Abstract
The fabrication of novel iron-doped barium strontium titanate thin films by means of radio frequency (RF) magnetron co-sputtering is shown. Investigations of the elemental composition and the dopant distribution in the thin films obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, Rutherford backscattering spectrometry, and time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy reveal a homogeneous dopant concentration throughout the thin film. The incorporation of the iron dopant and the temperature-dependent evolution of the crystal structure and morphology are analyzed by electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy, and scanning electron microscopy. In summary, these results emphasize the RF magnetron co-sputter process as a versatile way to fabricate doped thin films.

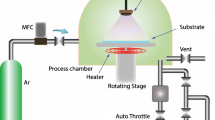
Cross section of the RF magnetron co-sputter setup and the X-ray phototelectron spectroscopy iron spectrum of a co-sputtered iron doped Barium strontium titanate thin film









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kozyrev A et al (1998) Microw. Symp. Dig.:985
Tombak A et al (2003) IEEE Trans Microw Theor Tech 51(2):462
Scheele P et al (2005) Micro Symp Dig: 6500
Horikawa T et al (1994) IEEE Trans Electron E77-C:385
Kim TS, Oh MH, Kim CH (1995) Thin Solid Films 254:273
Qadri SB et al (1995) Appl Phys Lett 66:1605
Tahan DM, Safari A, Klein LC (1996) J Am Ceram Soc 79:1593
Gao Y, Tran T, Alluri P (1999) Appl Phys Lett 75:415
Lee SY, Tseng TY (2003) Appl Phys Lett 80:1797
Chen SY, Wang HW, Huang LC (2001) Jpn J Appl Phys 40:4974
Saha S, Krupanidhi SB (2001) J Appl Phys 90:1250
Ahn KH, Baik S, Kim SS (2002) J Appl Phys 92:2651
Saha S, Krupanidhi SB (2011) Appl Phys Lett 79:111
Imai K, Takeno S, Nakamura K (2002) Jpn J Appl Phys 41:6060
Giere A et al (2008) Frequenz 62:47
Su B et al (2002) J Electrocer 9:111
Lutz H, Bruns M, Link F, Baumann H (1998) Thin Solid Films 332:230
Lutz H, Bruns M, Link F, Baumann H (1999) Surf Coat Tech 116–119:419
Kormunda M, Pavlik J, Mackova A, Malinski P (2010) Surf Coat Tech 205:120
Parry KL et al (2006) Surf Interface Anal 38:1497
Scofield JH (1976) J Electron Spectr Relat Phen 8:129
Tanuma S, Powell CJ, Penn DR (1994) Surf Interface Anal 21:165
Holländer B et al. (2000) Nucl Instr And Meth. In: Phys Res B 161–163:227
Doolittle LR (1985) Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, B Beam Interact Mater Atoms 9:344
Moulder JF, Stickle WF, Sobol PE, Bomben KD (1992) Handbook of X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. Perkin-Elmer Corporation, Minnesota
Viviani M et al (1999) J Eur Ceram Soc 19:1047
Miot C et al (1997) J Mater Res 12:2388
Hewitt RW, Winograd N (1980) J Appl Phys 51:2620
Fujisaki Y, Shimamoto Y, Matsui Y (1999) Jpn J Appl Phys Part 2 38: L52
Li XL et al (2005) Appl Phys Lett 87:222905
Craciun V, Singh RK (2000) Appl Phys Lett 76:1932
Fukuda Y et al (1989) Phys Rev B 39:11494
Meyer HM III et al (1989) Phys Rev B 38:6500
Sosulnikov MI, Teterin YA (1992) J Elec Spec Phen 59:111
Brundel CR, Chuang TJ, Wandelt K (1977) Surf Sci 68:459
Eichel RA (2011) Phys Chem Chem Phys 13:368–384
Drahus MD, Jakes P, Erdem E, Eichel RA (2011) Solid State Ionics 184:47–51
Meštric H, Eichel RA, Kloss T et al (2005) Phys Rev B 71:134109
Óvári L, Kiss J (2006) Appl Surf Sci 252:8624
Schafranek R et al (2009) J Eur Ceram Soc 29:1433
Yuzyuk YI, Alyoshin VA, Zakharachenko IN (2002) Phys Rev B 65:134107
Kuo SY, Liao WY, Hsieh WF (2001) Phys Rev B 64:224103
Cao LZ et al (2006) J Phys D 39:2819
Mandelbrot B (1982) The fractal geometry of nature. Freeman, New York
Tay ST et al (2000) J Appl Phys 88:5928
Fang TH et al (2006) Mat Sci Eng A426:157
Venkata Saravanan K, Ghanashyam Krishna M, James Raju KC (2009) J Appl Phys 106:114102
Acknowledgment
The authors gratefully acknowledge Mrs. V. Hermann and Mr. U. Geckle, KIT, for the assistance during the experimental work and like to thank Dr. H. H. Belz, ThermoFisher Scientific GmbH, Dreieich, Germany, for the Raman measurements, as well as Dr. Peter Jakes for experimental support and many helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the special paper collection on Solid State Analysis (FKA 16) with guest editor G. Friedbacher.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stemme, F., Geßwein, H., Drahus, M.D. et al. Characterization of non-stoichiometric co-sputtered Ba0.6Sr0.4(Ti1 − x Fe x )1 + x O3 − δ thin films for tunable passive microwave applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 403, 643–650 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5435-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5435-z