Abstract .
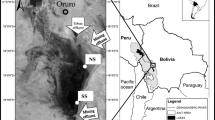
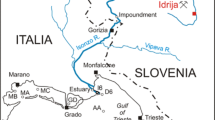
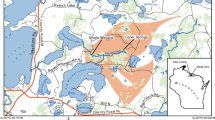
Comparative tests of net mercury methylation potentials, with cultivated and macrophyte-associated periphyton and using stable (200HgCl2 and CH3 199HgCl) and labeled (203HgCl2) mercury, have been conducted in the Everglades nutrient removal area (Florida, USA) and in a tropical coastal Brazilian lake (RJ, Brazil). More methylmercury was formed by macrophyte-associated (up to 17% of added 203Hg(II)) than cultivated (up to 1.6%) periphyton and methylmercury formation was lower in periphyton exposed to light (0.2%). High methylation was also observed for samples incubated with stable mercury isotopes (1.5–7.7% of added 200Hg(II)), confirming the results obtained with labeled mercury. Simultaneous addition of 200HgCl2 and CH3 199HgCl indicated that CH3 199HgCl had no inhibitory effect on Hg methylation. The elevated methylation potentials observed in macrophytes, because of their root-associated periphyton, might contribute significantly to the high levels of methylmercury observed in Everglades biota. Comparative mercury methylation tests were also conducted in the water of a stratified temperate lake (Wisconsin, USA). Similar trends were observed for both stable and radioisotopes, with increasing mercury methylation along the depth profile. The highest levels (0.9% 203Hg(II) and 0.8% 200Hg(II)) were obtained below the oxic/anoxic boundary, where sulfide starts to increase, probably as a result of the intense activity of sulfate-reducing bacteria in the anoxic layer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mauro, .J., Guimarães, .J., Hintelmann, .H. et al. Mercury methylation in macrophytes, periphyton, and water – comparative studies with stable and radio-mercury additions. Anal Bioanal Chem 374, 983–989 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-002-1534-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-002-1534-1