Abstract
Rationale
The loudness dependence of the auditory evoked potential (LDAEP) is considered a noninvasive in vivo marker of central serotonergic functioning in humans. Nevertheless, results of genetic association studies point towards a modulation of this biomarker by dopaminergic neurotransmission.
Objective
We examined the effect of dopaminergic modulation on the LDAEP using L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (levodopa)/benserazide (Madopar®) as a challenge agent in healthy volunteers.
Methods
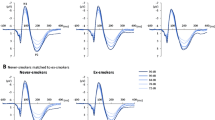
A double-blind placebo-controlled challenge design was chosen. Forty-two healthy participants (21 females and 21 males) underwent two LDAEP measurements, following a baseline LDAEP measurement either placebo or levodopa (levodopa 200 mg/benserazide 50 mg) were given orally. Changes in the amplitude and dipole source activity of the N1/P2 intensities (60, 70, 80, 90, and 100 dB) were analyzed.
Results
The participants of neither the levodopa nor the placebo group showed any significant LDAEP alterations compared to the baseline measurement. The test–retest reliability (Cronbachs Alpha) between baseline and intervention was 0.966 in the verum group and 0.759 in the placebo group, respectively.
Conclusions
The administration of levodopa showed no effect on the LDAEP. These findings are in line with other trials using dopamine receptor agonists.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Axelrod J, Tomchick R (1958) Enzymatic O-methylation of epinephrine and other catechols. J Biol Chem 233:702–705
Baribeau JC, Laurent JP (1987) The effect of selective attention on augmenting/intensity function of the early negative waves of AEPs. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol Suppl 40:68–75
Black KJ, Mink JW (2000) Response to levodopa challenge in Tourette syndrome. Mov Disord 15:1194–1198
Brocke B, Beauducel A, John R, Debener S, Heilemann H (2000) Sensation seeking and affective disorders: characteristics in the intensity dependence of acoustic evoked potentials. Neuropsychobiology 41:24–30
Cohen J (1992) A power primer. Psychol Bull 112(1):155–159
de la Fuente-Fernandez R, Sossi V, Huang Z, Furtado S, Lu JQ, Calne DB, Ruth TJ, Stoessl AJ (2004) Levodopa-induced changes in synaptic dopamine levels increase with progression of Parkinson's disease: implications for dyskinesias. Brain 127:2747–2754
Ebstein RP, Benjamin J, Belmaker RH (2000) Personality and polymorphisms of genes involved in aminergic neurotransmission. Eur J Pharmacol 410:205–214
Floel A, Breitenstein C, Hummel F, Celnik P, Gingert C, Sawaki L, Knecht S, Cohen LG (2005) Dopaminergic influences on formation of a motor memory. Ann Neurol 58:121–130
Funke B, Malhotra AK, Finn CT, Plocik AM, Lake SL, Lencz T, DeRosse P, Kane JM, Kucherlapati R (2005) COMT genetic variation confers risk for psychotic and affective disorders: a case control study. Behav Brain Funct 1:19
Gallinat J, Bottlender R, Juckel G, Munke-Puchner A, Stotz G, Kuss HJ, Mavrogiorgou P, Hegerl U (2000) The loudness dependency of the auditory evoked N1/P2-component as a predictor of the acute SSRI response in depression. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 148:404–411
Hagenmuller F, Hitz K, Darvas F, Kawohl W (2011) Determination of the Loudness Dependence of Auditory Evoked Potentials (LDAEP): single electrode estimation versus dipole source analysis. Hum Psychopharmacol Clin Exp 26:147–154
Hegerl U (1994) Event-related potentials in psychiatry: a new perspective. Pharmacopsychiatry 27:47–48
Hegerl U, Juckel G (1993) Intensity dependence of auditory evoked potentials as an indicator of central serotonergic neurotransmission: a new hypothesis. Biol Psychiatry 33:173–187
Hegerl U, Juckel G (1994) Auditory evoked dipole source activity: indicator of central serotonergic dysfunction in psychiatric patients? Pharmacopsychiatry 27:75–78
Hegerl U, Juckel G (2000) Identifying psychiatric patients with serotonergic dysfunctions by event-related potentials. World J Biol Psychiatry 1:112–118
Hegerl U, Gallinat J, Mrowinski D (1994) Intensity dependence of auditory evoked dipole source activity. Int J Psychophysiol 17:1–13
Hegerl U, Gallinat J, Juckel G (2001) Event-related potentials. Do they reflect central serotonergic neurotransmission and do they predict clinical response to serotonin agonists? J Affect Disord 62:93–100
Juckel G, Molnar M, Hegerl U, Csepe V, Karmos G (1997) Auditory-evoked potentials as indicator of brain serotonergic activity—first evidence in behaving cats. Biol Psychiatry 41:1181–1195
Juckel G, Hegerl U, Giegling I, Mavrogiorgou P, Wutzler A, Schuhmacher C, Uhl I, Brune M, Mulert C, Pogarell O, Rujescu D (2008a) Association of 5-HT1B receptor polymorphisms with the loudness dependence of auditory evoked potentials in a community-based sample of healthy volunteers. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 147B:454–458
Juckel G, Kawohl W, Giegling I, Mavrogiorgou P, Winter C, Pogarell O, Mulert C, Hegerl U, Rujescu D (2008b) Association of catechol-O-methyltransferase variants with loudness dependence of auditory evoked potentials. Hum Psychopharmacol 23:115–120
Kawohl W, Waberski TD, Darvas F, Norra C, Gobbele R, Buchner H (2007) Comparative source localization of electrically and pressure-stimulated multichannel somatosensory evoked potentials. J Clin Neurophysiol 24:257–262
Kawohl W, Giegling I, Mavrogiorgou P, Pogarell O, Mulert C, Moller HJ, Hegerl U, Rujescu D, Juckel G (2008a) Association of functional polymorphisms in NOS1 and NOS3 with loudness dependence of auditory evoked potentials. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 11:477–483
Kawohl W, Hegerl U, Muller-Oerlinghausen B, Juckel G (2008b) Insights in the central serotonergic function in patients with affective disorders. Neuropsychiatry 22:23–27
Khor SP, Hsu A (2007) The pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Curr Clin Pharmacol 2:234–243
Kumakura Y, Danielsen EH, Reilhac A, Gjedde A, Cumming P (2004) Levodopa effect on [18F]fluorodopa influx to brain: normal volunteers and patients with Parkinson's disease. Acta Neurol Scand 110:188–195
Lee TW, Yu YW, Chen TJ, Tsai SJ (2005) Loudness dependence of the auditory evoked potential and response to antidepressants in Chinese patients with major depression. J Psychiatry Neurosci 30:202–205
Lee IH, Yang YK, Chen PS, Huang HC, Yeh TL, Lu RB, Chiu NT, Yao WJ, Lin SH (2010) Loudness dependence of auditory evoked potentials (LDAEP) correlates with the availability of dopamine transporters and serotonin transporters in healthy volunteers—a two isotopes SPECT study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 214:617–624
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR (2006) Intermediate phenotypes and genetic mechanisms of psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:818–827
Micallef-Roll J, Rihet P, Hasbroucq T, Possamai C, Blin O (2001) Levodopa-induced drowsiness in healthy volunteers: results of a choice reaction time test combined with a subjective evaluation of sedation. Clin Neuropharmacol 24:91–94
Moret C, Briley M (2000) The possible role of 5-HT(1B/D) receptors in psychiatric disorders and their potential as a target for therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 404:1–12
Nicodemus KK, Kolachana BS, Vakkalanka R, Straub RE, Giegling I, Egan MF, Rujescu D, Weinberger DR (2007) Evidence for statistical epistasis between catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) and polymorphisms in RGS4, G72 (DAOA), GRM3, and DISC1: influence on risk of schizophrenia. Hum Genet 120:889–906
Norra C, Mrazek M, Tuchtenhagen F, Gobbele R, Buchner H, Sass H, Herpertz SC (2003) Enhanced intensity dependence as a marker of low serotonergic neurotransmission in borderline personality disorder. J Psychiatr Res 37:23–33
Norra C, Becker S, Brocheler A, Kawohl W, Kunert HJ, Buchner H (2008) Loudness dependence of evoked dipole source activity during acute serotonin challenge in females. Hum Psychopharmacol 23:31–42
O'Neill BV, Croft RJ, Leung S, Guille V, Galloway M, Phan KL, Nathan PJ (2006) Dopamine receptor stimulation does not modulate the loudness dependence of the auditory evoked potential in humans. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 188:92–99
O'Neill BV, Croft RJ, Nathan PJ (2008a) The loudness dependence of the auditory evoked potential (LDAEP) as an in vivo biomarker of central serotonergic function in humans: rationale, evaluation and review of findings. Hum Psychopharmacol 23:355–370
O'Neill BV, Guille V, Croft RJ, Leung S, Scholes KE, Phan KL, Nathan PJ (2008b) Effects of selective and combined serotonin and dopamine depletion on the loudness dependence of the auditory evoked potential (LDAEP) in humans. Hum Psychopharmacol 23:301–312
Park YM, Kim DW, Kim S, Im CH, Lee SH (2011) The loudness dependence of the auditory evoked potential (LDAEP) as a predictor of the response to escitalopram in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 213:625–632
Pogarell O, Tatsch K, Juckel G, Hamann C, Mulert C, Popperl G, Folkerts M, Chouker M, Riedel M, Zaudig M, Moller HJ, Hegerl U (2004) Serotonin and dopamine transporter availabilities correlate with the loudness dependence of auditory evoked potentials in patients with obsessive–compulsive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1910–1917
Simmons JG, Nathan PJ, Berger G, Allen NB (2011) Chronic modulation of serotonergic neurotransmission with sertraline attenuates the loudness dependence of the auditory evoked potential in healthy participants. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 217:101–110
Uhl I, Gorynia I, Gallinat J, Mulert C, Wutzler A, Heinz A, Juckel G (2006) Is the loudness dependence of auditory evoked potentials modulated by the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram in healthy subjects? Hum Psychopharmacol 21:463–471
Waberski TD, Gobbele R, Kawohl W, Cordes C, Buchner H (2003) Immediate cortical reorganization after local anesthetic block of the thumb: source localization of somatosensory evoked potentials in human subjects. Neurosci Lett 347:151–154
Wyss C (2009) The role of central serotonergic activity in schizophrenic negative symptoms. Master Thesis, University of Zurich
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Johannes Schley for support with the voluntary server of the University of Zürich and Barbara Rauscher and her team for taking the blood samples. This study has been funded by an unrestricted grant of Bristol-Myers Squibb. The authors disclose any further conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hitz, K., Heekeren, K., Obermann, C. et al. Examination of the effect of acute levodopa administration on the loudness dependence of auditory evoked potentials (LDAEP) in humans. Psychopharmacology 221, 389–396 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2586-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2586-8