Abstract
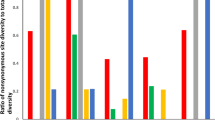
The prion diseases, such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease of humans and bovine spongiform encephalopathy, involve the aberrant metabolism and accumulation of prion protein PrP. There are three contradictory hypotheses about evolution of prion protein gene PRNP. Population genetic studies have proposed that PRNP could be under balancing selection, strong purifying selection, or mainly positive selection. We made use of the maximum likelihood tests for detection of positive selection at the amino acid level and present availability of PRNP coding sequences to contribute to these disagreements. Positive selection could occur at amino acids residing in active sites, and at amino acids involved in protein-protein interactions. Thus we tested a hypothesis that positive selection at the amino acid level in PrP might have taken place in human and related species from the superordinal group Euarchonta, as well as in bovine and related species from the superordinal clade Laurasiatheria. Our study and the present experimental evidences indicate that positive selection at the amino acid level might have taken place in the PrP signal sequences and conformationally plastic PrP regions, as well as at the protein X binding sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anisimova M, Yang Z (2007) Multiple hypothesis testing to detect lineages under positive selection that affects only a few sites. Mol Biol Evol 24:1219–1228
Anisimova M, Bielawski JP, Yang Z (2002) Accuracy and power of bayes prediction of amino acid sites under positive selection. Mol Biol Evol 19:950–958
Kaneko K, Zulianello L, Scott M, Cooper CM, Wallace AC, James TL, Cohen FE, Prusiner SB (1997) Evidence for protein X binding to a discontinuous epitope on the cellular prion protein during scrapie prion propagation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:10069–10074
Kreitman M, Di Rienzo A (2004) Balancing claims for balancing selection. Trends Genet 20:300–304
Mead S, Stumpf MP, Whitfield J, Beck JA, Poulter M, Campbell T, Uphill JB, Goldstein D, Alpers M, Fisher EM, Collinge J (2003) Balancing selection at the prion protein gene consistent with prehistoric kurulike epidemics. Science 300:640–643
Murphy WJ, Eizirik E, Johnson WE, Zhang YP, Ryder OA, O’Brien SJ (2001) Molecular phylogenetics and the origins of placental mammals. Nature 409:614–618
Perrier V, Kaneko K, Safar J, Vergara J, Tremblay P, DeArmond SJ, Cohen FE, Prusiner SB, Wallace AC (2002) Dominant-negative inhibition of prion replication in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13079–13084
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13363–13383
Schatzl HM, Da Costa M, Taylor L, Cohen FE, Prusiner SB (1995) Prion protein gene variation among primates. J Mol Biol 245:362–374
Seabury CM, Honeycutt RL, Rooney AP, Halbert ND, Derr JN (2004) Prion protein gene (PRNP) variants and evidence for strong purifying selection in functionally important regions of bovine exon 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15142–15147
Soldevila M, Andrés AM, Ramírez-Soriano A, Marquès-Bonet T, Calafell F, Navarro A, Bertranpetit J (2006) The prion protein gene in humans revisited: lessons from a worldwide resequencing study. Genome Res 16:231–239
van Rheede T, Smolenaars MM, Madsen O, de Jong WW (2003) Molecular evolution of the mammalian prion protein. Mol Biol Evol 20:111–121
Wong WS, Yang Z, Goldman N, Nielsen R (2004) Accuracy and power of statistical methods for detecting adaptive evolution in protein coding sequences and for identifying positively selected sites. Genetics 168:1041–1051
Acknowledgments
The calculations were carried out in the cluster Isabella, under the Sun Grid Engine software. MP would like to dedicate this work to the memory of Vera.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Prof. Vera Gamulin passed away.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Additional data file 1
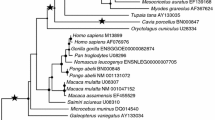
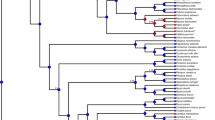
PRNP phylogenies. The ML phylogenetic trees of the Euarchonta (a) and Laurasiatheria (b) PRNPs were determined using PHYLIP using default settings (http://evolution.genetics.washington.edu/phylip/doc/main.html). We used these topologies for our ML tests for detection of positive selection at the amino acid level. Branch lengths were estimated using the M0 model (number of nucleotide substitutions per codon) (Wong et al. 2004). The foreground branches are indicated. PRNP GenBank accession numbers: Bos taurus AJ298878, Camelus dromedarius Y09760, Canis familiaris DQ444488, Cynocephalus variegatus AY133034, Diceros bicornis AY133052, Equus caballus AY133051, Erinaceus europaeus BN001181, Homo sapiens M13899, Macaca mulatta U08307, Manis sp. AY133050, Microcebus murinus DQ014540, Myotis lucifugus BN000992, Pongo pygmaeus abelii EMBL acc. number BN000848, Pteropus vampyrus BN000994, Saimiri sciureus U08310, Sorex araneus BN001182, Sus scrofa L07623, Talpa europaea AY133042, Tupaia tana AY133035. We annotated the E. europaeus and S. araneus PRNP coding sequences as the third party annotations and submitted them to EBI (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/embl/). (Eps 286 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Premzl, M., Gamulin, V. Positive Selection in Prion Protein. J Mol Evol 68, 205–207 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-008-9176-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-008-9176-3