Abstract
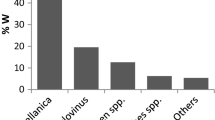
The feeding preferences of the coastal dolphins Pontoporia blainvillei and Sotalia guianensis in south-eastern Brazil (21º18′S–22º25′S) were assessed through the prey’s index of relative importance (IRI), total mercury concentration (Hgtot), and stable isotopic (δ15N and δ13C) to compare their efficiency in the discrimination of prey contribution to the predators’ diet. The IRI was the best tool to describe the dolphins’ preference, while Hgtot and δ15N seemed to be efficient as a trophic marker when the diet is made up of prey of varying sizes, as observed in S. guianensis. Both dolphins presented lighter δ15N than their prey species, which is an unusual pattern. However, as the sample size to isotope ratios analysis was small, especially to the dolphins, the results should be considered with caution, and further studies are necessary to corroborate these findings. The δ13C values characterized a typical coastal food chain, confirming the preferential area of these species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwell L, Hobson KA, Welch HE (1998) Biomagnification and bioaccumulation of mercury in an arctic marine food web: insights from stable nitrogen isotope analysis. Can J Fish Aq Sci 55:1114–1121
Bearhop S, Phillips RA, Thompson DR, Waldron S, Furnes RW (2000) Variability in mercury concentrations of great skuas Chataracta skua: the influence of colony, diet and trophic status inferred from stable isotope signatures. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 195:261–268
Capelli R, Drava G, De Pellegrini R, Minganti V, Poggi R (2000) Study of trace elements in organs and tissues of striped dolphins (Stenella coeruleoalba) found dead near the Ligurian Sea (Italy). Adv Environ Res 4:31–43
Capelli R, Das K, De Pellegrini R, Drava G, Lepoint G, Miglio C, Minganti V, Poggi R (2008) Distribution of trace elements in organs of six species of cetaceans from the Ligurian Sea (Mediterranean), and the relationship with stable carbon and nitrogen ratios. Sci Total Environ 390:569–578
Chen MH, Shih CC, Chou CL, Chou LS (2002) Mercury, organic-mercury and selenium in small cetaceans in Taiwanese waters. Mar Pollut Bull 45:237–245
Danilewicz D, Rosas F, Bastida R, Marijo J, Muelbert M, Rodríguez D, Lailson-Brito J Jr, Ruopollo V, Ramos R, Bassoi M, Ott PH, Caon G, Rocha AM, Catão-Dias JL, Secchi ER (2002) Report of the working group on biology and ecology. LAJAM Special Issue 1:25–42
Das K, Lepoint G, Loizeau V, Debacker V, Dauby P, Bouquegneau JM (2000) Tuna and dolphin associations in the North-East Atlantic: evidence of different ecological niches from stable isotope and heavy metal measurements. Mar Pollut Bull 40:102–109
Das K, Lepoint G, Leroy Y, Bouquegneau JM (2003a) Marine mammals from the southern North Sea: feeding ecology data from δ13C and δ15 N measurements. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 263:287–298
Das K, Beans C, Holsbeek L, Mauger G, Berrow SD, Rogan E (2003b) Marine mammals from northeast Atlantic: relationship between their trophic status as determined by δ13C and δ15 N measurements and their trace metal concentrations. Mar Environ Res 56:349–365
DeNiro MJ, Epstein S (1978) Influence of diet on the distribution of carbon isotopes in animals. Geoch Cosmochem Acta 42:495–506
Di Beneditto APM (2000) Ecologia alimentar de Pontoporia blainvillei e Sotalia fluviatilis (Cetacea) na costa norte do es-tado do Rio de Janeiro, Brasil. Thesis, Universidade Estadual do Norte Fluminense
Di Beneditto APM (2003) Interactions between gillnet fisheries and small cetaceans in northern Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: 2001–2002. LAJAM 2:79–86
Di Beneditto APM, Ramos RMA (2001) Biology and conservation of the franciscana (Pontoporia blainvillei) in the north of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. J Cetacean Res Manage 2:185–192
Di Beneditto APM, Ramos RMA (2004) Biology of the boto-cinza dolphin (Sotalia fluviatilis) in south-eastern Brazil. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 84:1245–1250
Di Beneditto APM, Siciliano S (2007) Stomach contents of the marine tucuxi dolphin (Sotalia guianensis) from Rio de Janeiro, south-eastern Brazil. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 87:253–254
Di Beneditto APM, Ramos RMA, Lima NRW (2001) Sightings of Pontoporia blainvillei (Gervais & D’Orbigny, 1844) and Sotalia fluviatilis (Gervais, 1853) (Cetacea) in South-eastern Brazil. Braz Arch Biol Tech 44:291–296
Di Beneditto APM, Santos MVB, Vidal MV Jr (2009) Comparison between the diet of two dolphins from south-eastern Brazil: proximate-composition and caloric value of prey species. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 89:903–905
Domi N, Bouquegneau K, Das K (2005) Feeding ecology of five commercial shark species of the Celtic Sea through stable isotope and trace metal analysis. Mar Environ Res 60:551–569
Endo T, Haraguchi K, Sakata M (2003) Renal toxicity in rats after oral administration of mercury contaminated boiled whale livers marketed for human consumption. Environ Contam Toxicol 44:412–416
Gray JS (2002) Biomagnification in marine systems: the perspective of an ecologist. Mar Pollut Bull 45:46–52
Hobson KA, Welch HE (1992) Determination of trophic relationships within a high Arctic food web using δ13C and δ15 N analysis. Mar Ecol Progs Ser 84:9–18
Hobson KA, Sease JL, Merrick RL, Piatt JF (1997) Investigating trophic relationships of pinnipeds in Alaska and Washington using stable isotopes ratios of nitrogen and carbon. Mar Mammal Sci 13:114–132
Hobson KA, Fisk A, Karnovsky N, Holst M, Gagnon J-M, Fortier M (2002) A stable isotope (d13C, d15 N) model for the North Water food web: implications for evaluating trophodynamics and the flow of energy and contaminants. Deep-Sea Res II 49:5131–5150
Instituto Brasileiro do Meio Ambiente e dos Recursos Naturais e Renováveis–IBAMA (2001) Mamíferos Aquáticos do Brasil. Plano de ação. Ed. Ministério do Meio Ambiente/IBAMA, Brasília
Jefferson TA, Leatherwood S, Webber MA (1993) FAO species identification guide: marine mammals of the world. Food and Agriculture Organization, Rome
Kehrig HA, Costa M, Moreira I, Malm O (2006) Total and methyl mercury in different species of mollusks from two estuaries in Rio de Janeiro State. J Braz Chem Soc 17:1409–1418
Kehrig HA, Fernandes KWG, Malm O, Seixas TG, Di Beneditto APM, Souza CMM (2009) Trophic transference of mercury and selenium in the Northern Coast of Rio de Janeiro. Quim Nova 32:1822–1828
Kiljunen M, Grey J, Sinisalo T, Harrod C, Immonen H, Jones RI (2006) A revised model for lipid-normalizing δ13C values from aquatic organisms, with implications for isotope mixing models. J Appl Ecol 43:1213–1222
Krishnan AA, Yousuf KS, Kumaran PL, Harish N, Anoop B, Afsal VV, Rajagopalan M, Vivekanandan E, Krishnakumar PK, Jayasankar P (2008) Stomach contents of cetaceans incidentally caught along Mangalore and Chennai coasts of India. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 76:909–913
Kurle CM, Worthy GAJ (2001) Stable isotope assessment of temporal and geographic differences in feeding ecology of northern fur seals (Callorhinus ursinus) and their prey. Oecologia 126:254–265
Lesage V, Hammil MO, Kovacs KM (2001) Marine mammals and the community structure of the Estuary and Gulf of St Lawrence, Canada: evidence from stable isotope analysis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 210:203–221
Loseto LL, Stern GA, Fergusson S (2008) Size and biomagnification: how habitat selection explains beluga mercury levels. Environ Sci Technol 42:3982–3988
Martins AS, Haimovici M, Palacios R (2005) Diet and feeding of the cutlassfish Trichiurus lepturus in the Subtropical Convergence Ecosystem of southern Brazil. J Mar Biol Assoc UK 85:1223–1229
Mason RP, Laporte JM, Andres S (2000) Factors controlling the bioaccumulation of mercury, methylmercury, arsenic, selenium and cadmium by freshwater invertebrates and fish. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 38:283–297
McCutchan JH Jr, Lewis WM, Kendall C, McGrath CC (2003) Variation in trophic shift for stable isotope ratios of carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur. Oikos 102:378–390
O’Shea TJ (1999) Environmental contaminants and marine mammals. In: Reynolds JE III, Rommel SA (eds) Biology of Marine Mammals, 1st edn. Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington, pp 485–563
Ohizumi H, Kuramochi T, Kubodera T, Yoshioka M, Miyazaki N (2003) Feeding habits of Dall’s porpoises (Phocoenoides dalli) in the subarctic North Pacific and the Bering Sea basin and the impact of predation on mesopelagic micronekton. Deep-Sea Res I 50:593–610
Parnell AC, Inger R, Bearhop S, Jackson AL (2010) Source partitioning using stable isotopes: coping with too much variation. PLoS ONE 5(3):e9672. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009672
Pauly D, Trites AW, Capuli E, Christensen V (1998) Diet composition and trophic levels of marine mammals. ICES J Mar Sci 55:467–481
Peterson BJ, Fry B (1987) Stable isotopes in ecosystem studies. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 18:293–320
Pierce GJ, Boyle PR (1991) A review of methods for diet analysis in piscivorous marine mammals. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 29:409–486
Pinkas L, Oliphant MS, Iverson IK (1971) Food habits of albacore, bluefin tuna and bonito in Californian waters. Calif Fish Game 152:1–105
Post DM, Layman CA, Arrington DA, Takimoto G, Quattrochi J, Montaña CG (2007) Getting to the fat of the matter: models, methods and assumptions for dealing with lipids in stable isotope analyses. Oecologia 152:179–189
Quinn MR, Feng X, Folt CL, Page Chamberlain C (2003) Analyzing trophic transfer of metal in stream food webs using nitrogen isotopes. Sci Total Environ 317:73–89
Ramos RMA (2001) Variação morfológica em Pontoporia blainvillei e Sotalia fluviatilis (Cetacea) no sudeste do Brasil. Thesis, Universidade Estadual do Norte Fluminense
Ruiz-Cooley RI, Gendron D, Aguíñiga S, Mesnick S, Carriquiry JD (2004) Trophic relationships between sperm whales and jumbo squid using stable isotopes of C and N. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 277:275–283
Santos MCO, Rosso S, Santos RA, Lucato SHB, Bassoi M (2002) Insights on small cetacean feeding habits in southeastern Brazil. Aquat Mamm 28:38–45
Siciliano S, Di Beneditto APM, Ramos RMA (2002) A toninha, Pontoporia blainvillei (Gervais & d’Orbigny, 1844) (Mammalia, Cetacea, Pontoporiidae), nos Estados do Rio de Janeiro e Espírito Santo, costa sudeste do Brasil: caracterização dos hábitats e possíveis fatores de isolamento das populações. Bol Mus Nac, N S, Zool 146:1–15
Siebert U, Joiris C, Holsbeek L, Benke H, Failing K, Frese K, Petzinger E (1999) Potential relation between mercury concentrations and necropsy findings in cetaceans from German waters of North and Baltic Seas. Mar Pollut Bull 38:285–295
Silva DS, Lucotte M, Roulet M, Poirier H (2005) Trophic structure and bioaccumulation of mercury in fish of three natural lakes of the Brazilian Amazon. Water Air Soil Poll 165:77–94
Sotiropoulos MA, Tonn WM, Wassenaar LI (2004) Effects of lipid extraction on stable carbon and nitrogen isotope analyses of fish tissues: potential consequences for food web studies. Ecol Freshw Fish 13:155–160
Sweeting CJ, Polunin NVC, Jennings S (2006) Effects of chemical lipid extraction and arithmetic lipid correction on stable isotope ratios of fish tissues. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 20:595–601
Watras CJ, Back RC, Halvorsen S, Hudson RJM, Morrison KA, Wentw SP (1998) Bioaccumulation of mercury in pelagic freshwater food webs. Sci Total Environ 219:183–208
Acknowledgments
We thank the fishermen from Atafona harbour and technician Silvana Ribeiro Gomes, who provided us with the dolphins and their prey specimens, Dra. Tércia Guedes Seixas, who conducted the total mercury analysis, the staff at the Centro de Energia Nuclear na Agricultura from Universidade de São Paulo—CENA/USP, who conducted the stable isotopes analysis, and Dr. Leandro Rabello Monteiro, who helped us with SIAR analysis. A.P.M. Di Beneditto was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico—CNPq (Proc. nº 300241/09-7) and Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro—FAPERJ (Proc. Nº E-26/103.038/08). This work was partially supported by CNPq INCT 573.601/08-9.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Harrod.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Di Beneditto, A.P.M., de Souza, C.M.M., Kehrig, H.A. et al. Use of multiple tools to assess the feeding preference of coastal dolphins. Mar Biol 158, 2209–2217 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1726-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00227-011-1726-3