Abstract
Introduction
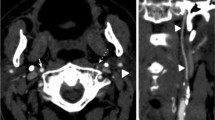
Novel postprocessing techniques have enabled accurate quantification of intracranial carotid atherosclerotic disease on CT Angiography (CTA). Our purpose was to estimate the prevalence of intracranial carotid artery disease, i.e., stenosis and calcium, on CTA in patients with recent neurological symptoms.
Methods
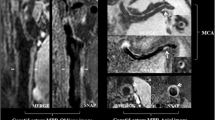
The degree of stenosis and calcium volume of 162 extracranial and intracranial internal carotid arteries (ICAs) was quantitatively measured on CTA images of 88 consecutive patients with recent neurological symptoms and extracranial ICA stenosis as screened by ultrasound. The prevalence of intracranial ICA stenosis and presence of calcium was estimated and correlated with extracranial ICA stenosis.
Results
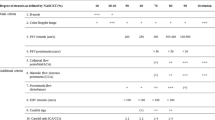
Intracranial ICA stenosis was observed in 83 % (95 %CI: 77–89 %) and 39 % (95 %CI: 31–47 %) for a stenosis of ≥30 % and ≥50 %, respectively. Only on the symptomatic side, a statistical significant correlation between intracranial and extracranial stenoses was observed (Pearson's r 0.32, P = 0.006). In the 37 arteries with an extracranial ICA stenosis of ≥70 %, 89 % (95 %CI: 79–99 %) and 46 % (95 %CI: 30–62 %) of the intracranial ICA showed a stenosis of ≥30 % and ≥50 %, respectively.
Conclusion
In our population of patients with recent neurological symptoms and extracranial stenosis as screened by ultrasound, CTA imaging resulted in a substantially higher prevalence of intracranial ICA disease than previously reported. This remarkably high prevalence of intracranial ICA disease on CTA may have important future implications for acute and preventive treatment strategies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett HJ, Taylor DW, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Ferguson GG, Haynes RB, Rankin RN, Clagett GP, Hachinski VC, Sackett DL, Thorpe KE, Meldrum HE, Spence JD (1998) Benefit of carotid endarterectomy in patients with symptomatic moderate or severe stenosis. North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. N Engl J Med 339:1415–1425
Bartlett ES, Walters TD, Symons SP, Aviv RI, Fox AJ (2008) Classification of carotid stenosis by millimeter CT angiography measures: effects of prevalence and gender. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1677–1683
Bash S, Villablanca JP, Jahan R, Duckwiler G, Tillis M, Kidwell C, Saver J, Sayre J (2005) Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusive disease: evaluation with CT angiography, MR angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1012–1021
Bleeker L, Marquering HA, van den Berg R, Nederkoorn PJ, Majoie CB (2012) Semi-automatic quantitative measurements of intracranial internal carotid artery stenosis and calcification using CT angiography. Neuroradiology
Bos D, van der Rijk MJ, Geeraedts TE, Hofman A, Krestin GP, Witteman JC, van der Lugt A, Ikram MA, Vernooij MW (2012) Intracranial carotid artery atherosclerosis: prevalence and risk factors in the general population. Stroke
Bouthillier A, van Loveren HR, Keller JT (1996) Segments of the internal carotid artery: a new classification. Neurosurgery 38:425–432, discussion 432–423
Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H, Stern BJ, Hertzberg VS, Frankel MR, Levine SR, Chaturvedi S, Kasner SE, Benesch CG, Sila CA, Jovin TG, Romano JG (2005) Comparison of warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med 352:1305–1316
de Weert TT, Cakir H, Rozie S, Cretier S, Meijering E, Dippel DW, van der Lugt A (2009) Intracranial internal carotid artery calcifications: association with vascular risk factors and ischemic cerebrovascular disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:177–184
Hass WK, Fields WS, North RR, Kircheff II, Chase NE, Bauer RB (1968) Joint study of extracranial arterial occlusion. II. Arteriography, techniques, sites, and complications. JAMA 203:961–968
Homburg PJ, Plas GJ, Rozie S, van der Lugt A, Dippel DW (2011) Prevalence and calcification of intracranial arterial stenotic lesions as assessed with multidetector computed tomography angiography. Stroke 42:1244–1250
Hong NR, Seo HS, Lee YH, Kim JH, Seol HY, Lee NJ, Suh SI (2010) The correlation between carotid siphon calcification and lacunar infarction. Neuroradiology
Kappelle LJ, Eliasziw M, Fox AJ, Sharpe BL, Barnett HJ (1999) Importance of intracranial atherosclerotic disease in patients with symptomatic stenosis of the internal carotid artery. The North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trail. Stroke 30:282–286
Luebke T, Aleksic M, Brunkwall J (2007) Meta-analysis of randomized trials comparing carotid endarterectomy and endovascular treatment. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 34:470–479
McKinney AM, Casey SO, Teksam M, Lucato LT, Smith M, Truwit CL, Kieffer S (2005) Carotid bifurcation calcium and correlation with percent stenosis of the internal carotid artery on CT angiography. Neuroradiology 47:1–9
Nguyen-Huynh MN, Wintermark M, English J, Lam J, Vittinghoff E, Smith WS, Johnston SC (2008) How accurate is CT angiography in evaluating intracranial atherosclerotic disease? Stroke 39:1184–1188
Ptak T, Hunter GH, Avakian R, Novelline RA (2003) Clinical significance of cavernous carotid calcifications encountered on head computed tomography scans performed on patients seen in the emergency department. J Comput Assist Tomogr 27:505–509
Samuels OB, Joseph GJ, Lynn MJ, Smith HA, Chimowitz MI (2000) A standardized method for measuring intracranial arterial stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:643–646
Takeuchi S, Karino T (2010) Flow patterns and distributions of fluid velocity and wall shear stress in the human internal carotid and middle cerebral arteries. World Neurosurg 73:174–185, discussion e127
Taoka T, Iwasaki S, Nakagawa H, Sakamoto M, Fukusumi A, Takayama K, Wada T, Myochin K, Hirohashi S, Kichikawa K (2006) Evaluation of arteriosclerotic changes in the intracranial carotid artery using the calcium score obtained on plain cranial computed tomography scan: correlation with angiographic changes and clinical outcome. J Comput Assist Tomogr 30:624–628
Willis BH (2008) Spectrum bias—why clinicians need to be cautious when applying diagnostic test studies. Fam Pract 25:390–396
Wong KS, Ng PW, Tang A, Liu R, Yeung V, Tomlinson B (2007) Prevalence of asymptomatic intracranial atherosclerosis in high-risk patients. Neurology 68:2035–2038
Woodcock RJ Jr, Goldstein JH, Kallmes DF, Cloft HJ, Phillips CD (1999) Angiographic correlation of CT calcification in the carotid siphon. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:495–499
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marquering, H.A., Nederkoorn, P.J., Bleeker, L. et al. Intracranial carotid artery disease in patients with recent neurological symptoms: high prevalence on CTA. Neuroradiology 55, 179–185 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1097-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-012-1097-6