Abstract
Rationale
The traditional antihistamine chlorpheniramine ameliorates panic attacks, phobias, and lowered mood, and this therapeutic effect is independent of the blockade of histamine H1 receptors. Since chlorpheniramine inhibits the reuptake of serotonin (5-HT), the anxiolytic-like effect of chlorpheniramine may be produced by an increase in serotonergic function.
Objective
To elucidate the mechanisms underlying the anxiolytic-like effects of chlorpheniramine in mice, we examined the involvement of 5-HT systems in the prefrontal cortex that is a crucial region in the regulation of emotional function.
Results
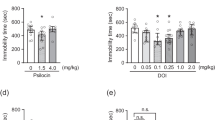
Chlorpheniramine (0.05–5 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently and significantly decreased the duration of freezing behavior in both the elevated open-platform and conditioned fear tests. The anti-freezing effects of chlorpheniramine (5 mg/kg, i.p.) in these tests were inhibited by pretreatment with the non-selective antagonist at 5-HT receptors, methiothepin (0.01 mg/kg, s.c.). In addition, the local injection of chlorpheniramine (10–100 ng/mouse) and 5-HT (1–10 μg/mouse) into the medial part of the prefrontal cortex (mPFC) dose-dependently and significantly decreased the duration of freezing behavior in the elevated open-platform test. In a microdialysis study, chlorpheniramine (0.5 and 5 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently and significantly increased the extracellular 5-HT level in the mPFC. In addition, the local perfusion of chlorpheniramine (10 and 30 μM), but not of the selective H1 receptor antagonist, cetirizine, into the mPFC markedly increased the extracellular 5-HT level in the mPFC.
Conclusion
The anxiolytic-like effect of chlorpheniramine is produced, at least in part, by the facilitation of serotonergic neurotransmission in the PFC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, Fujimoto T, Akaishi T, Misawa M (2009) Stimulation of basolateral amygdaloid serotonin 5-HT(2C) receptors promotes the induction of long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of anesthetized rats. Neurosci Lett 451:65–68
Beyer CE, Lin Q, Platt B, Malberg J, Hornby G, Sullivan KM, Smith DL, Lock T, Mitchell PJ, Hatzenbuhler NT, Evrard DA, Harrison BL, Magolda R, Pangalos MN, Schechter LE, Rosenzweig-Lipson S, Andree TH (2009) Preclinical characterization of WAY-211612: a dual 5-HT uptake inhibitor and 5-HT (1A) receptor antagonist and potential novel antidepressant. Br J Pharmacol 157:307–319
Bishop SJ (2007) Neurocognitive mechanisms of anxiety: an integrative account. Trends Cogn Sci 11:307–316
Bishop SJ (2009) Trait anxiety and impoverished prefrontal control of attention. Nat Neurosci 12:92–98
Blier P, de Montigny C (1994) Current advances and trends in the treatment of depression. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15:220–226
Carlsson A, Lindqvist M (1969) Central and peripheral monoaminergic membrane pump blockade by some addictive analgesics and antihistamines. J Pharm Pharmacol 21:460–464
Campiani G, Butini S, Gemma S, Nacci V, Fattorusso C, Catalanotti B, Giorgi G, Cagnotto A, Goegan M, Mennini T, Minetti P, Di Cesare MA, Mastroianni D, Scafetta N, Galletti B, Stasi MA, Castorina M, Pacifici L, Ghirardi O, Tinti O, Carminati P (2002) Pyrrolo[1, 3]benzothiazepine-based atypical antipsychotic agents. Synthesis, structure-activity relationship, molecular modeling, and biological studies. J Med Chem 45:344–359
Carpenter L, Anderson G, Pelton G, Gudin J (1999) Tryptophan depletion during continuous CSF sampling in healthy human subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 19:26–35
Charlton BG (2005) Self-management and pregnancy—safe interventions for panic, phobia and other anxiety-disorders might include over-the-counter (OTC) ‘SSRI’ antihistamines such as diphenhydramine and chlorpheniramine. Acta Psychiatr Scand 112:323
Charlton BG (2009) A model for self-treatment of four sub-types of symptomatic ‘depression’ using non-prescription agents: neuroticism (anxiety and emotional instability); malaise (fatigue and painful symptoms); demotivation (anhedonia) and seasonal affective disorder ‘SAD’. Med Hypotheses 72:1–7
Cools R, Calder AJ, Lawrence AD, Clark L, Bullmore E, Robbins TW (2005) Individual differences in threat sensitivity predict serotonergic modulation of amygdala response to fearful faces. Psychopharmacology 180:670–679
Cools R, Roberts AC, Robbins TW (2008) Serotoninergic regulation of emotional and behavioural control processes. Trends Cogn Sci 12:31–40
Delgado PL, Charney DS, Price LH, Aghajanian GK, Landis H, Heninger GR (1990) Serotonin function and the mechanism of antidepressant action. Reversal of antidepressant-induced remission by rapid depletion of plasma tryptophan. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:411–418
de Oliveira AR, Reimer AE, Brandão ML (2006) Dopamine D2 receptor mechanisms in the expression of conditioned fear. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 84:102–111
Dringenberg HC, de Souza-Silva MA, Schwarting RK, Huston JP (1998) Increased levels of extracellular dopamine in neostriatum and nucleus accumbens after histamine H1 receptor blockade. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 358:423–429
Evers EA, van der Veen FM, Jolles J, Deutz NE, Schmitt JA (2006) Acute tryptophan depletion improves performance and modulates the BOLD response during a Stroop task in healthy females. Neuroimage 32:248–255
Fanselow MS (1984) What is conditioned fear? Trends Neurosci 7:460–462
Fujisaki Y, Itoh Y, Oishi R (2002) In vivo evidence for a lack of central effect of ebastine, an antihistaminic agent, in rats: a microdialysis study. Jpn J Pharmacol 90:353–356
García M, Morán A, Martín ML, Ortizde Urbina AV, San Román L (2007) Diabetes-induced changes in 5-hydroxytryptamine modulation of vagally-induced bradycardia in rat heart. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34:1199–1206
Graeff F, Guimaraes F, De Andrade T, Deakin JFW (1996) Role of 5-HT in stress, anxiety and depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 54:129–141
Grillon C, Chavis C, Covington MF, Pine DS (2009) Two-week treatment with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram reduces contextual anxiety but not cued fear in healthy volunteers: a fear-potentiated startle study. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:964–971
Gupta A, Chatelain P, Massingham R, Jonsson EN, Hammarlund-Udenaes M (2006) Brain distribution of cetirizine enantiomers: comparison of three different tissue-to-plasma partition coefficients: K(p), K(p, u), and K(p, uu). Drug Metab Dispos 34:318–323
Guscott M, Bristow LJ, Hadingham K, Rosahl TW, Beer MS, Stanton JA, Bromidge F, Owens AP, Huscroft I, Myers J, Rupniak NM, Patel S, Whiting PJ, Hutson PH, Fone KC, Biello SM, Kulagowski JJ, McAllister G (2005) Genetic knockout and pharmacological blockade studies of the 5-HT7 receptor suggest therapeutic potential in depression. Neuropharmacology 48:492–502
Harmer CJ, Bhagwagar Z, Perrett DI, Völlm BA, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2003) Acute SSRI administration affects the processing of social cues in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:148–152
Hasenohrl RU, Weth K, Huston JP (1999) Intraventricular infusion of the histamine H1 receptor antagonist chlorpheniramine improves maze performance and has anxiolytic-like effects in aged hybrid Fischer 344xBrown Norway rats. Exp Brain Res 128:435–440
Hashimoto S, Inoue T, Koyama T (1996) Serotonin reuptake inhibitors reduce conditioned fear stress-induced freezing behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology 123:182–186
Hashimoto S, Inoue T, Koyama T (1999) Effects of conditioned fear stress on serotonin neurotransmission and freezing behavior in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 378:23–30
Heinz A, Mann K, Weinberger DR, Goldman D (2001) Serotonergic dysfunction, negative mood states, and response to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:487–495
Hellbom E (2006) Chlorpheniramine, selective serotonin-reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and over-the-counter (OTC) treatment. Med Hypotheses 66:689–690
Hellbom E, Humble M (2003) Panic disorder treated with the antihistamine chlorpheniramine. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 90:361
Héry F, Bourgoin S, Hamon M, Ternaux JP, Glowinski J (1977) Control of the release of newly synthetized 3H–5-hydroxytryptamine by nicotinic and muscarinic receptors in rat hypothalamic slices. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 296:91–97
Hirano S, Miyata S, Onodera K, Kamei J (2006) Effects of histamine H1 receptor antagonists on the depressive-like behavior in diabetic mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 83:214–220
Hirano S, Miyata S, Onodera K, Kamei J (2007) Involvement of dopamine D1 receptors and α1-adrenoceptors in the antidepressant-like effect of chlorpheniramine in the mouse tail suspension test. Eur J Pharmacol 562:72–76
Inoue T, Tsuchiya K, Koyama T (1996) Serotonergic activation reduces defensive freezing in the conditioned fear paradigm. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 53:825–831
Kubo N, Shirakawa O, Kuno T, Tanaka C (1987) Antimuscarinic effects of antihistamines: quantitative evaluation by receptor-binding assay. Jpn J Pharmacol 43:277–282
Koolhaas JM, Korte SM, De Boer SF, Van Der Vegt BJ, Van Reenen CG, Hopster H, De Jong IC, Ruis MA, Blokhuis HJ (1999) Coping styles in animals: current status in behavior and stress-physiology. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:925–935
Lidbrink P, Jonsson G, Fuxe K (1971) The effect of imipramine-like drugs and antihistamine drugs on uptake mechanisms in the central noradrenaline and 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons. Neuropharmacology 10:521–536
Luo DD, An SC, Zhang X (2008) Involvement of hippocampal serotonin and neuropeptide Y in depression induced by chronic unpredicted mild stress. Brain Res Bull 77:8–12
Maes M, Meltzer HY (1995) The serotonin hypothesis of major depression. In: Bloom FE, Kupfer DJ (eds) Psychopharmacology: the fourth generation of progress. Raven, New York, pp 933–944
Markus CR, Firk C, Gerhardt C, Kloek J, Smolders GF (2008) Effect of different tryptophan sources on amino acids availability to the brain and mood in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 201:107–114
Matsuzawa-Yanagida K, Narita M, Nakajima M, Kuzumaki N, Niikura K, Nozaki H, Takagi T, Tamai E, Hareyama N, Terada M, Yamazaki M, Suzuki T (2008) Usefulness of antidepressants for improving the neuropathic pain-like state and pain-induced anxiety through actions at different brain sites. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1952–1965
Miyamoto J, Tsuji M, Takeda H, Nawa H, Matsumiya T (2000) Pretreatment with diazepam suppresses the reduction in defensive freezing behavior induced by fluvoxamine in the conditioned fear stress paradigm in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 409:81–84
Miyata S, Shimoi T, Hirano S, Yamada N, Hata Y, Yoshikawa N, Ohsawa M, Kamei J (2007a) Effects of serotonergic anxiolytics on the freezing behavior in the elevated open-platform test in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 105:272–278
Miyata S, Yamada N, Hirano S, Tanaka S, Kamei J (2007b) Diabetes attenuates psychological stress-elicited 5-HT secretion in the prefrontal cortex but not in the amygdala of mice. Brain Res 1147:233–239
Moja E, Cipollo P, Castoldi D, Tofanetti O (1989) Dose-response decrease in plasma tryptophan and brain tryptophan and serotonin after tryptophan-free amino acids mixtures in rats. Life Sci 44:971–976
Murphy FC, Smith K, Cowen P, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2002) The effects of tryptophan depletion on cognitive and affective processing in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 163:42–53
Ochsner KN, Bunge SA, Gross JJ, Gabrieli JD (2002) Rethinking feelings: an FMRI study of the cognitive regulation of emotion. J Cogn Neurosci 14:1215–1229
Onodera K (1987) Muricidal suppression by chlorpheniramine and changes in brain levels following dietary-induced thiamine deficiency in rats. Physiol Behav 41:71–78
Onodera K, Ogura Y (1984) Effects of histaminergic drugs on muricide induced by thiamine deficiency. Jpn J Pharmacol 34:15–21
Onodera K, Yamatodani A, Watanabe T, Wada H (1994) Neuropharmacology of the histaminergic neuron system in the brain and its relationship with behavioral disorders. Prog Neurobiol 42:685–702
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Phelps EA, LeDoux JE (2005) Contributions of the amygdala to emotion processing: from animal models to human behavior. Neuron 48:175–187
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 229:327–336
Privou C, Knoche A, Hasenohrl RU, Huston JP (1998) The H1- and H2-histamine blockers chlorpheniramine and ranitidine applied to the nucleus basalis magnocellularis region modulate anxiety and reinforcement related processes. Neuropharmacology 37:1019–1032
Rogers RD, Blackshaw AJ, Middleton HC, Matthews K, Hawtin K, Crowley C, Hopwood A, Wallace C, Deakin JF, Sahakian BJ, Robbins TW (1999) Tryptophan depletion impairs stimulus-reward learning while methylphenidate disrupts attentional control in healthy young adults: implications for the monoaminergic basis of impulsive behavior. Psychopharmacology 146:482–491
Rogoz Z, Skuza G, Sowinska H (1981) Effects of antihistaminic drugs in tests for antidepressant action. Pol J Pharmacol Pharm 33:321–335
Roozendaal B, Hui GK, Hui IR, Berlau DJ, McGaugh JL, Weinberger NM (2006) Basolateral amygdala noradrenergic activity mediates corticosterone-induced enhancement of auditory fear conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 86:249–255
Rutz S, Riegert C, Rothmaier AK, Jackisch R (2007) Presynaptic modulation of 5-HT release in the rat septal region. Neuroscience 146:643–658
Sakurai E, Yamasaki S, Hikichi N, Onodera K (1991) Effects of d- and dl-chlorpheniramine on serotonin and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid levels in the regional parts of rat brain. Yakubutsu Seishin Kodo 11:237–244
Schoeffter P, Waeber C (1994) 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors with a 5-HT6 receptor-like profile stimulating adenylyl cyclase activity in pig caudate membranes. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 350:356–360
Shearman E, Rossi S, Sershen H, Hashim A, Lajtha A (2005) Locally administered low nicotine-induced neurotransmitter changes in areas of cognitive function. Neurochem Res 30:1055–1066
Shishido S, Oishi R, Saeki K (1991) In vivo effects of some histamine H1-receptor antagonists on monoamine metabolism in the mouse brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 343:185–189
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 85:367–370
Tanda G, Kopajtic TA, Katz JL (2008) Cocaine-like neurochemical effects of antihistaminic medications. J Neurochem 106:147–157
Tatsumi M, Groshan K, Blakely RD, Richelson E (1997) Pharmacological profile of antidepressants and related compounds at human monoamine transporters. Eur J Pharmacol 340:249–258
Tye NC, Everitt BJ, Iversen SD (1977) 5-Hydroxytryptamine and punishment. Nature 268:741–743
Van der Veen FM, Evers EA, Deutz NE, Schmitt JA (2007) Effects of acute tryptophan depletion on mood and facial emotion perception related brain activation and performance in healthy women with and without a family history of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:216–224
Van Praag HM (2004) Can stress cause depression? Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 28:891–907
Weisstaub NV, Zhou M, Lira A, Lambe E, González-Maeso J, Hornung JP, Sibille E, Underwood M, Itohara S, Dauer WT, Ansorge MS, Morelli E, Mann JJ, Toth M, Aghajanian G, Sealfon SC, Hen R, Gingrich JA (2006) Cortical 5-HT2A receptor signaling modulates anxiety-like behaviors in mice. Science 313:536–540
Wesołowska A (2008) The anxiolytic-like effect of the selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist SB-399885: the impact of benzodiazepine receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 580:355–360
Wesołowska A, Nikiforuk A, Stachowicz K, Tatarczyńska E (2006) Effect of the selective 5-HT7 receptor antagonist SB 269970 in animal models of anxiety and depression. Neuropharmacology 51:578–586
Wikberg-Matsson A, Wikberg JE, Uhlén S (1998) Characterization of alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes in the pig. Eur J Pharmacol 347:301–309
Williams WA, Shoaf SE, Hommer D, Rawlings R, Linnoila M (1999) Effects of acute tryptophan depletion on plasma and cerebrospinal fluid tryptophan and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in normal volunteers. J Neurochem 72:1641–1647
Young CS, Mason R, Hill SJ (1988) Inhibition by H1-antihistamines of the uptake of noradrenaline and 5-HT into rat brain synaptosomes. Biochem Pharmacol 37:976–978
Zahm DS, Brog JS (1992) On the significance of subterritories in the “accumbens” part of the rat ventral striatum. Neuroscience 50:751–767
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to UCB Japan for their gift of cetirizine. We thank Ms. M. Sakaki, Mr. Y. Suzuka, and Ms. S. Nagasawa for their excellent technical assistance. We are also deeply grateful to Mr. T. Masuzawa for statistical analysis.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyata, S., Hirano, S., Ohsawa, M. et al. Chlorpheniramine exerts anxiolytic-like effects and activates prefrontal 5-HT systems in mice. Psychopharmacology 213, 441–452 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1695-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1695-0