Abstract
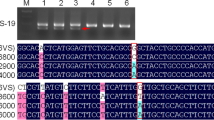
Saturation mapping of a very small genomic region is indispensable for map-based cloning. We applied a method based on sub-cloning and the Southern-hybridization technique for generating RFLP markers directly from yeast artificial chromosomes (YACs). Two YACs overlapping each other and covering the locus of the rice blast resistance gene, Pi-b, were used to construct a plasmid sub-library. Rice-specific and single-copy clones suitable as probes for RFLP analysis were selected from this sub-library by hybridization to the blots of digested DNAs of rice, YACs, and yeast. As a result, 22 markers were produced within a small chromosomal region including Pi-b. This case study shows that overlapping YACs known to cover the gene of interest are very useful in fine-scale physical mapping leading to map-based cloning of the target gene.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 May 1996 / Accepted: 2 August 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Monna, L., Miyao, A., Zhong, H. et al. Saturation mapping with subclones of YACs: DNA marker production targeting the rice blast disease resistance gene, Pi-b. Theor Appl Genet 94, 170–176 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050396
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050396