Abstract
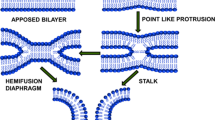
The main steps of viral membrane fusion are local membrane approach, hemifusion, pore formation, and pore enlargement. Experiments and theoretical analyses have helped determine the relative energies required for each step. Key protein structures and conformational changes of the fusion process have been identified. The physical deformations of monolayer bending and lipid tilt have been applied to the steps of membrane fusion. Experiment and theory converge to strongly indicate that, contrary to former conceptions, the fusion process is progressively more energetically difficult: hemifusion has a relatively low energy barrier, pore formation is more energy-consuming, and pore enlargement is the most difficult to achieve.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.G. Abrahamyan R.M. Markosyan F.S. Moore J.P. Cohen G.B. Melikyan (2003) ArticleTitleHuman immunodeficiency virus type 1 Env with an intersubunit disulfide bond engages coreceptors but requires bond reduction after engagement to induce fusion J. Virol 77 5829–5836 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.77.10.5829-5836.2003 Occurrence Handle12719576
R.T. Armstrong A.S. Kushnir J.M. White (2000) ArticleTitleThe transmembrane domain of influenza hemagglutinin exhibits a stringent length requirement to support the hemifusion to fusion transition J. Cell Biol 151 425–438 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.151.2.425 Occurrence Handle11038188
A.L. Barnett R.A. Davey J.M. Cunningham (2001) ArticleTitleModular organization of the Friend murine leukemia virus envelope protein underlies the mechanism of infection Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 4113–4118 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.071432398 Occurrence Handle11274436
J. Bentz A. Mittal (2003) ArticleTitleArchitecture of the influenza hemagglutinin membrane fusion site Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1614 24–35 Occurrence Handle12873763
E. Borrego-Diaz M.E. Peeples R.M. Markosyan G.B. Melikyan F.S. Cohen (2003) ArticleTitleCompletion of trimeric hairpin formation of influenza virus hemagglutinin promotes fusion pore opening and enlargement Virology 316 234–244 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.virol.2003.07.006 Occurrence Handle14644606
S. Bressanelli K. Stiasny S.L. Allison E.A. Stura S. Duquerroy J. Lescar F.X. Heinz F.A. Rey (2004) ArticleTitleStructure of a flavivirus envelope glycoprotein in its low-pH-induced membrane fusion conformation EMBO J. 23 728–738 Occurrence Handle10.1038/sj.emboj.7600064 Occurrence Handle14963486
P.A. Bullough F.M. Hughson J.J. Skehel D.C. Wiley (1994) ArticleTitleStructure of influenza haemagglutinin at the pH of membrane fusion Nature 371 37–43 Occurrence Handle10.1038/371037a0 Occurrence Handle8072525
J. Cao L. Bergeron E. Helseth M. Thali H. Repke J. Sodoroski (1993) ArticleTitleEffects of amino acid changes in the extracellular domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 envelope glycoprotein J. Virol 67 2747–2755 Occurrence Handle8474172
C.M. Carr P.S. Kim (1993) ArticleTitleA spring-loaded mechanism for the conformational change of influenza hemagglutinin Cell 73 823–832 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0092-8674(93)90260-W Occurrence Handle8500173
A. Chanturiya L.V. Chernomordik J. Zimmerberg (1997) ArticleTitleFlickering fusion pores comparable with initial exocytotic pores occur in protein-free phospholipid bilayers Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 94 14423–14428 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.94.26.14423 Occurrence Handle9405628
C.H. Chen T.J. Matthews C.B. McDanal M.L. Bolognesi D.P. Greenberg (1995) ArticleTitleA molecular clasp in the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) type 1 TM protein determines the anti-HIV activity of gp41 derivatives: implication for viral fusion J. Virol 69 3771–3777 Occurrence Handle7538176
J. Chen K.H. Lee D.A. Steinhauer D.J. Stevens J.J. Skehel D.C. Wiley (1998) ArticleTitleStructure of the hemagglutinin precursor cleavage site, a determinant of influenza pathogenicity and the origin of the labile conformation Cell 95 409–417 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81771-7 Occurrence Handle9814710
J. Chen J.J. Skehel D.C. Wiley (1999) ArticleTitleN- and C-terminal residues combine in the fusion-pH influenza hemagglutinin HA(2) subunit to form an N cap that terminates the triple- stranded coiled coil Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96 8967–8972 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.96.16.8967 Occurrence Handle10430879
J. Chen S.A. Wharton W. Weisshborn L.J. Calder F.M. Hughson J.J. Skehel D.C. Wiley (1995) ArticleTitleA soluble domain of the membrane-anchoring chain of influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA2) folds in Escherichia coli into the low-pH-induced conformation Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92 12205–12209 Occurrence Handle8618870
L. Chernomordik M.M. KozIov J. Zimmerberg (1995) ArticleTitleLipids in biological membrane fusion J. Membrane Biol 146 l–14 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00232676
L.V. Chernomordik V.A. Frolov E. Leikina P. Bronk J. Zimmerberg (1998) ArticleTitleThe pathway of membrane fusion catalyzed by influenza hemagglutinin: restriction of lipids, hemifusion, and lipidic fusion pore formation J.Cell Biol 140 1369–1382 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.140.6.1369 Occurrence Handle9508770
L.V. Chernomordik M.M. KozIov (2003) ArticleTitleProtein-lipid interplay in fusion and fission of biological membranes Annu Rev Biochem 72 175–207 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.biochem.72.121801.161504 Occurrence Handle14527322
L.V. Chernomordik G.B. Melikyan I.G. Abidor V.S. Markin Y.A. Chizmadzhev (1985) ArticleTitleThe shape of lipid molecules and monolayer membrane fusion Biochim. Biophys Acta. 812 643–655
L.V. Chernomordik S.I. Sukharev S.V. Popov V.F. Pastushenko A.V. Sokirko I.G. Abidor Y.A. Chizmadzhev (1987) ArticleTitleThe electrical breakdown of cell and lipid membranes: the similarity of phenomenologies Biochim. Biophys. Acta 902 360–373 Occurrence Handle3620466
Y.A. Chizmadzhev F.S. Cohen A. Shcherbakov J. Zimmerberg (1995) ArticleTitleMembrane mechanics can account for fusion pore dilation in stages Biophys. J. 69 2489–2500 Occurrence Handle8599655
Y.A. Chizmadzhev P.I. Kuzmin D.A. Kumenko J. Zimmerberg F.S. Cohen (2000) ArticleTitleDynamics of fusion pores connecting membranes of different tensions Biophys. J. 78 2241–2256 Occurrence Handle10777723
D.Z. Cleverley J. Lenard (1998) ArticleTitleThe transmembrane domain in viral fusion: essential role for a conserved glycine residue in vesicular stomatitis virus G protein Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 3425–3430 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.95.7.3425 Occurrence Handle9520382
F.S. Cohen R.M. Markosyan G.B. Melikyan (2002) ArticleTitleThe process of membrane fusion: nipples, hemifusion, pores, and pore growth Curr. Top. Membranes 52 501–529
F.S. Cohen G.B. Melikyan (1998) ArticleTitleMethodologies in the study of cell-cell fusion Methods 16 215–226 Occurrence Handle10.1006/meth.1998.0670 Occurrence Handle9790869
P.M. Colman M.C. Lawrence (2003) ArticleTitleThe structural biology of type I viral membrane fusion Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 4 309–319 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nrm1076 Occurrence Handle12671653
K.J. Cross S.A. Wharton J.J. Skehel D.C. Wiley D.A. Steinhauer (2001) ArticleTitleStudies on influenza haemagglutinin fusion peptide mutants generated by reverse genetics EMBO J. 20 4432–4442 Occurrence Handle10.1093/emboj/20.16.4432 Occurrence Handle11500371
J.W. Dubay S.J. Roberts B. Brody E. Hunter (1992) ArticleTitleMutations in the leucine zipper of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein affect fusion and infectivity J. Virol 66 4748–4756 Occurrence Handle1629954
S.R. Durell I. Martin M. Ruysschaert Y. Shai R. Blumenthal (1997) ArticleTitleWhat studies of fusion peptides tell us about viral envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion (review) Mol. Membr. Biol. 14 97–112 Occurrence Handle9394290
R.F. Epand J.C. Macosko C.J. Russel Y.K. Shin R.M. Epand (1999) ArticleTitleThe ectodomain of HA2 of influenza virus promotes rapid pH dependent membrane fusion J. Mol. Biol. 286 489–503 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jmbi.1998.2500 Occurrence Handle9973566
R.M. Epand R.F. Epand (2002) ArticleTitleThermal denaturation of influenza virus and its relationship to membrane fusion Biochem. J. 365 841–848 Occurrence Handle11994048
V. Frolov M. Cho T.S. Reese J. Zimmerberg (2000) ArticleTitleBoth hemifusion and fusion pores are induced by GPI-linked influenza hemagglutinin Traffic 1 622–630 Occurrence Handle10.1034/j.1600-0854.2000.010806.x Occurrence Handle11208150
N. Fuller R.P. Rand (2001) ArticleTitleThe influence of lysolipids on the spontaneous curvature and bending elasticity of phospholipid membranes Biophys. J. 81 243–254 Occurrence Handle11423410
D.L. Gibbons I. Erk B. Reilly J. Navaza M. Kielian F. Rey J. Lepault (2003) ArticleTitleVisualization of the target-membrane-inserted fusion protein of Semliki Forest virus by combined electron microscopy and crystallography Cell 114 573–583 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00683-4 Occurrence Handle13678581
D.L. Gibbons M.C. Vaney A. Roussel A. Vigouroux B. Reilly J. Lepault M. Kielian F.A. Rey (2004) ArticleTitleConformational change and protein-protein interactions of the fusion protein of Semliki Forest virus Nature 427 320–325 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature02239 Occurrence Handle14737160
H. Hamm M. Kozlov (2000) ArticleTitleElastic energy of tilt and bending of fluid membranes Eur. Phys. J. 3 323–335
M. Hamm M. Kozlov (1998) ArticleTitleTilt model of inverted amphipathic mesophases Eur. Phys. J.B 6 519–528
X. Han J.H. Bushweller D.S. Cafiso L.K. Tamm (2001) ArticleTitleMembrane structure and fusion-triggering conformational change of the fusion domain from influenza hemagglutinin Nature Strurt. Biol. 8 715–720 Occurrence Handle10.1038/90434
C. Harter P. James T. Bachi G. Semenza J. Brunner (1989) ArticleTitleHydrophobic binding of the ectodomain of influenza hemagglutinin to membranes occurs through the “fusion peptide” J. Biol. Chem. 264 6459–6464 Occurrence Handle2703499
C.A. Helm J.N. Israelachvilli P.M. McGuiggan (1992) ArticleTitleRole of hydrophobic forces in bilayer adhesion and fusion Biochemistry 31 1794–1805 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi00121a030 Occurrence Handle1737032
L.D. Hernandez L.R. Hoffman T.G. Wolfsberg J.M. White (1996) ArticleTitleVirus-cell and cell-cell fusion Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol. 12 627–661 Occurrence Handle8970739
C. Hu M. Ahmed T.J. Melia T.H. Sollner T. Mayer J.E. Rothman (2003) ArticleTitleFusion of cells by flipped SNAREs Science 300 1745–1749 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1084909 Occurrence Handle12805548
J. Israelachvili R. Pashley (1982) ArticleTitleThe hydrophobic interaction is long range, decaying exponentially with distance Nature 300 341–342 Occurrence Handle10.1038/300341a0 Occurrence Handle7144887
R. Jahn T. Lang T.C. Sudhof (2003) ArticleTitleMembrane fusion Cell 112 519–533 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(03)00112-0 Occurrence Handle12600315
I. Jelesarov M. Lu (2001) ArticleTitleThermodynamics of trimer-of-hairpins formation by the SIV gp41 envelope protein J. Mol. Biol. 307 637–656 Occurrence Handle10.1006/jmbi.2001.4469 Occurrence Handle11254387
H. Jin G.P. Leser R.A. Lamb (1994) ArticleTitleThe influenza virus hemagglutinin cytoplasmic tail is not essential for virus assembly or infectivity EMBO J. 13 5504–5515 Occurrence Handle7957116
G. Kemble T. Danieli J.M. White (1994) ArticleTitleLipid-anchored influenza hemagglutinin promotes hemifusion, not complete fusion Cell 76 383–391 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0092-8674(94)90344-1 Occurrence Handle8293471
G.W. Kemble Y.I. Henis J.M. White (1993) ArticleTitleGPI- and transmembrane-anchored influenza hemagglutinin differ in structure and receptor binding activity J. Cell. Biol. 122 1253–1265 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.122.6.1253 Occurrence Handle8397215
B. Kobe R.J. Center B.E. Kemp P. Poumbourios (1999) ArticleTitleCrystal structure of human T cell leukemia virus type 1 gp21 ectodomain crystallized as a maltose-binding protein chimera reveals structural evolution of retroviral transmembrane proteins Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96 4319–4324 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.96.8.4319 Occurrence Handle10200260
M.M. Kozlov V.S. Markin (1983) ArticleTitlePossible mechanism of membrane fusion Biofizika 28 255–261
Y. Kozlovsky L.V. Chernomordik M.M. Kozlov (2002) ArticleTitleLipid intermediates in membrane fusion: formation, structure, and decay of hemifusion diaphragm Biophys. J. 83 2634–2651 Occurrence Handle12414697
Y. Kozlovsky M.M. Kozlov (2002) ArticleTitleStalk model of membrane fusion: solution of energy crisis Biophys. J. 82 882–895 Occurrence Handle11806930
P.I. Kuzmin J. Zimmerberg Y.A. Chizmadzhev F.S. Cohen (2001) ArticleTitleA quantitative model for membrane fusion based on low-energy intermediates Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 7235–7240 Occurrence Handle10.1073/pnas.121191898 Occurrence Handle11404463
D. Leckband J. Israelachvili (2001) ArticleTitleIntermolecular forces in biology Q. Rev. Biophys. 34 105–267 Occurrence Handle11771120
J. Lee B.R. Lentz (1997) ArticleTitleEvolution of lipidic structures during model membrane fusion and the relation of this process to cell membrane fusion Biochemistry 36 6251–6259 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi970404c Occurrence Handle9174340
S. Leikin M.M. Kozlov N.L. Fuller R.P. Rand (1996) ArticleTitleMeasured effects of diacylglycerol on structural and elastic properties of phospholipid membranes Biophys. J. 71 2623–2632 Occurrence Handle8913600
S. Leikin V.A. Parsegian D.C Rau R.P Rand (1993) ArticleTitleHydration forces Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 44 369–395 Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.pc.44.100193.002101 Occurrence Handle8257560
S.L. Leikin M.M. Kozlov L.V. Chernomordik V.S. Markin Y.A. Chizmadzhev (1987) ArticleTitleMembrane fusion: overcoming of the hydration barrier and local restructuring J. Theor. Biol 129 411–425 Occurrence Handle3455469
E. Leikina D.L. LeDuc J.C. Macosko R. Epand Y.K. Shin L.V. Chernomordik (2001) ArticleTitleThe 1-127 HA2 construct of influenza virus hemagglutinin induces cell-cell hemifusion Biochemistry 40 8378–8386 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi010466+ Occurrence Handle11444985
Y. Li X. Han L.K. Tamm (2003) ArticleTitleThermodynamics of fusion peptide-membrane interactions Biochemistry 42 7245–7251 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi0341760 Occurrence Handle12795621
X. Lin C.A. Derdeyn R. Bluementhal J. West E. Hunter (2003) ArticleTitleProgressive truncations C terminal to the membrane-spanning domain of simian immunodeficiency virus Env reduce fusogenicity and increase concentration dependence of Env for fusion J. Virol 77 7067–7077 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.77.12.7067-7077.2003 Occurrence Handle12768026
M. Lindau W. Almers (1995) ArticleTitleStructure and function of fusion pores in exocytosis and ectoplasmic membrane fusion Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 7 509–517 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0955-0674(95)80007-7 Occurrence Handle7495570
M. Lu S.C. Blacklow P.S. Kim (1995) ArticleTitleA trimeric structural domain of the HIV-1 transmembrane glycoprotein Nat. Struct. Biol. 2 1075–1082 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nsb1295-1075 Occurrence Handle8846219
M. Lu H. Ji S. Shen (1999) ArticleTitleSubdomain folding and biological activity of the core structure from human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41: implications for viral membrane fusion J. Virol 73 4433–4438 Occurrence Handle10196341
M. Lu M.O. Stoller S. Wang J. Liu M.B. Fagan J.H. Numberg (2001) ArticleTitleStructural and functional analysis of interhelical interactions in the Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 gp41 envelope glycoprotein by alanine-scanning mutagenesis J. Virol 75 11146–11156 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.75.22.11146-11156.2001 Occurrence Handle11602754
V.S. Markin J.P. Albanesi (2002) ArticleTitleMembrane fusion: stalk model revisited Biophys. J. 82 693–712 Occurrence Handle11806912
V.S. Markin M.M. Kozlov V.L. Borovjagin (1984) ArticleTitleOn the theory of membrane fusion The stalk mechanism. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 3 361–377
R.M. Markosyan F.S. Cohen G.B. Melikyan (2000) ArticleTitleThe lipid-anchored ectodomain of influenza virus hemagglutinin (GPI-HA) is capable of inducing nonenlarging fusion pores Mol. Biol.Cell 11 1143–1152 Occurrence Handle10749920
R.M. Markosyan F.S. Cohen G.B. Melikyan (2003) ArticleTitleHIV-1 envelope proteins complete their folding into six-helix bundles immediately after fusion pore formation Mol. Biol. Cell 14 926–938 Occurrence Handle10.1091/mbc.E02-09-0573 Occurrence Handle12631714
R.M. Markosyan X. Ma M. Lu F.S. Cohen G.B. Melikyan (2002) ArticleTitleThe mechanism of inhibition of HIV-1 env-mediated cell-cell fusion by recombinant cores of gp41 ectodomain Virology 302 174–184 Occurrence Handle10.1006/viro.2002.1593 Occurrence Handle12429526
I. Markovic E. Leikina M. Zhukovsky J. Zimmerberg L.V. Chernomordik (2001) ArticleTitleSynchronized activation and refolding of influenza hemagglutinin in multimeric fusion machines J. Cell. Biol. 155 833–844 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.200103005 Occurrence Handle11724823
S. May (2002) ArticleTitleStructure and energy of fusion stalks: the role of membrane edges Biophys. J. 83 2969–2980 Occurrence Handle12496070
G.B. Melikyan S.A. Brener D.C. Ok F.S. Cohen (1997) ArticleTitleInner but not outer membrane leaflets control the transition from glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored influenza hemagglutinin-induced hemifusion to full fusion J. Cell. Biol. 136 995–1005 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.136.5.995 Occurrence Handle9060465
G.B. Melikyan H. Jin R.A. Lamb F.S. Cohen (1997) ArticleTitleThe role of the cytoplasmic tail region of influenza virus hemagglutinin in formation and growth of fusion pores Virology 235 118–128 Occurrence Handle10.1006/viro.1997.8686 Occurrence Handle9300043
G.B. Melikyan S. Lin M.G. Roth F.S. Cohen (1999) ArticleTitleAmino acid sequence requirements of the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains of influenza virus hemagglutinin for viable membrane fusion Mol. Biol. Cell 10 1821–1836 Occurrence Handle10359599
G.B. Melikyan R.M. Markosyan H. Hemmati M.K. Delmedico D.M Lambert F.S. Cohen (2000) ArticleTitleEvidence that the transition of HIV-1 gp41 into a six-helix bundle, not the bundle configuration, induces membrane fusion J. Cell. Biol. 151 413–424 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.151.2.413 Occurrence Handle11038187
G.B. Melikyan R.M. Markosyan M.G. Roth F.S. Cohen (2000) ArticleTitleA point mutation in the transmembrane domain of the hemagglutinin of influenza virus stabilizes a hemifusion intermediate that can transit to fusion Mol. Biol Cell 11 3765–3775 Occurrence Handle11071905
G.B. Melikyan J.M. White F.S. Cohen (1995) ArticleTitleGPI-anchored influenza hemagglutinin induces hemifusion to both red blood cell and planar bilayer membranes J. Cell 131 679–691 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.131.3.679
A. Mittal E. Leikina L.V. Chernomordik J. Bentz (2003) ArticleTitleKinetically differentiating influenza hemagglutinin fusion and hemifusion machines Biophys J. 85 1713–1724 Occurrence Handle12944286
Y. Modis S. Ogata D. Clements S.C. Harrison (2004) ArticleTitleStructure of the dengue virus envelope protein after membrane fusion Nature 427 313–319 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nature02165 Occurrence Handle14737159
M. Muller K. Katsov M. S chick (2003) ArticleTitleA new mechanism of model membrane fusion determined from Monte Carlo simulation Biophys. J. 85 1611–1623 Occurrence Handle12944277
I. Munoz-Barroso S. Durell K. Sakaguchi E. Appella R. Blumenthal (1998) ArticleTitleDilation of the human immunodeficiency virus- 1 envelope glycoprotein fusion pore revealed by the inhibitory action of a synthetic peptide from gp41 J. Cell. Biol. 140 315–323 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.140.2.315 Occurrence Handle9442107
I. Munoz-Barroso K. Salzwedel E. Hunter R. Blumenthal (1999) ArticleTitleRole of the membrane-proximal domain in the initial stages of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion J. Virol. 73 6089–6092 Occurrence Handle10364363
E. Neher (1974) ArticleTitleAsymmetric membranes resulting from the fusion of two black lipid bilayers Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 373 327–336 Occurrence Handle4139977
H. Noguchi M. Takasu (2001) ArticleTitleFusion pathways of vesicles: A Brownian dynamics simulation J. Chem. Phys. 115 9547–9551 Occurrence Handle10.1063/1.1414314
F. Nüssler M.J. Clague A. Herrmann (1997) ArticleTitleMeta-stability of the hemifusion intermediate induced by glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored influenza hemagglutinin Biophys. J. 173 2280–2291
D. Odell E. Wanas J. Yan H.P. Ghosh (1997) ArticleTitleInfluence of membrane anchoring and cytoplasmic domains on the fusogenic activity of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein G J. Virol. 71 7996–8000 Occurrence Handle9311894
C.C. Pak A. Puri R. Blumenthal (1997) ArticleTitleConformational changes and fusion activity of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: [125I] iodonaphthyl azide photolabeling studies in biological membranes Biochemistry 36 8890–8896 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi9702851 Occurrence Handle9220976
D.P. Pantazatos S.P. Pantazatos R.C. MacDonald (2003) ArticleTitleBilayer mixing, fusion, and lysis following the interaction of populations of cationic and anionic phospholipid bilayer vesicles J. Membrane Biol. 194 129–139 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s00232-003-2031-y
H.E. Park J.A. Gruenke J.M. White (2003) ArticleTitleLeash in the groove mechanism of membrane fusion Nat. Struct. Biol. 10 1048–1053 Occurrence Handle10.1038/nsb1012 Occurrence Handle14595397
V.A. Parsegian R.P. Rand D. Gingell (1984) ArticleTitleLessons for the study of membrane fusion from membrane interactions in phospholipid systems Ciba Found. Symp. 103 9–27 Occurrence Handle6561140
E.I. Pecheur D. Hoekstra J. Sainte-Marie L. Maurin A. Bienvenue J.R. Philippot (1997) ArticleTitleMembrane anchorage brings about fusogenic properties in a short synthetic peptide Biochemistry 36 3773–3781 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi9622128 Occurrence Handle9092806
H. Qiao R.T. Armstrong G.B. Melikyan F.S. Cohen J.M. White (1999) ArticleTitleA specific point mutant at position 1 of the influenza hemagglutinin fusion peptide displays a hemifusion phenotype Mol. Biol. Cell 10 2759–2769 Occurrence Handle10436026
D. Rapaport Y. Shai (1994) ArticleTitleInteraction of fluorescently labeled analogues of the amino-terminal fusion peptide of Sendai virus with phospholipid membranes J. Biol. Chem. 269 15124–15131 Occurrence Handle8195149
W. Rawicz K.C. Olbrich T. McIntosh D. Needham E. Evans (2000) ArticleTitleEffect of chain length and unsaturation on elasticity of lipid bilayers Biophys. J. 79 328–339 Occurrence Handle10866959
V. Razinkov G.B. Melikyan F.S. Cohen (1999) ArticleTitleHemifusion between cells expressing hemagglutinin (HA) of influenza virus and planar membranes can precede the formation of fusion pores that subsequently fully enlarge Biophys. J. 77 3144–3151 Occurrence Handle10585935
D.P. Remeta M. Krumbiegel C.A. Minetti A. Puri A. Ginsburg R. Blumenthal (2002) ArticleTitleAcid-induced changes in thermal stability and fusion activity of influenza hemagglutinin Biochemistry 41 2044–2054 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi015614a Occurrence Handle11827552
C.J. Russell T.S. Jardetzky R.A. Lamb (2001) ArticleTitleMembrane fusion machines of paramyxoviruses: capture of intermediates of fusion EMBO J. 20 4024–4034 Occurrence Handle10.1093/emboj/20.15.4024 Occurrence Handle11483506
K. Sackett Y. Shai (2003) ArticleTitleHow structure correlates to function for membrane associated HIV-1 gp41 constructs corresponding to the N-terminal half of the ectodomain J. Mol. Biol. 333 47–58 Occurrence Handle10.1016/j.jmb.2003.07.008 Occurrence Handle14516742
C. Schoch R. Blumenthal (1993) ArticleTitleRole of the fusion peptide sequence in initial stages of influenza hemagglutinin-induced cell fusion J. Biol. Chem. 268 9267–9274 Occurrence Handle8387488
M.P. Sheetz S.J. Singer (1974) ArticleTitleBiological membranes as bilayer couples A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 71 4457–4461
D.P. Siegel (1993) ArticleTitleEnergetics of intermediates in membrane fusion: comparison of stalk and inverted micellar intermediate mechanisms Biophys. J. 65 2124–2140 Occurrence Handle8298039
D.P. Siegel (1999) ArticleTitleThe modified stalk mechanism of lamellar/inverted phase transitions and its implications for membrane fusion Biophys. J. 76 291–313 Occurrence Handle9876142
J.J. Skehel D.C. Wiley (1998) ArticleTitleCoiled coils in both intracellular vesicle and viral membrane fusion Cell 95 871–874 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81710-9 Occurrence Handle9875840
T. Stegmann J.M. Delfino F.M. Richards A. Helenius (1991) ArticleTitleThe HA2 subunit of influenza hemagglutinin inserts into the target membrane prior to fusion J. Biol.Chem. 266 18404–18410 Occurrence Handle1917964
T. Stegmann R.W. Doms (1989) ArticleTitleProtein-mediated membrane fusion Annu, Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 18 187–211
J.A. Szule N.L. Fuller R.P. Rand (2002) ArticleTitleThe effects of acyl chain length and saturation of diacylglycerols and phosphatidylcholines on membrane monolayer curvature Biophys. J. 83 977–984 Occurrence Handle12124279
S.A. Tatulian P. Hinterdorfer G. Baber L.K. Tamm (1995) ArticleTitleInfluenza hemagglutinin assumes a tilted conformation during membrane fusion as determined by attenuated total reflection FTIR spectroscopy EMBO J. 14 5514–5523 Occurrence Handle8521808
G.M. Taylor D.A. Sanders (1999) ArticleTitleThe role of the membrane-spanning domain sequence in glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion Mol. Biol. Cell 10 2803–2815 Occurrence Handle10473628
F.W. Tse A. Iwata W. Almers (1993) ArticleTitleMembrane flux through the pore formed by a fusogenic viral envelope protein during cell fusion J. Cell Biol. 121 543–552 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.121.3.543 Occurrence Handle8486735
Y. Weng Z. Yang C.D. Weiss (2000) ArticleTitleStructure- function studies of the self-assembly domain of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transmembrane protein gp41 J. Virol. 74 5368–5372 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.74.11.5368-5372.2000 Occurrence Handle10799616
J.M. White I.A. Wilson (1987) ArticleTitleAnti-peptide antibodies detect steps in a protein conformational change: low-pH activation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin J. Cell. Biol. 105 2887–2896 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.105.6.2887 Occurrence Handle2447101
C.T. Wild D.C. Shugars T.K. Greenwell C.B. McDanal T.J. Matthews (1994) ArticleTitlePeptides corresponding to a predictive alpha-helical domain of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 gp41 are potent inhibitors of virus infection Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91 9770–9774 Occurrence Handle7937889
T. Wilk T. Pfeiffer A. Bukovsky G. Moldenhauer V. Bosch (1996) ArticleTitleGlycoprotein incorporation and HIV-1 infectivity despite exchange of the gp160 membrane-spanning domain Virology 218 269–274 Occurrence Handle10.1006/viro.1996.0190 Occurrence Handle8615034
I.A. Wilson J.J. Skehel D.C. Wiley (1981) ArticleTitleStructure of the haemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus at 3Å resolution Nature 289 366–373 Occurrence Handle10.1038/289366a0 Occurrence Handle7464906
L. Yang L. Ding H.W. Huang (2003) ArticleTitleNew phases of phospholipids and implications to the membrane fusion problem Biochemistry 42 6631–6635 Occurrence Handle10.1021/bi0344836 Occurrence Handle12779317
L. Yang H.W. Huang (2002) ArticleTitleObservation of a membrane fusion intermediate structure Science 297 1877–1879 Occurrence Handle10.1126/science.1074354 Occurrence Handle12228719
T. Zavorotinskaya Z. Qian J. Franks L.M. Albritton (2004) ArticleTitleA point mutation in the binding subunit of a retroviral envelope protein arrests virus entry at hemifusion J. Virol. 78 473–481 Occurrence Handle10.1128/JVI.78.1.473-481.2004 Occurrence Handle14671127
J. Zimmerberg R. Blumenthal D.P. Sarkar M. Curran S.J. Morris (1994) ArticleTitleRestricted movement of lipid and aqueous dyes through pores formed by influenza hemagglutinin during cell fusion J. Cell. Biol. 127 1885–1894 Occurrence Handle10.1083/jcb.127.6.1885 Occurrence Handle7806567
Acknowledgments
We thank Drs. Leonid Chernomordik, Yuri Chizmadzhev, Michael Kozlov, Peter Kuzmin, and Joshua Zimmerberg for discussions over many years on the theory of membrane mechanics and its application to membrane fusion. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants GM-27367 and GM-54787.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cohen, F., Melikyan, G. The Energetics of Membrane Fusion from Binding, through Hemifusion, Pore Formation, and Pore Enlargement. J Membrane Biol 199, 1–14 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-004-0669-8
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-004-0669-8