Abstract
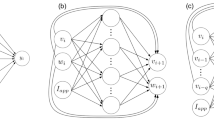
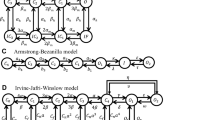
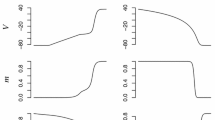
Nonequilibrium response spectroscopy (NRS), the technique of using rapidly fluctuating voltage pulses in the study of ion channels, is applied here. NRS is known to drive an ensemble of ion channels far from equilibrium where, it has been argued, new details of ion channel kinetics can be studied under nonequilibrium conditions. In this paper, a single-pulse NRS technique with custom-designed waveforms built from wavelets is used. The pulses are designed to produce different responses from two competing models of a human heart isoform of the sodium channel (hH1a). Experimental data using this new type of pulses are obtained through whole-cell recordings from mammalian cells (HEK 293). Wavelet analysis of the model response and the experimental data is introduced to show how these NRS pulses can aid in distinguishing the better of the two models and thus introduces another important application of this new technique.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hosein-Sooklal, A., Kargol, A. Wavelet Analysis of Nonequilibrium Ionic Currents in Human Heart Sodium Channel (hH1a). J. Membrane Biol. 188, 199–212 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-001-0188-9
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-001-0188-9