Abstract
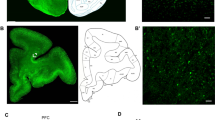
The posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) has recently been implicated in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia, through both animal and human studies. We have recently shown abnormal glutamate, GABA, and muscarinic receptor binding in the PCC in schizophrenia. In addition, there is evidence for an abnormal endogenous cannabinoid system in schizophrenia. The endogenous cannabinoid system, including CB1 receptors, is proposed to play a role in modulating neurotransmission via affecting the release of a variety of neurotransmitters, (e.g. GABA). In the present study, we used quantitative autoradiography to investigate the binding of [3H]CP-55940 to CB1 receptors in the PCC in schizophrenia subjects compared to controls. A significant 25% increase in CB1 binding was found in the superficial layers (layer I, II) of the PCC of schizophrenia subjects compared to controls, none of whom had recently used cannabis. There was no statistical difference in CB1 binding in the deeper layers (layers III–VI) between the two groups. There were no significant correlations between CB1 binding density and age, PMI, pH, brain weight, freezer storage time, or final recorded antipsychotic drug dose. These results show an increase in CB1 receptor density in the PCC in schizophrenia, and therefore provide support for a role of the endogenous cannabinoid system in schizophrenia.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameri A (1999) The effects of cannabinoids on the brain. Prog Neurobiol 58:315–348
Biegon A, Kerman IA (2001) Autoradiographic study of pre- and postnatal distribution of cannabinoid receptors in human brain. Neuroimage 14:1463–1468
Cloez-Tayarani I, Cardona A, Rousselle JC, Massot O, Edelman L, Fillion G (1997) Autoradiographic characterization of [3H]-5-HT-moduline binding sites in rodent brain and their relationship to 5-HT1B receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9899–9904
Dean B, Sundram S, Bradbury R, Scarr E, Copolov D (2001) Studies on [3H]CP-55940 binding in the human central nervous system: regional specific changes in density of cannabinoid-1 receptors associated with schizophrenia and cannabis use. Neuroscience 103:9–15
Felder CC, Veluz JS, Williams HL, Briley EM, Matsuda LA (1992) Cannabinoid agonists stimulate both receptor- and non-receptor-mediated signal transduction pathways in cells transfected with and expressing cannabinoid receptor clones (erratum appears in Mol Pharmacol 1994 Aug; 46(2):397). Mol Pharmacol 42:838–845
Glass M, Dragunow M, Faull RL (1997) Cannabinoid receptors in the human brain: a detailed anatomical and quantitative autoradiographic study in the fetal, neonatal and adult human brain. Neuroscience 77:299–318
Harper C, Garrick T, Matsumoto I, Pfefferbaum A, Adalsteinsson E, Sullivan E, Dodd P, Lewohl J, Butterworth R (2003) How important are brain banks for alcohol research? Alcoholism Clin Exp Res 27:310–323
Hartman M, Steketee MC, Silva S, Lanning K, McCann H (2003) Working memory and schizophrenia: evidence for slowed encoding. Schizophr Res 59:99–113
Haznedar MM, Buchsbaum MS, Hazlett EA, Shihabuddin L, New A, Siever LJ (2004) Cingulate gyrus volume and metabolism in the schizophrenia spectrum. Schizophr Res 71(2–3):249–262
Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Little MD, Johnson MR, Melvin LS, de Costa BR, Rice KC (1990) Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:1932–1936
Iversen L (2003) Cannabis and the brain. Brain 126:1252–1270
Katona I, Sperlagh B, Magloczky Z, Santha E, Kofalvi A, Czirjak S, Mackie K, Vizi ES, Freund TF (2000) GABAergic interneurons are the targets of cannabinoid actions in the human hippocampus. Neuroscience 100:797–804
Katona I, Sperlagh B, Sik A, Kafalvi A, Vizi ES, Mackie K, Freund TF (1999) Presynaptically located CB1 cannabinoid receptors regulate GABA release from axon terminals of specific hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci 19:4544–4558
Leweke FM, Giuffrida A, Wurster U, Emrich HM, Piomelli D (1999) Elevated endogenous cannabinoids in schizophrenia. Neuroreport 10:1665–1669
Mai J, Asscheuer J, Pazinos G (1997) Atlas of the Human Brain. Academic, San Diego
Newell KA, Zavitsanou K, Huang XF (2005) Ionotropic glutamate receptor binding in the posterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia patients. Neuroreport 16:1363–1367
Newell KA, Zavitsanou K, Kum Jew S, Huang XF (2006) Alterations of Muscarinic and GABA receptor binding in the posterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia. Prog Neuro-Psychoph (in press)
Olney JW, Farber NB (1995) Glutamate receptor dysfunction and schizophrenia (see comment). Arch Gen Psychiat 52:998–1007
Olney JW, Labruyere J, Price MT (1989) Pathological changes induced in cerebrocortical neurons by phencyclidine and related drugs (see comment). Science 244:1360–1362
Ong WY, Mackie K (1999) A light and electron microscopic study of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor in primate brain. Neuroscience 92:1177–1191
Pertwee RG (1999) Pharmacology of cannabinoid receptor ligands. Curr Med Chem 6:635–664
Reibaud M, Obinu MC, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Bohme GA, Imperato A (1999) Enhancement of memory in cannabinoid CB1 receptor knock-out mice. Eur J Pharmacol 379: R1–R2
Schlicker E, Kathmann M (2001) Modulation of transmitter release via presynaptic cannabinoid receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 22:565–572
Sharp FR, Butman M, Koistinaho J, Aardalen K, Nakki R, Massa SM, Swanson RA, Sagar SM (1994) Phencyclidine induction of the hsp 70 stress gene in injured pyramidal neurons is mediated via multiple receptors and voltage gated calcium channels. Neuroscience 62:1079–1092
Sundram S, Bradbury R, Copolov D, Dean B (2000) The effects of antipsychotic drug treatment on cannabinoid receptors in rat brain. In: Proceedings of the Australian neuroscience society, Melbourne, Australia, vol 11, p 75
Tendolkar I, Weis S, Guddat O, Fernandez G, Brockhaus-Dumke A, Specht K, Klosterkotter J, Reul J, Ruhrmann S (2004) Evidence for a dysfunctional retrosplenial cortex in patients with schizophrenia: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study with a semantic-perceptual contrast. Neurosci Lett 369:4–8
Tsou K, Brown S, Sanudo-Pena MC, Mackie K, Walker JM (1998) Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83:393–411
Vogt BA, Finch DM, Olson CR (1992) Functional heterogeneity in cingulate cortex: the anterior executive and posterior evaluative regions. Cereb Cortex 2:435–443
Vogt BA, Pandya DN, Rosene DL (1987) Cingulate cortex of the rhesus monkey: I. Cytoarchitecture and thalamic afferents. J Comp Neurol 262:256–270
Zavitsanou K, Garrick T, Huang XF (2004) Selective antagonist [3H]SR141716A binding to cannabinoid CB1 receptors is increased in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia. Prog Neuro-Psychoph 28:355–360
Zimmer A, Zimmer AM, Hohmann AG, Herkenham M, Bonner TI (1999) Increased mortality, hypoactivity, and hypoalgesia in cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice (see comment). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5780–5785
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the St. George Foundation, and the Neuroscience Institute of Schizophrenia and Allied Disorders (NISAD) utilizing infrastructure funding from NSW Health. Post-mortem brain tissues were received from the NSW Tissue Resource Center, which is supported by the University of Sydney, NISAD, National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and NSW Department of Health. The Beta Imager was provided with funds raised by the Wollongong Lord Mayor’s Schizophrenia Awareness Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Newell, K.A., Deng, C. & Huang, XF. Increased cannabinoid receptor density in the posterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia. Exp Brain Res 172, 556–560 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0503-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0503-x