Abstract
This paper reports a novel application of microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) of polyphenols from brewer’s spent grains (BSG). A 24 orthogonal composite design was used to obtain the optimal conditions of MAE. The influence of the MAE operational parameters (extraction time, temperature, solvent volume and stirring speed) on the extraction yield of ferulic acid was investigated through response surface methodology. The results showed that the optimal conditions were 15 min extraction time, 100 °C extraction temperature, 20 mL of solvent, and maximum stirring speed. Under these conditions, the yield of ferulic acid was 1.31 ± 0.04% (w/w), which was fivefold higher than that obtained with conventional solid–liquid extraction techniques. The developed new extraction method considerably reduces extraction time, energy and solvent consumption, while generating fewer wastes. HPLC-DAD-MS analysis indicated that other hydroxycinnamic acids and several ferulic acid dehydrodimers, as well as one dehydrotrimer were also present, confirming that BSG is a valuable source of antioxidant compounds.

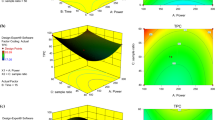
Response surface of FA yield (Y, %, w/w) as a function of extraction time (X 1) and the other variables studied: a solvent volume (X 3); b temperature (X 2)




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fillaudeau L, Blanpain-Avet P, Daufin G (2006) J Clean Prod 14(5):463–471
Mussatto SI (2009) Biotechnological Potential of Brewing Industry By-Products. In: Nigam P, Pandey A (eds) Biotechnology for agro-industrial residues utilisation. Springer, Netherlands, pp 313–326
Mussatto SI, Dragone G, Roberto IC (2007) Ind Crop Prod 25(2):231–237
Aliyu S, Bala M (2011) Afr J Biotechnol 10(3):324–331
Naczk M, Shahidi F (2004) J Chromatogr 1054(1–2):95–111
Ou S, Kwok K-C (2004) J Sci Food Agric 84(11):1261–1269
Shahidi F, Chandrasekara A (2010) Phytochem Rev 9(1):147–170
Kroon PA, Williamson G (1999) J Sci Food Agric 79(3):355–361
Bartolomé B, Gómez-Cordovés C (1999) J Sci Food Agric 79(3):435–439
Bartolomé B, Santos M, Jiménez JJ, del Nozal MJ, Gómez-Cordovés C (2002) J Cereal Sci 36(1):51–58
Dvorakova M, Moreira MM, Dostalek P, Skulilova Z, Guido LF, Barros AA (2008) J Chromatogr 1189(1–2):398–405
Kalia K, Sharma K, Singh HP, Singh B (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56(21):10129–10134
Szwajgier D, Waśko A, Targoński Z, Niedźwiadek M, Bancarzewska M (2010) J Inst Brew 116(3):293–303
Sousa AMM, Alves VD, Morais S, Delerue-Matos C, Gonçalves MP (2010) Bioresour Technol 101(9):3258–3267
Sun Y, Liao X, Wang Z, Hu X, Chen F (2007) Eur Food Res Technol 225(3):511–523
Bélanger J, Paré J (2006) Anal Bioanal Chem 386(4):1049–1058
Sparr Eskilsson C, Björklund E (2000) J Chromatogr 902(1):227–250
Bai X-L, Yue T-L, Yuan Y-H, Zhang H-W (2010) J Sep Sci 33(23–24):3751–3758
Pan X, Niu G, Liu H (2003) Chem Eng Process 42(2):129–133
Zhang L, Wang Y, Wu D, Xu M, Chen J (2011) Molecules 16(6):4428–4437
Hong N, Yaylayan VA, Raghavan GSV, Paré JRJ, Bélanger JMR (2001) Nat Prod Lett 15(3):197–204
Liazid A, Palma M, Brigui J, Barroso CG (2007) J Chromatogr 1140:29–34
Oufnac DS, Xu Z, Sun T, Sabliov C, Prinyawiwatkul W, Godber JS (2007) Cereal Chem 84(2):125–129
Inglett GE, Rose DJ, Stevenson DC, Chen D, Biswas A (2009) Cereal Chem 86(6):661–664
Athanasios M, Georgios L, Michael K (2007) Food Chem 102(3):606–611
Montgomery DC (1991) Design and analysis of experiments
Garg UK, Kaur MP, Garg VK, Sud D (2008) Bioresour Technol 99(5):1325–1331
Masmoudi M, Besbes S, Chaabouni M, Robert C, Paquot M, Blecker C, Attia H (2008) Carbohydr Polym 74(2):185–192
Mussatto SI, Roberto IC (2005) J Sci Food Agric 85(14):2453–2460
Rubilar M, Pinelo M, Shene C, Sineiro J, Nuñez MJ (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55(25):10101–10109
Hernanz D, Nuñez V, Sancho AI, Faulds CB, Williamson G, Bartolomé B, Gómez-Cordovés C (2001) J Agric Food Chem 49(10):4884–4888
Alonso-Salces RM, Korta E, Barranco A, Berrueta LA, Gallo B, Vicente F (2001) J Chromatogr 933(1–2):37–43
Khan MK, Abert-Vian M, Fabiano-Tixier A-S, Dangles O, Chemat F (2010) Food Chem 119(2):851–858
Louli V, Ragoussis N, Magoulas K (2004) Bioresour Technol 92(2):201–208
Dobberstein D, Bunzel M (2010) J Agric Food Chem 58(16):8927–8935
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by Fundação para a Ciência e a Tecnologia (FCT) through grant no. PEst-C/EQB/LA0006/2011. M.M.M. wishes to acknowledge FCT for her PhD studentship (SFRH/BD/60577/2009). The authors also thank UNICER – Bebidas de Portugal for their support, including the supply of brewer’s spent grain samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the special issue Euroanalysis XVI (The European Conference on Analytical Chemistry) with guest editor Slavica Ražić.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moreira, M.M., Morais, S., Barros, A.A. et al. A novel application of microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenols from brewer’s spent grain with HPLC-DAD-MS analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 403, 1019–1029 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5703-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5703-y