Abstract
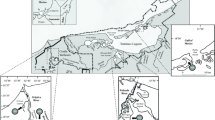
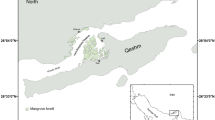
We used multiple stable-isotope analysis to investigate the importance of seagrasses, mangroves and other primary sources (macroalgae, seston) to the food webs supporting penaeid prawns in the Embley River estuary and adjacent off-shore waters in the north-eastern Gulf of Carpentaria, Australia. Mangroves, seagrass and macroalgae/seston were well separated on the basis of their δ13C values in both the dry and the wet seasons. In contrast, only macroalgae and seston (phytoplankton and zooplankton), which had similar δ13C values, were separated by their δ15N values. The primary source of carbon supporting food webs of several species of juvenile penaeid prawns clearly depended on the location within the estuary. The δ13C values of juvenile prawns (Penaeus esculentus, P. semisulcatus and Metapenaeus spp.) in seagrass beds were close to those of seagrass and seagrass epiphytes, particularly in the dry season. This was despite the proximity of the seagrass to mangroves and the presence of mangrove detritus in the seagrass beds. Juvenile prawns (P. merguiensis, P. semisulcatus, and Metapenaeus spp.) in an upstream mangrove creek had δ13C values that were midway between those of mangroves and seagrass, and close to those of macroalgae and seston during the dry season. Mangroves could have made a significant contribution to the carbon assimilated by juvenile prawns at this site, but only if it is assumed that the remainder of the carbon is ultimately derived from a seagrass source. The δ13C values of adults of three species of prawns in offshore waters were very similar and were much higher than those of mangroves. The considerable amount of mangrove/terrestrial carbon exported from tropical Australian estuaries during the wet season is therefore unlikely to contribute to offshore food webs supporting adult prawns. Furthermore, the contribution of mangrove/terrestrial sources to the food webs of juvenile prawns appears to be limited to a very small spatial scale – within the mangrove fringe of small creeks and mainly during the wet season.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 January 1997 / Accepted: 13 August 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Loneragan, N., Bunn, S. & Kellaway, D. Are mangroves and seagrasses sources of organic carbon for penaeid prawns in a tropical Australian estuary? A multiple stable-isotope study. Marine Biology 130, 289–300 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050248
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002270050248