Abstract
Rationale
Potential mechanisms of action of topiramate include alterations of glutamatergic and GABAergic systems. In particular, topiramate has been shown to increase occipital cortex GABA levels, as measured using proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS).
Objectives
The purpose of this study was to measure the effect of acute oral topiramate on the GABA precursors glutamate and glutamine in the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) and occipital lobe (OL) using high-field (4.0 T) proton MRS (1H MRS).
Methods
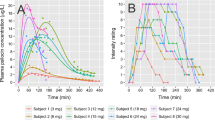
Proton MR spectra were acquired from healthy men at three times: at baseline and 2 and 6 h after ingesting 50 (N=5) or 100 mg (N=5) of topiramate. Blood samples were acquired prior to each scan for the purpose of obtaining serum topiramate levels.
Results
A 100-mg dose of topiramate significantly increased ACC glutamine levels within 2 h of ingestion and OL glutamine levels within 6 h of ingestion. There were no measured significant effects of topiramate on ACC or OL glutamate levels.
Conclusions
A 100-mg dose of oral topiramate increased serum topiramate and ACC glutamine levels within 2 h. OL glutamine levels increased within 6 h. Increased brain glutamine levels may be a consequence of topiramate positively modulating GABAA receptors. This result is of interest given the possible role for topiramate in the treatment of epilepsy, migraine headache, bipolar disorder, eating disorders, and alcohol dependence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Angehagen M, Ben-Menachem E, Ronnback L, Hansson E (2003a) Novel mechanisms of action of three antiepileptic drugs, vigabatrin, tiagabine, and topiramate. Neurochem Res 28:333–340
Angehagen M, Ben-Menachem E, Ronnback L, Hansson E (2003b) Topiramate protects against glutamate- and kainate-induced neurotoxicity in primary neuronalastroglial cultures. Epilepsy Res 54:63–71
Angehagen M, Ronnback L, Hansson E, Ben-Menachem E (2005) Topiramate reduces AMPA-induced Ca(2+) transients and inhibits GluR1 subunit phosphorylation in astrocytes from primary cultures. J Neurochem 94:1124–1130
Arnone D (2005) Review of the use of topiramate for treatment of psychiatric disorders. Ann Gen Psychiatry 4:5
Bearden CE, Hoffman KM, Cannon TD (2001) The neuropsychology and neuroanatomy of bipolar affective disorder: a critical review. Bipolar Disord 3:106–150 (discussion 151–153)
Benes FM, Todtenkopf MS, Logiotatos P, Williams M (2000) Glutamate decarboxylase(65)-immunoreactive terminals in cingulate and prefrontal cortices of schizophrenic and bipolar brain. J Chem Neuroanat 20:259–269
Blumberg HP, Leung HC, Skudlarski P, Lacadie CM, Fredericks CA, Harris BC, Charney DS, Gore JC, Krystal JH, Peterson BS (2003) A functional magnetic resonance imaging study of bipolar disorder: state- and trait-related dysfunction in ventral prefrontal cortices. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:601–609
Chang L, Cloak CC, Ernst T (2003) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies of GABA in neuropsychiatric disorders. J Clin Psychiatry 64(Suppl 3):7–14
Chang K, Adleman NE, Dienes K, Simeonova DI, Menon V, Reiss A (2004) Anomalous prefrontal–subcortical activation in familial pediatric bipolar disorder: a functional magnetic resonance imaging investigation. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:781–792
Cooper J, Bloom F, Roth R (2003) Amino acid transmitters. In: Cooper J, Bloom F, Roth R (eds) The biochemical basis of neuropharmacology. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 105–150
Cutrer FM (2001) Antiepileptic drugs: how they work in headache. Headache 41(Suppl 1):S3–S10
Davanzo P, Thomas MA, Yue K, Oshiro T, Belin T, Strober M, McCracken J (2001) Decreased anterior cingulate myo-inositol/creatine spectroscopy resonance with lithium treatment in children with bipolar disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:359–369
Elliott P, Hawthorne G (2005) Imputing missing repeated measures data: how should we proceed? Aust N Z J Psychiatry 39:575–582
Follett PL, Deng W, Dai W, Talos DM, Massillon LJ, Rosenberg PA, Volpe JJ, Jensen FE (2004) Glutamate receptor-mediated oligodendrocyte toxicity in periventricular leukomalacia: a protective role for topiramate. J Neurosci 24:4412–4420
Gibbs JW 3rd, Sombati S, DeLorenzo RJ, Coulter DA (2000) Cellular actions of topiramate: blockade of kainate-evoked inward currents in cultured hippocampal neurons. Epilepsia 41(Suppl 1):S10–S16
Gruber SA, Rogowska J, Yurgelun-Todd DA (2004) Decreased activation of the anterior cingulate in bipolar patients: an fMRI study. J Affect Disord 82:191–201
Gruetter R (2002) In vivo 13C NMR studies of compartmentalized cerebral carbohydrate metabolism. Neurochem Int 41:143–154
Gruetter R, Adriany G, Choi IY, Henry PG, Lei H, Oz G (2003) Localized in vivo 13C NMR spectroscopy of the brain. NMR Biomed 16:313–338
Hetherington HP, Pan JW, Chu WJ, Mason GF, Newcomer BR (1997) Biological and clinical MRS at ultra-high field. NMR Biomed 10:360–371
Hyder F, Patel AB, Gjedde A, Rothman DL, Behar KL, Shulman RG (2006) Neuronal–glial glucose oxidation and glutamatergic–GABAergic function. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab DOI 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600263
Kanda T, Kurokawa M, Tamura S, Nakamura J, Ishii A, Kuwana Y, Serikawa T, Yamada J, Ishihara K, Sasa M (1996) Topiramate reduces abnormally high extracellular levels of glutamate and aspartate in the hippocampus of spontaneously epileptic rats (SER). Life Sci 59:1607–1616
Ke Y, Cohen BM, Bang JY, Yang M, Renshaw PF (2000) Assessment of GABA concentration in human brain using two-dimensional proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Psychiatry Res 100:169–178
Keltner JR, Wald LL, Frederick BD, Renshaw PF (1997) In vivo detection of GABA in human brain using a localized double-quantum filter technique. Magn Reson Med 37:366–371
Ketter TA, Wang PW, Becker OV, Nowakowska C, Yang YS (2003) The diverse roles of anticonvulsants in bipolar disorders. Ann Clin Psychiatry 15:95–108
Korpi ER, Grunder G, Luddens H (2002) Drug interactions at GABA(A) receptors. Prog Neurobiol 67:113–159
Kuzniecky R, Hetherington H, Ho S, Pan J, Martin R, Gilliam F, Hugg J, Faught E (1998) Topiramate increases cerebral GABA in healthy humans. Neurology 51:627–629
Kuzniecky R, Ho S, Pan J, Martin R, Gilliam F, Faught E, Hetherington H (2002) Modulation of cerebral GABA by topiramate, lamotrigine, and gabapentin in healthy adults. Neurology 58:368–372
McLean MA, Simister RJ, Barker GJ, Duncan JS (2004) Discrimination between neurochemical and macromolecular signals in human frontal lobes using short echo time proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Faraday Discuss 126:93–102 (discussion 169–183)
Novotny EJ Jr, Fulbright RK, Pearl PL, Gibson KM, Rothman DL (2003) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy of neurotransmitters in human brain. Ann Neurol 54(Suppl 6):S25–S31
Petroff OA, Hyder F, Mattson RH, Rothman DL (1999) Topiramate increases brain GABA, homocarnosine, and pyrrolidinone in patients with epilepsy. Neurology 52:473–478
Petroff OA, Errante LD, Rothman DL, Kim JH, Spencer DD (2002) Glutamate–glutamine cycling in the epileptic human hippocampus. Epilepsia 43:703–710
Provencher SW (2001) Automatic quantitation of localized in vivo 1H spectra with LCModel. NMR Biomed 14:260–264
Rothman DL, Petroff OA, Behar KL, Mattson RH (1993) Localized 1H NMR measurements of gamma-aminobutyric acid in human brain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:5662–5666
Strakowski SM, Adler CM, Holland SK, Mills NP, DelBello MP, Eliassen JC (2005) Abnormal FMRI brain activation in euthymic bipolar disorder patients during a counting Stroop interference task. Am J Psychiatry 162:1697–1705
White HS (2005) Molecular pharmacology of topiramate: managing seizures and preventing migraine. Headache 45(Suppl 1):S48–S56
White HS, Brown SD, Woodhead JH, Skeen GA, Wolf HH (2000) Topiramate modulates GABA-evoked currents in murine cortical neurons by a nonbenzodiazepine mechanism. Epilepsia 41(Suppl 1):S17–S20
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the National Institutes of Mental Health (MH01798) and Drug Abuse (DA014013) for support. The authors would also like to acknowledge the assistance of Janis Breeze, MS, for help with the statistical analyses. All the experiments performed comply with the current laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0617-7
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, C.M., Wardrop, M., Frederick, B.d. et al. Topiramate raises anterior cingulate cortex glutamine levels in healthy men; a 4.0 T magnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Psychopharmacology 188, 236–243 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0451-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0451-y