Purpose:
To examine various kinds of endogenous hypoxia markers’ expression in the tissues of uterine cervix cancer and to elucidate the characteristics and pitfalls when they are used as a hypoxia marker, by comparing these expressions with tumor oxygen partial pressure (pO2) values.
Patients and Methods:
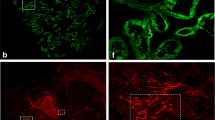
Assessment of pO2 using polarographic oxygen electrodes was performed in 69 patients with cervix carcinomas. Biopsies were taken from the region of electrode measurements. Expression of endogenous hypoxic markers in biopsy specimens such as vascular endothelial growth factor, glucose transporter-1 (GLUT-1), involucrin, and osteopontin was detected by immunohistochemistry. A double immunolabeling technique with GLUT-1 and MIB-1 as a marker of proliferation was also performed.
Results:
There was no significant correlation between expression of endogenous hypoxic markers and pO2. The only significant association seen was between the fraction of necrosis and pO2. A significant but weak correlation was found among expression of endogenous hypoxic markers. The levels of necrosis were related negatively with levels of expression of endogenous hypoxic markers. The double immunolabeling technique with GLUT-1 and MIB-1 indicated that there were about 20% MIB-1-positive tumor cells without GLUT-1 expression in tissues adjacent to areas of necrosis.
Conclusion:
The existence of necrosis affected the expression of endogenous hypoxic markers. Some hypoxic tumor cells without expressions of hypoxia markers can maintain clonogenicity and influence the treatment results. The combined use of hypoxic markers is recommended because their expression is influenced by factors other than hypoxia.
Ziel:
Prüfung der Expression verschiedener endogener Hypoxiemarker in Zervixkarzinom-Geweben und Ermitteln ihrer Eignung als Marker zur Hypoxiemessung durch Vergleich mit den Werten des Sauerstoffpartialdrucks (pO2) im Tumor.
Patienten und Methodik:
Polarographische pO2-Bestimmungen wurden bei 69 Zervixkarzinom-Patientinnen durchgeführt. Es wurden aus dem Bereich der Messelektrode Biopsien genommen. In den Gewebeproben wurde immunhistologisch die Expression endogener Hypoxiemarker—wie Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), Glukose-Transporter-1 (GLUT-1), Involucrin und Osteopontin—nachgewiesen. Eine immunhistologische Doppelmarkierung mit GLUT-1 and MIB-1 als Proliferationsmarker wurde ebenfalls durchgeführt.
Ergebnisse:
Es bestand keine signifikante Korrelation zwischen der Expression endogener Hypoxiemarker und pO2. Die einzige signifikante Assoziation fand sich zwischen Nekrose-Anteil und pO2. Es zeigte sich eine signifikante, aber schwache Korrelation unter den exprimierten endogenen Hypoxiemarkern. Das Ausmaß der Nekrose korrelierte negativ mit den Spiegeln der exprimierten endogenen Hypoxiemarker. Die immunhistologische Doppelmarkierung mit GLUT-1 und MIB-1 ergab, dass etwa 20% der MIB- 1-positiven Tumorzellen in der Umgebung nekrotischer Bereiche kein GLUT-1 bildeten.
Schlussfolgerung:
Nekrose beeinflusst die Expression endogener Hypoxiemarker. Einige hypoxische Tumorzellen, die keine Hypoxiemarker exprimieren, können klonogen bleiben und die Behandlungsergebnisse beeinflussen. Empfohlen wird die Anwendung einer Kombination von Hypoxiemarkern, da deren Expression auch durch Hypoxie-unabhängige Faktoren beeinflusst wird.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakata, Ki., Someya, M., Nagakura, H. et al. A Clinical Study of Hypoxia Using Endogenous Hypoxic Markers and Polarographic Oxygen Electrodes. Strahlenther Onkol 182, 511–517 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-006-1532-x
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-006-1532-x