Abstract.
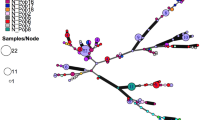
Western white pine (Pinus monticola) is an economically and ecologically important species from western North America that has declined over the past several decades mainly due to the introduction of blister rust (Cronartium ribicola) and reduced opportunities for regeneration. Amplified fragment length polymorphism (AFLP) was used to assess the genetic variation in northern Idaho populations of western white pine (including rust-resistant breeding stock) in relation to blister rust. A total of 176 individuals from four populations was analyzed using 163 AFLP loci. Within populations, an average 31.3% of the loci were polymorphic (P), and expected heterozygosity (H e) was 0.123. Genetic differentiation values (G st) showed that 9.4% of detected genetic variation was explained by differences among populations. The comparison between the rust-resistant breeding stock and a corresponding sample derived from multiple natural populations produced similar values of P (35% vs. 34.4%) and H e (0.134 vs. 0.131). No apparent signs of a genetic bottleneck caused by rust-resistance breeding were found. However, a comparison of two natural populations from local geographic areas showed that the population with low pressure from blister rust had higher polymorphism and heterozygosity than the population that had experienced high mortality due to blister rust: P (30.7% vs. 25.1%) and H e (0.125 vs. 0.100), respectively. In addition, the population from low blister-rust pressure had twice as many unique alleles as the blister rust-selected population. The genetic distance and Dice's similarity coefficients among the four populations indicated that the local population that survived high blister-rust pressure was genetically similar to the rust-resistant breeding stock.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, .MS., Brunsfeld, .S., McDonald, .G. et al. Effect of white pine blister rust (Cronartium ribicola) and rust-resistance breeding on genetic variation in western white pine (Pinus monticola). Theor Appl Genet 106, 1004–1010 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1141-8
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-002-1141-8