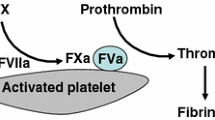
Abstract
Recombinant activated coagulation factor VII (rFVIIa) was developed for the treatment of patients with hemophilia who have developed inhibitors against the factor they are missing. Hemophilia is a serious bleeding disorder and patients with hemophilia develop repeated spontaneous CNS, joint and muscle bleeding. Any trauma, even mild events, may cause life-threatening bleeding, and without treatment, these patients have a life expectancy of about 16 years. Thus, hemophilia can be regarded as a model of severe bleeding, and an agent capable of inducing hemostasis in severe hemophilia independent of the hemophilia proteins (FVIII or FIX) may also be effective in patients without hemophilia who experience serious bleeds. The availability of rFVIIa stimulated research on the role of FVII and tissue factor (TF) in the hemostatic process. As a result, a picture partly different from the one suggested by previous models [1, 2] has emerged. These previous models basically neglected the role of cells and cell membranes. The importance of platelets and platelet membrane phospholipids in hemostasis has been demonstrated, and the new concept of the hemostatic process, focusing on cell surfaces, has been outlined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davie EW, Ratnoff O (1964) Waterfall sequence for intrinsic blood clotting. Science 145:1310–1312
MacFarlane RG (1964) An enzyme cascade in the blood clotting mechanism, and its function as a biochemical amplifier. Nature 202:498–499
Rapaport SI, Rao LV (1992) Initiation and regulation of tissue factor-dependent blood coagulation. Arterioscler Thromb 12:1111–1121
Wildgoose P, Nemerson Y, Hansen LL, Nielsen EE, Glazer S, Hedner U (1992) Measurement of basal levels of factor VIIa in hemophilia A and B patients. Blood 80:25–28
Hedner U, Erhardtsen E (2003) Potential role of recombinant factor VIIa as a hemostatic agent. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol 1:112–119
Chen VM, Ahamed J, Versteeg HH, Berndt MC, Ruf W, Hogg PJ (2006) Evidence for activation of tissue factor by an allosteric disulfide bond. Biochemistry 45:12020–12028
Pendurthi UR, Ghosh S, Mandal S, Rao LVM (2006) Tissue factor activation: is disulfide switching a general regulatory mechanism? Blood (ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts) 108: Abstract 1747
Mandal SK, Pendurthi UR, Rao LVM (2007) Tissue factor trafficking in fibroblasts: involvement of protease activated receptor-mediated cell signaling. Blood. DOI 10.1182/blood-2006-10-050476
Konkle B, Friedrich U, Abrams Z (2006) Secondary prophylactic treatment with rFVIIa in patients with haemophilia A or B and inhibitors with high requirements for on-demand treatment. Poster presentation at the World Fed Haemophilia, Vancouver, Canada, May 2006. Haemophilia 12: Abstract 14 PO 363
Hedner U (2006) Potential role of recombinant factor FVIIa in prophylaxis in severe hemophilia patients with inhibitors. J Thromb Haemost 4:2498–2500
Bevers EM, Comfurius P, Zwaal RF (1991) Platelet procoagulant activity: physiological significance and mechanisms of exposure. Blood Rev 5:146–154
Monroe DM, Roberts HR, Hoffman M (1994) Platelet procoagulant complex assembly in a tissue factor-initiated system. Br J Haematol 88:364–371
Monroe DM, Hoffman M, Olivier JA, Roberts HR (1997) Platelet activity of high-dose factor VIIa is independent of tissue factor. Br J Haematol 99:642–647
Walsh PN (2004) Platelet coagulation-protein interactions. Semin Thromb Hemost 30:461–471
Monroe DM, Hoffman M, Roberts HR (2002) Platelets and thrombin generation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:1381–1389
Hedner U (2006) Mechanism of action, development and clinical experience of recombinant FVIIa. J Biotechnol 124:747–757
He S, Jacobsson Ekman G, Hedner U (2005) The effect of platelets on fibrin gel structure formed in the presence of recombinant factor VIIa in hemophilia plasma and in plasma from a patient with Glanzmann thrombasthenia. J Thromb Haemost 3:272–279
Galán AM, Tonda R, Pino M, Reverter JC, Ordinas A, Escolar G (2003) Increased local procoagulant action: a mechanism contributing to the favorable hemostatic effect of recombinant FVIIa in PLT disorders. Transfusion 43:885–891
Kenet G, Walden R, Eldad A, Martinowitz U (1999) Treatment of traumatic bleeding with recombinant factor VIIa. Lancet 354:1879
Martinowitz U, Kenet G, Lubetski A, Luboshitz J, Segal E (2002) Possible role of recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa) in the control of hemorrhage associated with massive trauma. Can J Anaesth 49:S15–S20
Martinowitz U, Michaelson M; The Israeli Multidisciplinary rFVIIa Task Force (2005) Guidelines for the use of recombinant activated factor VII (rFVIIa) in uncontrolled bleeding: a report by the Israeli Multidisciplinary rFVIIa Task Force. J Thromb Haemost 3:640–648
Segal S, Shemesh IY, Blumental R, Yoffe B, Laufer N, Mankuta D, Mazor M, Zohar S, Schiff E, Martinovitz U (2004) The use of recombinant factor VIIa in severe postpartum hemorrhage. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 83:771–772
Grounds M (1995) Recombinant factor VIIa (rfVIIa) and its use in severe bleeding in surgery and trauma: a review. Blood Rev 17:S11–S21
Eikelboom JW, Bird R, Blythe D, Coyle L, Gan E, Harvey M, Isbister J, Leahy M, McIlroy D, Rahimpanah F, Ramanthan S, Strasser S, Ward C, Watts A, Towler S, Yi Q (2003) Recombinant activated factor VII for the treatment of life-threatening haemorrhage. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 14:713–717
Ahonen J, Jokela R (2005) Recombinant factor VIIa for life-threatening post-partum haemorrhage. Br J Anaesth 94:592–595
Boffard KD, Riou B, Warren B, Choong PI, Rizoli S, Rossaint R, Axelsen M, Kluger Y; NovoSeven Trauma Study Group (2005) Recombinant factor VIIa as adjunctive therapy for bleeding control in severely injured trauma patients: two parallel randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials. J Trauma 59:8–18
Friederich PW, Henny CP, Messelink EJ, Geerdink MG, Keller T, Kurth KH, Büller HR, Levi M (2003) Effect of recombinant activated factor VII on perioperative blood loss in patients undergoing retropubic prostatectomy: a double-blind placebo-controlled randomised trial. Lancet 361:201–205
Astrup T (1991) Fibrinolysis: past and present, a reflection of fifty years. Semin Thromb Hemost 17:161–174
Andersson L (1964) Antifibrinolytic treatment with epsilon-aminocaproic acid in connection with prostatectomy. Acta Chir Scand 127:552–564
Andersson L (1974) Local fibrinolysis. In: Nilsson IM (ed) Haemorrhagic and thrombotic diseases. John Wiley & Sons, London, pp 155–182
Mayer SA, Brun NC, Begtrup K, Broderick J, Davis S, Diringer MN, Skolnick BE, Steiner T; Recombinant Activated Factor VII Intracerebral Hemorrhage Trial Investigators (2005) Recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N Engl J Med 352:777–785
Counsell C, Boonyakarnkul S, Dennis M, et al (1955) Primary intracerebral haemorrhage in the Oxfordshire Community Stroke Project. 2. Prognosis. Cerebrovasc Dis 5:26–34
Steiner T, Kaste M, Forsting M, Mendelow D, Kwiecinski H, Szikora I, Juvela S, Marchel A, Chapot R, Cognard C, Unterberg A, Hacke W (2006) Recommendations for the management of intracranial haemorrhage - Part 1: Spontaneous Intracerebral Haemorrhage The European Stroke Initiative Writing Committee and the Writing Committee for the EUSI Executive Committee. Cerebrovasc Dis 22:294–316
Mendelow AD, Gregson BA, Fernandes HM, Murray GD, Teasdale GM, Hope DT, Karimi A, Shaw MD, Barer DH; STICH investigators (2005) Early surgery versus initial conservative treatment in patients with spontaneous supratentorial intracerebral haematomas in the International Surgical Trial in Intracerebral Haemorrhage (STICH): a randomised trial. Lancet 365:387–397
Lyden PD, Shuaib A, Lees KR, et al (2007) Final results of CHANT: a study of the safety and tolerability of NXY-059 in intracerebral hemorrhage (abstract). Stroke 38:475
Brott T, Broderick J, Kothari R, et al (1997) Early hemorrhage growth in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 28:1–5
Davis SM, Broderick J, Hennerici M, Brun NC, Diringer MN, Mayer SA, Begtrup K, Steiner T; Recombinant Activated Factor VII Intracerebral Hemorrhage Trial Investigators (2006) Hematoma growth is a determinant of mortality and poor outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 66(8):1175–1181
Broderick JP, Diringer MN, Hill MD, Brun NC, Mayer SA, Steiner T, Skolnick BE, Davis SM (2007) Determinants of intracerebral hemorrhage growth: an exploratory analysis. Stroke 38:1072–1075
Steiner T, Diringer MN, Schneider D, Mayer SA, Begtrup K, Broderick J, Skolnick B, Davis SM (2006) Dynamics of intraventricular hemorrhage in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: risk factors, clinical impact, and effect of hemostatic therapy, with recombinant activated factor VII. Neurosurgery 59(4):767–773
Rice KM, Savidge GF (1996) Recombinant factor VIIa (r-FVIIa) in haemophilia management. Transfus Sci 17(3):339–340
Arkin S, Cooper HA, Hutter JJ, Miller S, Schmidt ML, Seibel NL, Shapiro A, Warrier I (1998) Activated recombinant human coagulation factor VII therapy for intracranial hemorrhage in patients with hemophilia A or B inhibitors. Results of the NovoSeven emergency-use program. Haemostasis 28:93–98
Mayer SA, Brun N, Broderick J, et al (2005) Safety and feasibility of recombinant factor VIIa for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 36:74–79
Mayer SA, Brun NC, Broderick J, Davis SM, Diringer MN, Skolnick BE, Steiner T; United States NovoSeven ICH Trial Investigators (2006) Recombinant activated factor VII for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. US phase IIa trial. Neurocrit Care 4:206–214
Conflict of interest statement
We are both employed by Novo Nordisk A/S, the manufacturer of rFVIIa (NovoSeven).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This paper is one of a series of invited reviews.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hedner, U., Brun, N.C. Recombinant factor VIIa (rFVIIa): its potential role as a hemostatic agent. Neuroradiology 49, 789–793 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0240-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0240-2