Abstract
Rationale
The ionotropic NMDA glutamate receptor is composed of NR1 and NR2 (NR2A-D) subunits. While there is compelling evidence that NMDA receptors modulate behavioral effects of ethanol, there is little understanding of how the subunit composition of the NMDA receptor mediates these effects.
Objectives
In the current study, we assessed the relative roles of NMDA subunits via phenotypic assessment of ethanol-related behaviors in NR2A knockout (KO) mice.
Results
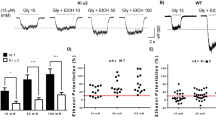
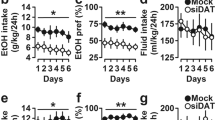
Results demonstrated that NR2A KO and heterozygous mice failed to show evidence of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference. As compared to wild-type (WT) controls, KO mice showed impaired motor coordination at baseline and, in some instances, following ethanol treatment on the accelerating rotarod, balance beam, and wire-hang tests. By contrast, open field locomotor-stimulant, sedative/hypnotic, and hypothermic responses to ethanol were not different between genotypes, nor was voluntary ethanol consumption and preference in a two-bottle choice paradigm. Blood ethanol concentrations were lower in KO than WT mice following intraperitoneal ethanol injection.
Conclusions
Results suggest that the loss of NR2A subunit-containing NMDA receptors impairs the ability to form or express learned reward-related responses to ethanol and causes deficits in motor coordination. However, the loss of NR2A does not alter other measures of acute ethanol intoxication or ethanol consumption, possibly implicating other NMDA subunits in these effects. These data provide novel insight into the role of NMDA receptors in modulating the behavioral effects of ethanol.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachtell RK, Weitemier AZ, Ryabinin AE (2004) Lesions of the Edinger–Westphal nucleus in C57BL/6J mice disrupt ethanol-induced hypothermia and ethanol consumption. Eur J Neurosci 20:1613–1623
Bienkowski P, Koros E, Kostowski W, Danysz W (1999) Effects of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists on reinforced and nonreinforced responding for ethanol in rats. Alcohol 18:131–137
Boehm SL 2nd, Schafer GL, Phillips TJ, Browman KE, Crabbe JC (2000) Sensitivity to ethanol-induced motor incoordination in 5-HT(1B) receptor null mutant mice is task-dependent: implications for behavioral assessment of genetically altered mice. Behav Neurosci 114:401–409
Boyce-Rustay JM, Cunningham CL (2004) The role of NMDA receptor binding sites in ethanol place conditioning. Behav Neurosci 118:822–834
Boyce-Rustay JM, Holmes A (2005) Functional roles of NMDA receptor NR2A and NR2B subunits in the acute intoxicating effects of ethanol in mice. Synapse 56:222–225
Boyce-Rustay JM, Holmes A (2006) Genetic inactivation of the NMDA receptor NR2A subunit has anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology (in press) DOI:10.1038/sj.npp.1301039
Crabbe JC, Cotnam CJ, Cameron AJ, Schlumbohm JP, Rhodes JS, Metten P, Wahlsten D (2003a) Strain differences in three measures of ethanol intoxication in mice: the screen, dowel and grip strength tests. Genes Brain Behav 2:201–213
Crabbe JC, Metten P, Yu CH, Schlumbohm JP, Cameron AJ, Wahlsten D (2003b) Genotypic differences in ethanol sensitivity in two tests of motor incoordination. J Appl Physiol 95:1338–1351
Cryan JF, Holmes A (2005) The ascent of mouse: advances in modelling human depression and anxiety. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:775–790
Cull-Candy S, Brickley S, Farrant M (2001) NMDA receptor subunits: diversity, development and disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:327–335
Doyle KM, Feerick S, Kirkby DL, Eddleston A, Higgins GA (1998) Comparison of various N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists in a model of short-term memory and on overt behaviour. Behav Pharmacol 9:671–681
Grant KA, Colombo G (1993) Discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol: effect of training dose on the substitution of N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 264:1241–1247
Holmes A (2001) Targeted gene mutation approaches to the study of anxiety-like behavior in mice. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:261–273
Holmes A, Lachowicz JE, Sibley DR (2004) Phenotypic analysis of dopamine receptor knockout mice; recent insights into the functional specificity of dopamine receptor subtypes. Neuropharmacology 47:1117–1134
Holmes A, le Guisquet AM, Vogel E, Millstein RA, Leman S, Belzung C (2005) Early life genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors shaping emotionality in rodents. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29(8):1335–1346
Hundt W, Danysz W, Holter SM, Spanagel R (1998) Ethanol and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor complex interactions: a detailed drug discrimination study in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 135:44–51
Kadotani H, Hirano T, Masugi M, Nakamura K, Nakao K, Katsuki M, Nakanishi S (1996) Motor discoordination results from combined gene disruption of the NMDA receptor NR2A and NR2C subunits, but not from single disruption of the NR2A or NR2C subunit. J Neurosci 16:7859–7867
Kelly MA, Rubinstein M, Phillips TJ, Lessov CN, Burkhart-Kasch S, Zhang G, Bunzow JR, Fang Y, Gerhardt GA, Grandy DK, Low MJ (1998) Locomotor activity in D2 dopamine receptor-deficient mice is determined by gene dosage, genetic background, and developmental adaptations. J Neurosci 18:3470–3479
Khanna JM, Shah G, Chau A (1997) Effect of NMDA antagonists on rapid tolerance to ethanol under two different testing paradigms. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 57:693–697
Kishimoto Y, Kawahara S, Mori H, Mishina M, Kirino Y (2001) Long-trace interval eyeblink conditioning is impaired in mutant mice lacking the NMDA receptor subunit epsilon 1. Eur J Neurosci 13:1221–1227
Kiyama Y, Manabe T, Sakimura K, Kawakami F, Mori H, Mishina M (1998) Increased thresholds for long-term potentiation and contextual learning in mice lacking the NMDA-type glutamate receptor epsilon1 subunit. J Neurosci 18:6704–6712
Lovinger DM (1995) Developmental decrease in ethanol inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat neocortical neurons: relation to the actions of ifenprodil. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:164–172
Lovinger DM, White G, Weight FF (1989) Ethanol inhibits NMDA-activated ion current in hippocampal neurons. Science 243:1721–1724
Magnusson KR, Nelson SE, Young AB (2002) Age-related changes in the protein expression of subunits of the NMDA receptor. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 99:40–45
Masood K, Wu C, Brauneis U, Weight FF (1994) Differential ethanol sensitivity of recombinant N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits. Mol Pharmacol 45:324–329
Mirshahi T, Woodward JJ (1995) Ethanol sensitivity of heteromeric NMDA receptors: Effects of subunit assembly, glycine and NMDAR1 Mg2+-insensitive mutants. Neuropharmacology 34:347–355
Miyakawa T, Yagi T, Kitazawa H, Yasuda M, Kawai N, Tsuboi K, Niki H (1997) Fyn-kinase as a determinant of ethanol sensitivity: relation to NMDA-receptor function. Science 278:698–701
Miyamoto Y, Yamada K, Noda Y, Mori H, Mishina M, Nabeshima T (2001) Hyperfunction of dopaminergic and serotonergic neuronal systems in mice lacking the NMDA receptor {epsilon}1 subunit. J Neurosci 21:750–757
Miyamoto Y, Yamada K, Nagai T, Mori H, Mishina M, Furukawa H, Noda Y, Nabeshima T (2004) Behavioural adaptations to addictive drugs in mice lacking the NMDA receptor epsilon1 subunit. Eur J Neurosci 19:151–158
Nakazawa K, McHugh TJ, Wilson MA, Tonegawa S (2004) NMDA receptors, place cells and hippocampal spatial memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:361–372
Piasecki J, Koros E, Dyr W, Kostowski W, Danysz W, Bienkowski P (1998) Ethanol-reinforced behaviour in the rat: effects of uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonist, memantine. Eur J Pharmacol 354:135–143
Rassnick S, Pulvirenti L, Koob GF (1992) Oral ethanol self-administration in rats is reduced by the administration of dopamine and glutamate receptor antagonists into the nucleus accumbens. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 109:92–98
Rustay NR, Wahlsten D, Crabbe JC (2003) Influence of task parameters on rotarod performance and sensitivity to ethanol in mice. Behav Brain Res 141:237–249
Sah P, Lopez De Armentia M (2003) Excitatory synaptic transmission in the lateral and central amygdala. Ann N Y Acad Sci 985:67–77
Sakimura K, Kutsuwada T, Ito I, Manabe T, Takayama C, Kushiya E, Yagi T, Aizawa S, Inoue Y, Sugiyama H (1995) Reduced hippocampal LTP and spatial learning in mice lacking NMDA receptor epsilon 1 subunit. Nature 373:151–155
Sanger DJ (1993) Substitution by NMDA antagonists and other drugs in rats trained to discriminate ethanol. Behav Pharmacol 4:523–528
Schorge S, Colquhoun D (2003) Studies of NMDA receptor function and stoichiometry with truncated and tandem subunits. J Neurosci 23:1151–1158
Shelton KL, Balster RL (1997) Effects of gamma-aminobutyric acid agonists and N-methyl-D-aspartate antagonists on a multiple schedule of ethanol and saccharin self-administration in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:1250–1260
Silveri MM, Spear LP (2002) The effects of NMDA and GABAA pharmacological manipulations on ethanol sensitivity in immature and mature animals. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:449–456
Sprengel R, Suchanek B, Amico C, Brusa R, Burnashev N, Rozov A, Hvalby O, Jensen V, Paulsen O, Andersen P, Kim JJ, Thompson RF, Sun W, Webster LC, Grant SG, Eilers J, Konnerth A, Li J, McNamara JO, Seeburg PH (1998) Importance of the intracellular domain of NR2 subunits for NMDA receptor function in vivo. Cell 92:279–289
Takahashi T, Feldmeyer D, Suzuki N, Onodera K, Cull-Candy SG, Sakimura K, Mishina M (1996) Functional correlation of NMDA receptor epsilon subunits expression with the properties of single-channel and synaptic currents in the developing cerebellum. J Neurosci 16:4376–4382
Vezina P, Stewart J (1987) Morphine conditioned place preference and locomotion: the effect of confinement during training. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 93:257–260
Watanabe M, Mishina M, Inoue Y (1994) Distinct spatiotemporal expressions of five NMDA receptor channel subunit mRNAs in the cerebellum. J Comp Neurol 343:513–519
Watanabe D, Inokawa H, Hashimoto K, Suzuki N, Kano M, Shigemoto R, Hirano T, Toyama K, Kaneko S, Yokoi M, Moriyoshi K, Suzuki M, Kobayashi K, Nagatsu T, Kreitman RJ, Pastan I, Nakanishi S (1998) Ablation of cerebellar Golgi cells disrupts synaptic integration involving GABA inhibition and NMDA receptor activation in motor coordination. Cell 95:17–27
Weitlauf C, Honse Y, Auberson YP, Mishina M, Lovinger DM, Winder DG (2005) Activation of NR2A-containing NMDA receptors is not obligatory for NMDA receptor-dependent long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 25:8386–8390
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Masayoshi Mishina for providing the breeding stocks used for these studies, Dr. David Lovinger for helpful comments on an earlier version of the manuscript. Research was supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Research supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism Intramural Research Program.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boyce-Rustay, J.M., Holmes, A. Ethanol-related behaviors in mice lacking the NMDA receptor NR2A subunit. Psychopharmacology 187, 455–466 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0448-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-006-0448-6