Abstract.
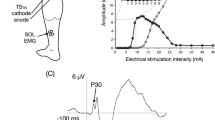
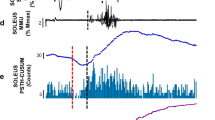
The present study was designed to examine the effects of median nerve stimulation on motoneurones of remote muscles in healthy subjects using H-reflex, averaged EMG and PSTH methods. Stimulation of the median nerve induced facilitation of soleus H-reflex from about 50 ms and it reached a peak at about 100 ms of conditioning-test interval. Afferents that induced the facilitation consisted of at least two types of fibres, the high-threshold cutaneous fibres and the low-threshold fibres. When the effects were examined by the averaged surface EMG and PSTH, no facilitation but rather inhibition or inhibition-facilitation was induced in all tested muscles except for the upper limb muscles on the stimulated side. The inhibition latency was shortest in masseter muscle and longest in leg muscles, while values for the contralateral upper limb muscles were in the middle, indicating that the onset of inhibition was delayed from rostral to caudal muscles. Inputs from the median nerve converged to inhibitory interneurones, which mediate the masseter inhibitory reflex. Our findings suggested that inputs from the median nerve initially ascend to the brain, at least to the brainstem, and then descend to the spinal cord. Therefore, inhibition induced by median nerve stimulation was not considered as an interlimb reflex mediated by a propriospinal pathway, but long-loop reflex, at least via the pons. The discrepancy between the results of reflex and motor units suggests that facilitation of soleus H-reflex following median nerve stimulation was mainly due to reduced presynaptic inhibition.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Calancie B (1991) Interlimb reflexes following cervical spinal cord injury in man. Exp Brain Res 85:458–469
Calancie B, Molano MR, Broton JG (2002) Interlimb reflexes and synaptic plasticity become evident months after human spinal cord injury. Brain 125:1150–1161
Cavallari P, Katz R, Penicaud A (1992) Pattern of projections of group I afferents from elbow muscles to motoneurones supplying wrist muscles in man. Exp Brain Res 91:311–319
Crone C, Hultborn H, Mazieres L, Morin C, Nielsen J, Pierrot-Deseilligny E (1990) Sensitivity of monosynaptic test reflexes to facilitation and inhibition as a function of the test reflex size: a study in man and the cat. Exp Brain Res 81:35–45
Delwaide PJ, Crenna P (1984) Cutaneous nerve stimulation and motoneuronal excitability. II: evidence for non-segmental influences. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:190–196
Delwaide PJ, Toulouse P (1981) Facilitation of monosynaptic reflexes by voluntary contraction of muscles in remote parts of the body. Mechanisms involved in the Jendrassik maneuver. Brain 104:701–719
Delwaide PJ, Figiel C, Richelle C (1977) Effects of postural changes of the upper limb on reflex transmission in the lower limb. Cervicolumbar reflex interactions in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 40:616–621
Deriu F, Milia M, Sau G, Podda MV, Ortu E, Chessa G, Aiello I, Tolu E (2002) Non-nociceptive upper limb afferents modulate masseter muscle EMG activity in man. Exp Brain Res 143:286–294
Ellaway PH (1978) Cumulative sum technique and its application to the analysis of peristimulus time histograms. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 45:302–304
Fournier E, Meunier S, Pierrot-Deseilligny E, Shindo M (1986) Evidence for interneuronally mediated Ia excitatory effects to human quadriceps motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 377:143–169
Gassel MM (1970) A critical review of evidence concerning long-loop reflexes excited by muscle afferents in man. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 33:358–362
Kearney RE, Chan CWY (1981) Interlimb reflexes evoked in human arm muscles by ankle displacement. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 52:65–71
Logigian EL, Plotkin GM, Shefner JM (1999) The cutaneous silent period is mediated by spinal inhibitory pathway. Muscle Nerve 22:467–472
Manconi FM, Syed NA, Floeter MK (1998) Mechanisms underlying spinal motor neuron excitability during the cutaneous silent period in humans. Muscle Nerve 21:1256–1264
Meier-Ewert K, Hümme U, Dahm J (1972) New evidence favouring long loop reflexes in man. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr 215:121–128
Meinck HM, Piesiur-Strehlow B (1981) Reflexes evoked in leg muscles from arm afferents: a propriospinal pathway in man? Exp Brain Res 43:78–86
Miller S, Van der Burg J, Van der Meche FGA (1975) Coordination of movements of the hindlimbs and forelimbs in different forms of locomotion in normal and decerebrate cat. Brain Res 91:217–237
Ongerboer de Visser BW, Cruccu G, Manfredi M, Koelman JH (1989) Effects of brainstem lesions on the masseter inhibitory reflex. Functional mechanisms of reflex pathways. Brain 113:781–792
Piesiur-Strehlow B, Meinck HM (1980) Response patterns of human lumbo-sacral motoneurone pools to distant somatosensory stimuli. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol 48:673–682
Schomburg ED, Meinck HM, Haustein J, Roesler J (1978) Functional organization of the spinal reflex pathways from forelimb afferents to hindlimb motoneurones in the cat. Brain Res 139:21–33
Shimamura M, Livingston RB (1963) Longitudinal conduction systems serving spinal and brain-stem coordination. J Neurophysiol 26:258–272
Zehr EP, Collins DF, Chua R (2001) Human interlimb reflexes evoked by electrical stimulation of cutaneous nerves innervating the hand and foot. Exp Brain Res 140:495–504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kagamihara, Y., Hayashi, A., Masakado, Y. et al. Long-loop reflex from arm afferents to remote muscles in normal man. Exp Brain Res 151, 136–144 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1436-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-003-1436-2