JR (1977) The effects of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on developing chicken embryos. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 5:483–489
Augspurger TP (2006) The wood duck (Aix sponsa) as a sentinel of exposure to and effects of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans at contaminated sites. PhD dissertation, Nicholas School of the Environment and Earth Sciences, Graduate School, Duke University, Durham, NC
Augspurger TP, Echols KR, Peterman PH, May TW, Tillitt DE, Di Giulio RT (2008) Accumulation of environmental contaminants in wood duck (Aix sponsa) eggs with emphasis on polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and polychlorinated dibenzofurans. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol (this issue). doi:10.1007/s00244-008-9199-1
Beeman DK (1996) The hepatic cytochrome P450-associated monooxygenase activities of wood ducks (Aix sponsa) as biomarkers of PCDD/PCDF exposure: a laboratory and field study. PhD dissertation, North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Beeman DK, Augspurger T (1996) Dioxins and furans in wood duck eggs from the lower Roanoke River, North Carolina. U.S. fish and wildlife service report No. 94-4N38. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Raleigh, NC
Blankenship AL, Hilscherova K, Nie M, Coady KK, Villalobos SA, Kannan K, Powell DC, Bursian SJ, Giesy JP (2003) Mechanisms of TCDD-induced abnormalities and embryo lethality in white leghorn chickens. Comp Biochem Physiol C 136:47–62
Bosveld ATC, Van den Berg M (1994) Effects of polychlorinated biphenyls, dibenzo-p-dioxins, and dibenzofurans on fish-eating birds. Environ Rev 2:147–166
Bosveld ATC, Kennedy SW, Seinen W, Van den Berg M (1997) Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase (EROD) inducing potencies of planar chlorinated hydrocarbons in primary cultures of hepatocytes from different developmental stages of the chicken. Arch Toxicol 71:746–750
Brunström B (1988) Sensitivity of embryos from duck, goose, herring gull, and various chicken breeds to 3,3′, 4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl. Poult Sci 67:52–57
Brunström B, Halldin K (1998) EROD induction by environmental contaminants in avian embryo livers. Comp Biochem Physiol C 121:213–219
Brunström B, Lund J (1988) Differences between chick and turkey embryos in sensitivity to 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl and in concentration / affinity of the hepatic receptor for 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Comp Biochem Physiol C 91:507–512
Brunström B, Reutergårdh L (1986) Differences in sensitivity of some avian species to the toxicity of a PCB, 3,3′, 4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl, injected into their eggs. Environ Pollut A 42:37–45
Carvalho PS, Tillitt DE (2004) 2,3,7,8-TCDD effects on visual structure and function in swim-up rainbow trout. Environ Sci Technol 38:6300–6306
Cheung MO, Gilbert EF, Peterson RE (1981) Cardiovascular teratogenicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the chick embryo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 61:197–204
Custer TW, Custer CM, Hines RK (2002) Dioxins and congener-specific polychlorinated biphenyls in three avian species from the Wisconsin River, Wisconsin. Environ Pollut 119:323–332
Custer CM, Custer TW, Rosiu CJ, Melancon MJ, Bickham JW, Matson CW (2005) Exposure and effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in tree swallows (Tachycineta bicolor) nesting along the Woonasquatucket River, Rhode Island, USA. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:93–109
de Roode DF, van den Brink NW (2002) Uptake of injected PCBs from the yolk by the developing chicken embryo. Chemosphere 48:195–199
de Roode DF, Balk L, Koeman JH, Bosveld ATC (2000) Development of a bioassay to test the possible role of thiamine disturbance as a mechanism behind pollution-induced reproductive failures in birds. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:386–391
DeWitt JC, Meyer EB, Henshel DS (2005a) Environmental toxicity studies using chickens as surrogates for wildlife: effects of vehicle volume. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:260–269
DeWitt JC, Meyer EB, Henshel DS (2005b) Environmental toxicity studies using chickens as surrogates for wildlife: effects of injection day. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 48:270–277
DeWitt JC, Millsap DS, Yeager RL, Heise SS, Sparks DW, Henshel DS (2006) External heart deformities in passerine birds exposed to environmental mixtures of polychlorinated biphenyls during development. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:541–550
Doty HA (1972) Hatchability tests with eggs from captive wood ducks. Poult Sci 51:849–853
Fernie KJ, Smits JE, Bortolotti GR, Bird DM (2001) In ovo exposure to polychlorinated biphenyls: reproductive effects on second-generation American kestrels. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 40:544–550
Gannon M, Gilday D, Rifkind AB (2000) TCDD induces CYP1A4 and CYP1A5 in chick liver and kidney and only CYP1A4, an enzyme lacking arachidonic acid epoxygenase activity, in myocardium and vascular endothelium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 164:24–37
Giesy JP, Ludwig JP, Tillitt DE (1994) Deformities in birds of the Great Lakes region: assigning causality. Environ Sci Technol 28:128A–135A
Gilday D, Gannon M, Yutzey K, Bader D, Rifkind AB (1996) Molecular cloning and expression of two novel avian cytochrome P450 1A enzymes induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. J Biol Chem 271:33054–33059
Gilday D, Bellward GD, Sanderson JT, Janz DM, Rifkind AB (1998) 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) induces hepatic cytochrome P450-dependent arachidonic acid epoxygenation in diverse avian orders: regioisomer selectivity and immunochemical comparison of the TCDD-induced P450s to CYP1A4and 1A5. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 150:106–116
Grasman KA, Fox GA, Scanlon PF, Ludwig JP (1996) Organochlorine-associated immunosuppression in prefledgling Caspian terns and herring gulls from the Great Lakes: an ecoepidemiological study. Environ Health Perspect 104(Suppl 4):829–842
Grasman KA, Scanlon PF, Fox GA (1998) Reproductive and physiological effects of environmental contaminants in fish-eating birds of the Great Lakes: a review of historical trends. Environ Monit Assess 53:117–145
Head J (2006) Variation in the cytochrome P4501A response to dioxin-like compounds in avian species. Thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy. Ottawa-Carleton Institute of Biology, University of Ottawa
Head JA, Kennedy SW (2007) Differential expression, induction, and stability of CYP1A4 and CYP1A5 mRNA in chicken and herring gull embryo hepatocytes. Comp Biochem Physiol C 145:617–624
Heinz G (2003) The use of egg injections to rank the sensitivities of avian embryos to methylmercury. CALFED Bay-Delta project final progress report. USGS Patuxent Wildlife Research Center, Laurel, MD
Heinz GH, Hoffman DJ, Kondrad SL, Erwin CA (2006) Factors affecting the toxicity of methylmercury injected into eggs. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:264–279
Henny CJ, Grove RA, Bentley VR (2000) Effects of selenium, mercury, and boron on waterbird egg hatchability at Stillwater, Malheur, Seedskadee, Ouray, and Benton Lake national wildlife refuges and surrounding vicinities. National irrigation water quality program information report No. 5. Bureau of Reclamation, Denver, CO
Henshel DS, Hehn B, Wagey R, Vo M, Steeves JD (1997) The relative sensitivity of chicken embryos to yolk- or air-cell-injected 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:725–732
Hoffman DJ, Melancon MJ, Eismann JD, Klein PN (1995) Comparative toxicity of planar PCB congeners by egg injection. Abstracts: 16th annual meeting of the society of environmental toxicology and chemistry. Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, p 207
Hoffman DJ, Rice CP, Kubiak TJ (1996) PCBs and dioxins in birds. In: Beyer WN, Heinz GH, Redmon-Norwood AW (eds) Environmental contaminants in wildlife: interpreting tissue concentrations. Lewis, Boca Raton, FL, pp 165–207
Hoffman DJ, Melancon MJ, Klein PN, Eismann JD, Spann JW (1998) Comparative developmental toxicity of planar polychlorinated biphenyl congeners in chickens, American kestrels, and common terns. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:747–757
Hornung MW, Miller L, Goodman B, Melancon MJ, Peterson RE (1998) Lack of developmental and reproductive toxicity of 2,3,3′,4,4′-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 105) in ring-necked pheasants. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 35:646–653
Janz DM, Bellward GD (1996) In ovo 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure in three avian species. 1. Effects on thyroid hormones and growth during the perinatal period. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 139:281–291
Jin X, Kennedy SW, Di Muccio T, Moon TW (2001) Role of oxidative stress and antioxidant defense in 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl-induced toxicity and species-differential sensitivity in chicken and duck embryos. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 172:241–248
Karchner SI, Franks DG, Kennedy SW, Hahn ME (2006) The molecular basis for differential dioxin sensitivity in birds: role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:6252–6257
Kennedy SW, Lorenzen A, James CA, Collins BT (1993) Ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase and porphyrin analysis in chicken embryo hepatocyte cultures with a fluorescence multiwell plate reader. Anal Biochem 211:102–112
Kennedy SW, Lorenzen A, Jones SP, Hahn ME, Stegeman JJ (1996) Cytochrome P4501A induction in avian hepatocyte cultures: a promising approach for predicting the sensitivity of avian species to toxic effects of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 141:214–230
Kubiak TJ, Harris HJ, Smith LM, Schwartz TR, Stalling DL, Trick JA, Sileo L, Docherty DE, Erdman TC (1989) Microcontaminants and reproductive impairment of the Forster’s tern on Green Bay, Lake Michigan—1983. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 18:706–727
Lavoie ET, Grasman KA (2007) Effects of in ovo exposure to PCBs 126 and 77 on mortality, deformities and post-hatch immune function in chickens. J Toxicol Environ Health A 70:547–558
Lim J, DeWitt JC, Sanders RA, Watkins JBIII, Henshel DS (2007) Suppression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced oxidative stress in chicken liver during development. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 52:590–595
Maervoet J, Beck V, Roelens SA, Covaci A, Voorspoels S, Geuns JMC, Darras VM, Schepens P (2005) Uptake and tissue-specific distribution of selected polychlorinated biphenyls in developing chicken embryos. Environ Toxicol Chem 24:597–602
McCarty JP, Secord AL (1999) Nest-building behavior in PCB-contaminated tree swallows. Auk 116:55–63
McKernan M, Rattner B, Hale B, Ottinger M (2007) Egg incubation position affects toxicity of air cell administered polychlorinated biphenyl 126 (3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl) in chicken (Gallus gallus) embryos. Environ Toxicol Chem 26:2724–2727
Meyer JM, Nacci DE, Di Giulio RT (2002) Cytochrome P4501A (CYP1A) in killifish (Fundulus heteroclitus): heritability of altered expression and relationship to survival in contaminated sediments. Toxicol Sci 68:69–81
Nosek JA, Sullivan JR, Craven SR, Gendron-Fitzpatrick A, Peterson RE (1993) Embryotoxicity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in the ring-necked pheasant. Environ Toxicol Chem 12:1215–1222
Powell DC, Aulerich RJ, Meadows JC, Tillitt DE, Giesy JP, Stromborg KL, Bursian SJ (1996) Effects of 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 126) and 2, 3, 7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) injected into the yolks of chicken (Gallus domesticus) eggs prior to incubation. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 31:404–409
Powell DC, Aulerich RJ, Meadows JC, Tillitt DE, Powell JF, Restum JC, Stromborg KL, Giesy JP, Bursian SJ (1997) Effects of 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl (PCB 126), 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD), or an extract derived from field-collected cormorant eggs injected into double-crested cormorant (Phalacrocorax auritus) eggs. Environ Toxicol Chem 16:1450–1455
Powell DC, Aulerich RJ, Meadows JC, Tillitt DE, Kelly ME, Stromborg KL, Melancon MJ, Fitzgerald SD, Bursian SJ (1998) Effects of 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl and 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin injected into the yolks of double-crested cormorants (Phalacrocorax auritus) eggs prior to incubation. Environ Toxicol Chem 17:2035–2040
Rice CP, O’Keefe P, Kubiak T (2003) Sources, pathways, and effects of PCBs, dioxins, and dibenzofurans. In: Hoffman DJ, Rattner BA, Burton GA Jr, Cairns J Jr (eds) Handbook of ecotoxicology, 2nd edn. Lewis, Boca Raton, FL, pp 501–574
Roelens SA, Beck V, Maervoet J, Aerts G, Reyns GE, Schepens P, Darras DM (2005) The dioxin-like PCB 77 but not the ortho-substituted PCB 153 interferes with chicken embryo thyroid hormone homeostasis and delays hatching. Gen Comp Endocrinol 143:1–9
Saita E, Hayama S, Kajigaya H, Yoneda K, Watanabe G, Taya K (2004) Histologic changes in thyroid glands from great cormorant (Phalacrocorax carbo) in Tokyo Bay, Japan: possible association with environmental contaminants. J Wildlife Dis 40:763–768
Sanderson JT, Bellward GD (1995) Hepatic microsomal ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase-inducing potency in ovo and cytosolic Ah receptor binding affinity of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin: comparison of four avian species. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 132:131–145
Summer CL, Giesy JP, Bursian SJ, Render JA, Kubiak TJ, Jones PD, Verbrugge DA, Aulerich RJ (1996) Effects induced by feeding organochlorine-contaminated carp from Saginaw Bay, Lake Huron, to laying white Leghorn hens. II. Embryotoxic and teratogenic effects. J Toxicol Environ Health 49:409–438
Suter GWII, Traas TP, Posthuma L (2002) Issues and practices in the derivation and use of species sensitivity distributions. In: Posthuma L, Suter GWII, Traas TP (eds) Species sensitivity distributions in ecotoxicology. Lewis, Boca Raton, FL, pp 437–474
Thiel DA, Martin SG, Duncan JW, Lemke MJ, Lance WR, Peterson RE (1989) Evaluation of the effects of dioxin-contaminated sludges on wild birds. Proceedings 1988 technical association of pulp and paper environmental conference, Charleston, SC, USA, April 18–20, pp 145–158
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (2003) Analyses of laboratory and field studies of reproductive toxicity in birds exposed to dioxin-like compounds for use in ecological risk assessment. NCEA-CIN-1337. Office of Research and Development. National Center for Environmental Assessment, Cincinnati, OH
Van den Berg M, Birnbaum L, Bosveld ATC, Brunström B, Cook P, Feeley M, Giesy JP, Hanberg A, Hasegawa R, Kennedy SW, Kubiak T, Larsen JC, Rolaf van Leeuwem FX, Djien Liem AK, Nolt C, Peterson RE, Poellinger L, Safe S, Schrenk D, Tillitt D, Tysklind M, Younes M, Waern F, Zacharewski T (1998) Toxic equivalency factors (TEFs) for PCBs, PCDDs, PCDFs for humans and wildlife. Environ Health Perspect 106:775–792
Van den Hurk P, Wiley FE, Lavoie ET, Grasman KA, Bowerman WW (2007) Activity patterns of biotransformation enzymes in juvenile chickens after in ovo dosage of PCB126. Comp Biochem Physiol C 146:301–307
Volz DC, Bencic DC, Hinton DE, Law JM, Kullman SW (2005) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD) induces organ- specific differential gene expression in male Japanese medaka (Oryzias latipes). Toxicol Sci 85:572–584
Walker MK, Catron TF (2000) Characterization of cardiotoxicity induced by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related chemicals during early chick embryo development. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 167:210–221
Walker MK, Heid SE, Smith SM, Swanson HI (2000) Molecular characterization and developmental expression of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor from the chick embryo. Comp Biochem Physiol C 126:305–319
White DH, Hoffman DJ (1995) Effects of polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans on nesting wood ducks (Aix sponsa) at Bayou Meto, Arkansas. Environ Health Perspect 103:37–39
Zhao F, Mayura K, Kocurek N (1997) Inhibition of 3,3′,4,4′,5-pentachlorobiphenyl-induced chicken embryotoxicity by 2,2′,4,4′5,5′-hexachlorobiphenyl. Fundam Appl Toxicol 35:1–8
Acknowledgments
We thank Gary Heinz for help with data analyses. Mike and Ali Lubbock (Sylvan Heights Waterfowl), Bernie Good, Holliday Obrecht, and Frank McGilvery assisted in egg collections. Dosing solutions were prepared by Diane Nicks and John Meadows. Matti Kiupel coordinated histology. Assistance with biochemical assays and image analyses was offered by Deena Wassenberg, Ron Hardman, Jeff Whyte, and Mandy Annis. Sara Ward assisted in the field and lab. Lab space was loaned by Greg Cope, Randy Rose, and Frank Edens. Funding was provided through USFWS’s Environmental Contaminants Program (Study ID No. 200240001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Augspurger, T.P., Tillitt, D.E., Bursian, S.J. et al. Embryo Toxicity of 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-Dioxin to the Wood Duck (Aix sponsa). Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 55, 659–669 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9198-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00244-008-9198-2