Abstract
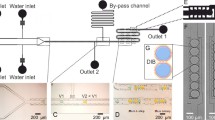
We describe a system that provides a rapid and simple way of forming suspended lipid bilayers within a microfluidic platform from an aqueous droplet. Bilayer lipid membranes are created in a polymeric device by contacting monolayers formed at a two-phase liquid–liquid interface. Microdroplets, containing membrane proteins, are injected onto an electrode positioned above an aperture machined through a conical cavity that is filled with a lipid–alkane solution. The formation of the BLM depends solely on the device geometry and leads to spontaneous formation of lipid bilayers simply by dispensing droplets of buffer. When an aqueous droplet containing transmembrane proteins or proteoliposomes is injected, straightforward electrophysiology measurements are possible. This method is suitable for incorporation into lab-on-a-chip devices and allows for buffer exchange and electrical measurements.

Bilayer lipid membranes are formed in a polymeric device by injecting water droplets, containing membrane proteins, directly onto an electrode positioned above an aperture machined into a conical cavity, which is initially filled with a lipid-alkane solution. The water droplet slides down the electrode to the aperture at the bottom of the conical reservoir. The geometry of this system enables the spontaneous formation of a BLM. Ion channel activity is recorded between an electrode in the bottom channel and the electrode in the droplet. The technique is scalable and could be configured as a high throughput multi-site biosensing or drug screening platform.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tien HT (1974) Bilayer lipid membranes (BLM). Theory and practice. Dekker, New York
Montal M, Mueller P (1972) Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 69:3561–3566
Cooper MA (2004) J Mol Recognit 17:286–315
Castellana ET, Cremer PS (2006) Surf Sci Rep 61:429–444
Tien HT, Ottova AL (1998) Electrochim Acta 43:3587–3610
Mischak H, Apweiler R, Banks RE, Conaway M, Coon J, Dominiczak A, Ehrich JH, Fliser D, Girolami M, Hermjakob H, Hochstrasser D, Jankowski J, Julian BA, Kolch W, Massy ZA, Neusuess C, Novak J, Peter K, Rossing K, Schanstra J, Semmes OJ, Theodorescu D, Thongboonkerd V, Weissinger EM, Van Eyk JE, Yamamoto T (2007) Proteomics Clin Appl 1:148–156
Vitzthum F, Behrens F, Anderson NL, Shaw JH (2005) J Prot Res 4:1086–1097
Andersson M, Okeyo G, Wilson D, Keizer H, Moe P, Blount P, Fine P, Dodabalapur A, Duran RS (2008) Biosens Bioelectron 23:919–923
Le Pioufle B, Suzuki H, Tabata KV, Noji H, Takeuchi S (2008) Anal Chem 80:328–332
Maurer JA, White VE, Dougherty DA, Nadeau JL (2007) Biosens Bioelectron 22:2577–2584
Zagnoni M, Sandison M, Marius P, Lee AG, Morgan H (2007) Lab Chip 7:1176–1183
Malmstadt N, Nash MA, Purnell RF, Schmidt JJ (2006) Nano Letters 6:1961–1965
Schmitt EK, Vrouenraets M, Steinem C (2006) Biophys J 91:2163–2171
White RJ, Ervin EN, Yang T, Chen X, Daniel S, Cremer PS, White HS (2007) J Am Chem Soc 129:11766–11775
Sandison ME, Zagnoni M, Morgan H (2007) Langmuir 23:8277–8284
Holden MA, Needham D, Bayley H (2007) J Am Chem Soc 129:8650–8655
Funakoshi K, Suzuki H, Takeuchi S (2006) Anal Chem 78:8169–8174
Heron AJ, Thompson JR, Mason AE, Wallace MI (2007) J Am Chem Soc 129:16042–16047
Poulos JL, Tae-Joon Jeon, Damoiseaux R, Gillespie EJ, Bradley KA, Schmidt JJ (2008) Biosens Bioelectron. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2008.08.041
Marius P, Alvis SJ, East JM, Lee AG (2005) Biophys J 89:4081–4089
Andersen OS, Koeppe RE, Roux B (2005) IEEE Trans Nanobiosci 4:10–20
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 6th Framework Programme of the European Commission, under the contract NMP4-CT-2005-017114 “RECEPTRONICS”, and the UK Interdisciplinary Research Centre in Bio-Nanotechnology (R45659/01). KcsA was a kind gift of Prof. A. Lee from the School of Biological Sciences, University of Southampton.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zagnoni, M., Sandison, M.E., Marius, P. et al. Bilayer lipid membranes from falling droplets. Anal Bioanal Chem 393, 1601–1605 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2588-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2588-5