Abstract
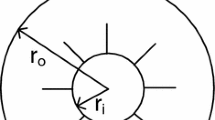
Laminar natural convection of Cu-water nano-fluid between two horizontal concentric cylinders with radial fins attached to the inner cylinder is studied numerically. The inner and outer cylinders are maintained at constant temperature. The governing equations in the polar two-dimensional space with the respective boundary conditions are solved using the finite volume method. The hybrid-scheme is used to discretize the convection terms. In order to couple the velocity field and the pressure in the momentum equations, the well known semi-implicit method for pressure linked equation reformed algorithm is adopted. Using the developed code, a parametric study is undertaken, and the effects of the Rayleigh number, Number of fins, length of the fins and the volume fraction of nano-particles on the fluid flow and heat transfer inside the annuli are investigated. In this study, two cases with different number of fins are considered. It is observed from the results that the average Nusselt number increases with increasing both the Rayleigh number and the volume fraction of the nano-particles. Moreover, the average Nusselt number decreases by increasing the fins’ length and the number of fins. Heat transfer rate increases by increasing the fins’ length at all Rayleigh numbers, but it increases by increasing the number of fins at high Rayleigh numbers.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- c p :
-
Specific heat (kJ kg−1 K−1)
- D :
-
Inner cylinder diameter
- g :
-
Gravitational acceleration (m s−2)
- h :
-
Heat transfer coefficient (W m−2 K−1)
- l :
-
Gap width between cylinders
- L :
-
Dimensionless length
- l fin :
-
Fin length
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- kr :
-
Ratio of fin conductivity to the conductivity of base fluid
- Nu :
-
Nusselt number
- p :
-
Pressure (Nm−2)
- P :
-
Dimensionless pressure
- Pr :
-
Prandtl number
- r :
-
Radial coordinate
- R :
-
Dimensionless radial distance
- Ra :
-
Rayleigh number
- T :
-
Temperature (K)
- \( \bar{T} \) :
-
Dimensionless temperature
- u, v :
-
Velocity components
- U, V :
-
Dimensionless velocity components
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- β :
-
Thermal expansion coefficient (K−1)
- φ :
-
Nano-particle volume fraction
- ν :
-
Kinematic viscosity (m2 s−1)
- θ :
-
Angle
- ψ :
-
Stream function (m2 s−1)
- Ψ :
-
Dimensionless stream function
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (N s m−2)
- Avg :
-
Average
- f :
-
Fluid
- i :
-
Inner
- nf :
-
Nano-fluid
- o :
-
Outer
References
Kuhen TH, Goldstein RJ (1976) An experimental and theoretical study of natural convection in the annulus between horizontal concentric cylinders. Fluid Mech J 74:695–719
Kuhen TH, Goldstein RJ (1978) An experimental study of natural convection heat transfer in concentric and eccentric horizontal cylindrical annuli. ASME J Heat Transf 100:635–640
Kumar R (1988) Study of natural convection in horizontal annuli. Int J Heat Mass Transf 31:1137–1148
Ho CJ, Li YH, Chen TC (1989) A numerical study of natural convection in concentric and eccentric horizontal cylindrical annuli with mixed boundary conditions. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 10:40–47
Yeh CL (2002) Numerical investigation of three-dimensional natural convection inside horizontal concentric annulus with specified wall temperature or heat flux convection in a horizontal annulus driven by inner heat generating solid cylinder. Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:775–784
Chai JC, Patankar SV (1993) Laminar natural convection in internally finned horizontal annulus. Numer Heat Transf 24:67–87
Rahnama M, Farhadi M (2004) Effect of radial fins on two-dimensional turbulent natural convection in a horizontal annulus. Int J Therm Sci 43:255–264
Maxwell JC (1873) Electricity and magnetism. Clarendon Press, Oxford, UK
Choi SUS (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluid with nanoparticles, developments and applications of non-Newtonian flow. ASME FED 231:99–105
Behzadmehr A, Saffar-Avval M, Galanis N (2007) Prediction of turbulent forced convection of a nanofluid in a tube with uniform heat flux using a two phase approach. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 28:211–219
Bianco V, Chiacchio F, Manca O, Nardini S (2009) Numerical investigation of nanofluids forced convection in circular tubes. J Appl Therm Eng 29:3632–3642
Santra AK, Sen S, Chakraborty N (2009) Study of heat transfer due to laminar flow of copper–water nanofluid through two isothermally heated parallel plates. Int J Therm Sci 48:391–400
Putra N, Roetzel W, Das SK (2003) Natural convection of nanofluids. Heat Mass Transf 39(8–9):775–784
Wen D, Ding Y (2005) Formulation of nanofluids for natural convective heat transfer applications. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 26(6):855–864
Jou RY, Tzeng SC (2006) Numerical research of nature convective heat transfer enhancement filled with nanofluids in rectangular enclosures. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 33:727–736
Ho CJ, Liu WK, Chang YS, Lin CC (2010) Natural convection heat transfer of alumina-water nanofluid in vertical square enclosures: an experimental study. Int J Therm Sci 49(8):1345–1353
Aminossadati SM, Ghasemi B (2011) Enhanced natural convection in an isosceles triangular enclosure filled with a nanofluid. Comput Math Appl 61(7):1739–1753
Cho CC, Chen CL, Chen CK (2012) Natural convection heat transfer performance in complex-wavy-wall enclosed cavity filled with nanofluid. Int J Therm Sci 60:255–263
Arefmanesh A, Amini M, Mahmoodi M, Najafi M (2012) Buoyancy-driven heat transfer analysis in two-square duct annuli filled with a nanofluid. Eur J Mech B Fluids 33:95–102
Mokhtari Moghari R, Akbarinia A, Shariat M, Talebi F, Laur R (2011) Two phase mixed convection Al2O3–water nanofluid flow in an annulus. Int J Multiph Flow 37(6):585–595
Parvin S, Nasrin R, Alim MA, Hossain NF, Chamkha AJ (2012) Thermal conductivity variation on natural convection flow of water–alumina nanofluid in an annulus. Int J Heat Mass Transf 55(19–20):5268–5274
Soleimani Sl, Sheikholeslami M, Ganji DD, Gorji-Bandpay M (2012) Natural convection heat transfer in a nanofluid filled semi-annulus enclosure. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 39(4):565–574
Abu-Nada E, Masoud Z, Hijazi A (2008) Natural convection heat transfer enhancement in horizontal concentric annuli using nanofluids. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf 35:657–665
Abu-Nada E (2009) Effect of variable viscosity and thermal conductivity of Al2O3-water nanofluid on heat transfer enhancement in natural convection. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 30:679–690
Incropera DP, Witt D (2005) Introduction to heat transfer, 3rd edn. Wiley, London
Kenjeres S, Hanjalic K (1995) Prediction of turbulent thermal convection in concentric and eccentric horizontal annuli. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 16:429–439
Acknowledgment
The authors wish to thank the Energy Research Institute of the University of Kashan for their support regarding this research (Grant No. 65473).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sheikhzadeh, G.A., Arbaban, M. & Mehrabian, M.A. Laminar natural convection of Cu-water nanofluid in concentric annuli with radial fins attached to the inner cylinder. Heat Mass Transfer 49, 391–403 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-012-1084-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-012-1084-9